Abstract
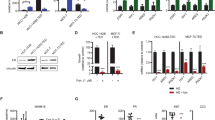
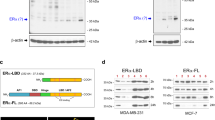
We earlier identified a lysine to arginine transition at residue 303 (K303R) in estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in invasive breast cancers, which confers resistance to the aromatase inhibitor (AI) anastrozole (Ana) when expressed in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Here, we show that AI resistance arises through an enhanced cross talk of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R)/insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1/Akt pathway with ERα, and the serine (S) residue 305 adjacent to the K303R mutation has a key function in mediating this cross talk. The ERα S305 residue is an important site that modifies response to tamoxifen; thus, we questioned whether this site could also influence AI response. We generated stable transfectants-expressing wild-type, K303R ERα or a double K303R/S305A mutant receptor, and found that the AI-resistant phenotype associated with expression of the K303R mutation was dependent on activation of S305 within the receptor. Ana significantly reduced growth in K303R/S305A-expressing cells. Preventing S305 phosphorylation with a blocking peptide inhibited IGF-1R/IRS-1/Akt activation and also restored AI sensitivity. Our data suggest that the K303R mutation and the S305 ERα residue may be a novel determinant of AI response in breast cancer, and blockade of S305 phosphorylation represents a new therapeutic strategy for treating tumors resistant to hormone therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoulnik IU, Tong XW, Fischer DC, Korner K, Atkinson NE, Edwards DP et al. (2004). A germline variation in the progesterone receptor gene increases transcriptional activity and may modify ovarian cancer risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89: 6340–6347.
Arteaga CL, Osborne CK . (1989). Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res 49: 6237–6241.
Backer JM, Myers Jr MG, Shoelson SE, Chin DJ, Sun XJ, Miralpeix M et al. (1992). Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J 11: 3469–3479.
Barone I, Cui Y, Herynk MH, Corona-Rodriguez A, Giordano C, Selever J et al. (2009). Expression of the K303R estrogen receptor-alpha breast cancer mutation induces resistance to an aromatase inhibitor via addiction to the PI3K/Akt kinase pathway. Cancer Res 69: 4724–4732.
Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T . (2001). Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 411: 355–365.
Brenet F, Socci ND, Sonenberg N, Holland EC . (2009). Akt phosphorylation of La regulates specific mRNA translation in glial progenitors. Oncogene 28: 128–139.
Burtrum D, Zhu Z, Lu D, Anderson DM, Prewett M, Pereira DS et al. (2003). A fully human monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor blocks ligand-dependent signaling and inhibits human tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 63: 8912–8921.
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H . (2001). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276: 9817–9824.
Conway K, Parrish E, Edmiston SN, Tolbert D, Tse CK, Geradts J et al. (2005). The estrogen receptor-alpha A908G (K303R) mutation occurs at a low frequency in invasive breast tumors: results from a population-based study. Breast Cancer Res 7: R871–R880.
Cui Y, Zhang M, Pestell R, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Fuqua SA . (2004). Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha blocks its acetylation and regulates estrogen sensitivity. Cancer Res 64: 9199–9208.
Deeb A, Jaaskelainen J, Dattani M, Whitaker HC, Costigan C, Hughes IA . (2008). A novel mutation in the human androgen receptor suggests a regulatory role for the hinge region in amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal interactions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 3691–3696.
Encarnacion CA, Ciocca DR, McGuire WL, Clark GM, Fuqua SA, Osborne CK . (1993). Measurement of steroid hormone receptors in breast cancer patients on tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 26: 237–246.
Evan GI, Brown L, Whyte M, Harrington E . (1995). Apoptosis and the cell cycle. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7: 825–834.
Faus H, Haendler B . (2006). Post-translational modifications of steroid receptors. Biomed Pharmacother 60: 520–528.
Fontenot DR, den Hollander P, Vela EM, Newman R, Sastry JK, Kumar R . (2007). Dynein light chain 1 peptide inhibits human immunodeficiency virus infection in eukaryotic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363: 901–907.
Foulstone E, Prince S, Zaccheo O, Burns JL, Harper J, Jacobs C et al. (2005). Insulin-like growth factor ligands, receptors, and binding proteins in cancer. J Pathol 205: 145–153.
Fuqua SA, Wiltschke C, Zhang QX, Borg A, Castles CG, Friedrichs WE et al. (2000). A hypersensitive estrogen receptor-alpha mutation in premalignant breast lesions. Cancer Res 60: 4026–4029.
Giordano C, Cui Y, Barone I, Ando S, Mancini MA, Berno V et al. (2010). Growth factor-induced resistance to tamoxifen is associated with a mutation of estrogen receptor alpha and its phosphorylation at serine 305. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119: 71–85.
Haelens A, Tanner T, Denayer S, Callewaert L, Claessens F . (2007). The hinge region regulates DNA binding, nuclear translocation, and transactivation of the androgen receptor. Cancer Res 67: 4514–4523.
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B et al. (1998). Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 351: 1393–1396.
Herynk MH, Beyer AR, Cui Y, Weiss H, Anderson E, Green TP et al. (2006). Cooperative action of tamoxifen and c-Src inhibition in preventing the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5: 3023–3031.
Herynk MH, Parra I, Cui Y, Beyer A, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG et al. (2007). Association between the estrogen receptor alpha A908G mutation and outcomes in invasive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13: 3235–3243.
Holm C, Kok M, Michalides R, Fles R, Koornstra RH, Wesseling GJ et al. (2009). Phosphorylation of the oestrogen receptor alpha at serine 305 and prediction of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Pathol 217: 372–379.
Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long BJ, Macedo L, Goloubeva OG, Brodie AM . (2005). Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in xenografts and cells during prolonged treatment with aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Cancer Res 65: 5380–5389.
Kim MY, Woo EM, Chong YT, Homenko DR, Kraus WL . (2006). Acetylation of estrogen receptor alpha by p300 at lysines 266 and 268 enhances the deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transactivation activities of the receptor. Mol Endocrinol 20: 1479–1493.
Ksiezak-Reding H, Pyo HK, Feinstein B, Pasinetti GM . (2003). Akt/PKB kinase phosphorylates separately Thr212 and Ser214 of tau protein in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1639: 159–168.
Lee AV, Jackson JG, Gooch JL, Hilsenbeck SG, Coronado-Heinsohn E, Osborne CK et al. (1999). Enhancement of insulin-like growth factor signaling in human breast cancer: estrogen regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol Endocrinol 13: 787–796.
Likhite VS, Stossi F, Kim K, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA . (2006). Kinase-specific phosphorylation of the estrogen receptor changes receptor interactions with ligand, deoxyribonucleic acid, and coregulators associated with alterations in estrogen and tamoxifen activity. Mol Endocrinol 20: 3120–3132.
Manning BD, Cantley LC . (2002). Hitting the target: emerging technologies in the search for kinase substrates. Sci STKE 2002: PE49.
Martin LA, Farmer I, Johnston SR, Ali S, Marshall C, Dowsett M . (2003). Enhanced estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, ERBB2, and MAPK signal transduction pathways operate during the adaptation of MCF-7 cells to long term estrogen deprivation. J Biol Chem 278: 30458–30468.
McGuire Jr WL, Jackson JG, Figueroa JA, Shimasaki S, Powell DR, Yee D . (1992). Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) expression by breast cancer cells: use of IGFBP-1 as an inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor action. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 1336–1341.
Michalides R, Griekspoor A, Balkenende A, Verwoerd D, Janssen L, Jalink K et al. (2004). Tamoxifen resistance by a conformational arrest of the estrogen receptor alpha after PKA activation in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 5: 597–605.
Nakajima H, Mizuta N, Sakaguchi K, Fujiwara I, Yoshimori A, Takahashi S et al. (2008). Development of HER2-antagonistic peptides as novel anti-breast cancer drugs by in silico methods. Breast Cancer 15: 65–72.
Rayala SK, Kumar R . (2007). Sliding p21-activated kinase 1 to nucleus impacts tamoxifen sensitivity. Biomed Pharmacother 61: 408–411.
Rayala SK, Talukder AH, Balasenthil S, Tharakan R, Barnes CJ, Wang RA et al. (2006). P21-activated kinase 1 regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha activation involves serine 305 activation linked with serine 118 phosphorylation. Cancer Res 66: 1694–1701.
Romano A, Lindsey PJ, Fischer DC, Delvoux B, Paulussen AD, Janssen RG et al. (2006). Two functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human progesterone receptor gene (+331 G/A and progins) and the predisposition for breast and/or ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 101: 287–295.
Sabnis GJ, Jelovac D, Long B, Brodie A . (2005). The role of growth factor receptor pathways in human breast cancer cells adapted to long-term estrogen deprivation. Cancer Res 65: 3903–3910.
Sachdev D, Hartell JS, Lee AV, Zhang X, Yee D . (2004). A dominant negative type I insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits metastasis of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 279: 5017–5024.
Sachdev D, Yee D . (2007). Disrupting insulin-like growth factor signaling as a potential cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 1–12.
Salerno M, Sisci D, Mauro L, Guvakova MA, Ando S, Surmacz E . (1999). Insulin receptor substrate 1 is a target for the pure antiestrogen ICI 1 82 780 in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 81: 299–304.
Santen RJ, Song RX, Zhang Z, Kumar R, Jeng MH, Masamura S et al. (2005). Adaptive hypersensitivity to estrogen: mechanisms and clinical relevance to aromatase inhibitor therapy in breast cancer treatment. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 95: 155–165.
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK . (2004). Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10: 331S–336S.
Skolnik EY, Lee CH, Batzer A, Vicentini LM, Zhou M, Daly R et al. (1993). The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J 12: 1929–1936.
Song RX, Barnes CJ, Zhang Z, Bao Y, Kumar R, Santen RJ . (2004). The role of Shc and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in mediating the translocation of estrogen receptor alpha to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2076–2081.
Staka CM, Nicholson RI, Gee JM . (2005). Acquired resistance to oestrogen deprivation: role for growth factor signalling kinases/oestrogen receptor cross-talk revealed in new MCF-7X model. Endocr Relat Cancer 12 (Suppl 1): S85–S97.
Subramanian K, Jia D, Kapoor-Vazirani P, Powell DR, Collins RE, Sharma D et al. (2008). Regulation of estrogen receptor alpha by the SET7 lysine methyltransferase. Mol Cell 30: 336–347.
Tharakan R, Lepont P, Singleton D, Kumar R, Khan S . (2008). Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha, serine residue 305 enhances activity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 295: 70–78.
Umayahara Y, Kawamori R, Watada H, Imano E, Iwama N, Morishima T et al. (1994). Estrogen regulation of the insulin-like growth factor I gene transcription involves an AP-1 enhancer. J Biol Chem 269: 16433–16442.
Varricchio L, Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Yamaguchi H, de Falco A, Di Domenico M et al. (2007). Inhibition of estradiol receptor/Src association and cell growth by an estradiol receptor alpha tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide. Mol Cancer Res 5: 1213–1221.
Wiseman LR, Johnson MD, Wakeling AE, Lykkesfeldt AE, May FE, Westley BR . (1993). Type I IGF receptor and acquired tamoxifen resistance in oestrogen-responsive human breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer 29A: 2256–2264.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NCI RO1 CA72038 to SAWF. We thank Mrs. Robin Sample for excellent administrative assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barone, I., Iacopetta, D., Covington, K. et al. Phosphorylation of the mutant K303R estrogen receptor α at serine 305 affects aromatase inhibitor sensitivity. Oncogene 29, 2404–2414 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.520
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.520
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Estrogen receptor α K303R mutation reorganizes its binding to forkhead box protein A1 regions and induces chromatin opening
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
The ubiquitin ligase RNF2 stabilizes ERα and modulates breast cancer progression
Human Cell (2022)
-
Detection of ESR1 mutations in plasma and tumors from metastatic breast cancer patients using next-generation sequencing
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2017)
-
G9a-mediated methylation of ERα links the PHF20/MOF histone acetyltransferase complex to hormonal gene expression
Nature Communications (2016)
-
ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2016)