Abstract
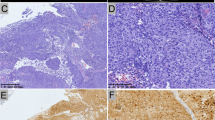
A human endogenous retrovirus type E (HERV-E) was recently found to be selectively expressed in most renal cell carcinomas (RCCs). Importantly, antigens derived from this provirus are immunogenic, stimulating cytotoxic T cells that kill RCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we show HERV-E expression is restricted to the clear cell subtype of RCC (ccRCC) characterized by an inactivation of the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor-suppressor gene with subsequent stabilization of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs)-1α and -2α. HERV-E expression in ccRCC linearly correlated with HIF-2α levels and could be silenced in tumor cells by either transfection of normal VHL or small interfering RNA inhibition of HIF-2α. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we demonstrated that HIF-2α can serve as transcriptional factor for HERV-E by binding with HIF response element (HRE) localized in the proviral 5′ long terminal repeat (LTR). Remarkably, the LTR was found to be hypomethylated only in HERV-E-expressing ccRCC while other tumors and normal tissues possessed a hypermethylated LTR preventing proviral expression. Taken altogether, these findings provide the first evidence that inactivation of a tumor suppressor gene can result in aberrant proviral expression in a human tumor and give insights needed for translational research aimed at boosting human immunity against antigenic components of this HERV-E.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bregni M, Dodero A, Peccatori J, Pescarollo A, Bernardi M, Sassi I et al. (2002). Nonmyeloablative conditioning followed by hematopoietic cell allografting and donor lymphocyte infusions for patients with metastatic renal and breast cancer. Blood 99: 4234–4236.
Childs R, Chernoff A, Contentin N, Bahceci E, Schrump D, Leitman S et al. (2000). Regression of metastatic renal-cell carcinoma after nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 343: 750–758.
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ . (2005). Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 353: 2477–2490.
Cohen C, Lock WM, Mager DL . (2009). Endogenous retroviral LTRs as promoters for human genes: a critical assessment. Gene 448: 105–114.
Florl A, Lower R, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Schulz WA . (1999). DNA methylation and expression of LINE-1 and HERV-K provirus sequences in urothelial and renal cell carcinomas. Br J Cancer 80: 1312–1321.
Ghosh A, Shanafelt T, Cimmino A, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu C et al. (2009). Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood 113: 5568–5574.
Gimenez J, Montgiraud C, Pichon JP, Bonnaud B, Arsac M, Ruel K et al. (2010). Custom human endogenous retroviruses dedicated microarray identifies self-induced HERV-W family elements reactivated in testicular cancer upon methylation control. Nucleic Acid Res 38: 2229–2246.
Gnarra JR, Zhou S, Merrill MJ, Wagner JR, Krumm A, Papavassiliou E et al. (1996). Post-transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by the product of the VHL tumor suppressor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 10589–10594.
Hahn S, Ugurel S, Hanschmann KM, Strobel H, Tondera C, Schadendorf D et al. (2008). Serological response to human endogenous retrovirus K in melanoma patients correlates with survival probability. AIDS Res Human Retroviruses 24: 717–723.
Hsiao F, Tai A, Deglon A, Sutkowski N, Longnecker R, Huber B . (2009). EBV LMP-2A employs a novel mechanism to transactivate the HERV-K18 superantigen through its ITAM. Virology 385: 261–266.
Hsiao F, Lin M, Tai A, Chen G, Huber B. . (2006). Epstein-Barr virus transactivates the HERV-K18 superantigen by docking to the human complement receptor 2 (CD21) on primary B-cells. J Immunol 177: 2056–2060.
Iliopoulos O, Levy AP, Jiang C, Kaelin WG, Goldberg MA . (1996). Negative regulation of hypoxia-inducible genes by the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 10595–10599.
Kaelin WG. . (2009). Treatment of kidney cancer: insights provided by the VHL tumor-suppressor protein. Cancer 115: 2262–2272.
Kim CM, Vocke CD, Torres-Cabala C, Yang Y, Schmidt LS, Walter MM et al. (2006). Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and 2alpha in genetically distinct early renal cortical tumors. J Urol 175: 1908–1914.
Krieg M, Haas R, Brauch H, Acker T, Flamme I, Plate KH . (2000). Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha under normoxic conditions in renal carcinoma cells by von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene loss of function. Oncogene 19: 5435–5443.
Lavie L, Kitova M, Maldener E, Meese E, Mayer J . (2005). CpG methylation directly regulates transcriptional activity of the human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K (HML-2). J Virol 79: 876–883.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. (1999). The tumor suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399: 271–275.
Menendez L, Benigno BB, McDonald JF . (2004). LI and HERV-W retrotransposons are hypomethylated in human ovarian carcinomas. Mol Cancer 3: 12–17.
Nickerson M, Jaeger E, Shi Y, Durocher J, Mahurkar S, Zaridze D et al. (2008). Improved identification of von Hippel-Lindau gene alterations in clear cell renal tumors. Clinical Cancer Res 14: 4726–4734.
Rao S, Abdul T, Kurlander R, Harashima N, Lundqvist A, Hong J et al. (2008). The human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) derived kidney cancer antigen CT-RCC1 induces proliferation of CD8+ antigen-specific T-cells in vitro that kill renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and is up-regulated by inhibiting histone deacetylase. Proceedings of the 99th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, San Diego, CA, USA.
Rini BI, Zimmerman T, Stadler WM, Gajewski TF, Vogelzang NJ . (2002). Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation of renal cell cancer after nonmyeloablative chemotherapy: feasibility, engraftment, and clinical results. J Clin Oncol 20: 2017–2024.
Romanish MT, Cohen CJ, Mager DL . (2010). Potential mechanisms of endogenous retroviral-mediated genomic instability in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 20: 246–253.
Ruprecht K, Mayer J, Sauter M, Roemer K, Mueller-Lantzsch N . (2008). Endogenous retroviruses and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 65: 3366–3382.
Sandlund J, Ljungberg B, Wikstrom P, Grankvist K, Lindh G, Rasmuson T . (2009). Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α mRNA expression in human renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol 48: 909–914.
Szpakowski S, Sun X, Lage JM, Dyer A, Rubinstein J, Kowalski D et al. (2009). Loss of epigenetic silencing in tumors preferentially affects primate-specific retroelements. Gene 448: 151–167.
Takahashi Y, Harashima N, Kajigaya S, Yokoyama H, Cherkasova E, McCoy J et al. (2008). Regression of kidney cancer following allogeneic stem-cell transplantation associated with T-cells recognizing a HERV-E antigen. J Clin Invest 118: 1099–1109.
Turner KJ, Moore JW, Jones A, Taylor CF, Cuthbert-Heavens D, Han C et al. (2002). Expression of hypoxia-inducible factors in human renal cell cancer: relationship to angiogenesis and to the von Hippel-Lindau gene mutation. Cancer Res 62: 2957–2961.
Wang-Johanning F, Radvanyi L, Rycaj K, Plummer J, Yan P, Sastry KJ et al. (2008). Human endogenous retrovirus K triggers an antigen-specific immune response in breast cancer patients. Cancer Res 68: 5869–5877.
Wenger RH, Kvietikova I, Rolfs A, Camenisch G, Gassmann M . (1998). Oxygen-regulated erythropoietin gene expression is dependent on a CpG methylation-free hypoxia-inducible factor-1 DNA-binding site. Eur J Biochem 253: 771–777.
Wright TM, Rathmell WK . (2010). Identification of Ror2 as a hypoxia-inducible factor target in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem 285: 12916–12924.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the intramural research program of NIH, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Hematology Branch. We wish to acknowledge ACKC (Action to Cure Kidney Cancer) for their support of the ACKC fellow who conducted this research and the Dean R O’Neill Memorial Fellowship for generous contributions supporting this research. We also thank Bill and Giuliana Rancic for their contributions supporting kidney cancer research. We thank Robert Worrell for his assistance in providing tissue samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cherkasova, E., Malinzak, E., Rao, S. et al. Inactivation of the von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor leads to selective expression of a human endogenous retrovirus in kidney cancer. Oncogene 30, 4697–4706 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.179
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.179
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hypoxic microenvironment shapes HIV-1 replication and latency
Communications Biology (2020)