Abstract
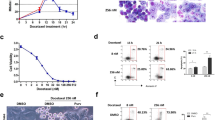
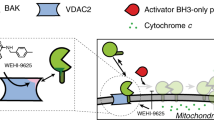
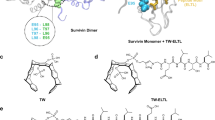
Survivin is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family and has an essential role in mitosis. Survivin is overexpressed in a large variety of human cancers and represents an attractive target for cancer therapy. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Her/neu-transformed human tumors in particular exhibit high levels of survivin. The survivin protein forms dimers through a conserved region that is critical for subcellular localization and biological functions of the protein. We identified small molecules that target a specific cavity adjacent to the survivin dimerization surfaces. S12, a lead compound identified in the screen, can bind to the survivin protein at the intended target site. Moreover, S12 alters spindle formation, causing mitotic arrest and cell death, and inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cell death occurs in premetaphase stage following mitotic arrest and is not a consequence of general toxicity. Thus, the study validates a novel therapeutic target site in the survivin protein and provides a promising strategy to develop a new class of therapeutic small molecules for the treatment of human cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsztein AM, Kandels-Lewis SE, Mackay AM, Earnshaw WC . (1998). INCENP centromere and spindle targeting: identification of essential conserved motifs and involvement of heterochromatin protein HP1. J Cell Biol 143: 1763–1774.
Altieri DC . (2003). Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 46–54.
Asanuma H, Torigoe T, Kamiguchi K, Hirohashi Y, Ohmura T, Hirata K et al. (2005). Survivin expression is regulated by coexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and epidermal growth factor receptor via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 11018–11025.
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V, Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S et al. (1999). Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol Chem 274: 22932–22940.
Chantalat L, Skoufias DA, Kleman JP, Jung B, Dideberg O, Margolis RL . (2000). Crystal structure of human survivin reveals a bow tie-shaped dimer with two unusual alpha-helical extensions. Mol Cell 6: 183–189.
DesJarlais RL, Sheridan RP, Seibel GL, Dixon JS, Kuntz ID, Venkataraghavan R . (1988). Using shape complementarity as an initial screen in designing ligands for a receptor binding site of known three-dimensional structure. J Med Chem 31: 722–729.
Giodini A, Kallio MJ, Wall NR, Gorbsky GJ, Tognin S, Marchisio PC et al. (2002). Regulation of microtubule stability and mitotic progression by survivin. Cancer Res 62: 2462–2467.
Goshima G, Vale RD . (2003). The roles of microtubule-based motor proteins in mitosis: comprehensive RNAi analysis in the Drosophila S2 cell line. J Cell Biol 162: 1003–1016.
Goshima G, Nedelec F, Vale RD . (2005). Mechanisms for focusing mitotic spindle poles by minus end-directed motor proteins. J Cell Biol 171: 229–240.
Jeyaprakash AA, Klein UR, Lindner D, Ebert J, Nigg EA, Conti E . (2007). Structure of a Survivin-Borealin-INCENP core complex reveals how chromosomal passengers travel together. Cell 131: 271–285.
Kappler M, Bache M, Bartel F, Kotzsch M, Panian M, Wurl P et al. (2004). Knockdown of survivin expression by small interfering RNA reduces the clonogenic survival of human sarcoma cell lines independently of p53. Cancer Gene Ther 11: 186–193.
Kelly AE, Ghenoiu C, Xue JZ, Zierhut C, Kimura H, Funabiki H . (2010). Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 330: 235–239.
Khodjakov A, Copenagle L, Gordon MB, Compton DA, Kapoor TM . (2003). Minus-end capture of preformed kinetochore fibers contributes to spindle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 160: 671–683.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC et al. (1998). Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature 396: 580–584.
Li F, Ackermann EJ, Bennett CF, Rothermel AL, Plescia J, Tognin S et al. (1999). Pleiotropic cell-division defects and apoptosis induced by interference with survivin function. Nat Cell Biol 1: 461–466.
Li F, Ling X . (2006). Survivin study: an update of ″what is the next wave″? J Cell Physiol 208: 476–486.
Maiato H, Rieder CL, Khodjakov A . (2004). Kinetochore-driven formation of kinetochore fibers contributes to spindle assembly during animal mitosis. J Cell Biol 167: 831–840.
Maiato H, Sunkel CE . (2004). Kinetochore-microtubule interactions during cell division. Chromosome Res 12: 585–597.
Murali R, Cheng X, Berezov A, Du X, Schon A, Freire E et al. (2005). Disabling TNF receptor signaling by induced conformational perturbation of tryptophan-107. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 10970–10975.
Nicholson DW . (2000). From bench to clinic with apoptosis-based therapeutic agents. Nature 407: 810–816.
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M et al. (1995). Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376: 37–43.
Noton EA, Colnaghi R, Tate S, Starck C, Carvalho A, Ko Ferrigno P et al. (2006). Molecular analysis of survivin isoforms: evidence that alternatively spliced variants do not play a role in mitosis. J Biol Chem 281: 1286–1295.
Rieder CL . (2005). Kinetochore fiber formation in animal somatic cells: dueling mechanisms come to a draw. Chromosoma 114: 310–318.
Rodel F, Hoffmann J, Distel L, Herrmann M, Noisternig T, Papadopoulos T et al. (2005). Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res 65: 4881–4887.
Rosa J, Canovas P, Islam A, Altieri DC, Doxsey SJ . (2006). Survivin modulates microtubule dynamics and nucleation throughout the cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell 17: 1483–1493.
Rosenthal DS, Ding R, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Vaillancourt JP, Nicholson DW, Smulson M . (1997). Intact cell evidence for the early synthesis, and subsequent late apopain-mediated suppression, of poly(ADP-ribose) during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 232: 313–321.
Sampath SC, Ohi R, Leismann O, Salic A, Pozniakovski A, Funabiki H . (2004). The chromosomal passenger complex is required for chromatin-induced microtubule stabilization and spindle assembly. Cell 118: 187–202.
Skoufias DA, Mollinari C, Lacroix FB, Margolis RL . (2000). Human survivin is a kinetochore-associated passenger protein. J Cell Biol 151: 1575–1582.
Sun C, Nettesheim D, Liu Z, Olejniczak ET . (2005). Solution structure of human survivin and its binding interface with Smac/Diablo. Biochemistry 44: 11–17.
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA, Vigna N, Oltersdorf T et al. (1998). IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res 58: 5315–5320.
Uren AG, Wong L, Pakusch M, Fowler KJ, Burrows FJ, Vaux DL et al. (2000). Survivin and the inner centromere protein INCENP show similar cell-cycle localization and gene knockout phenotype. Curr Biol 10: 1319–1328.
Verdecia MA, Huang H, Dutil E, Kaiser DA, Hunter T, Noel JP . (2000). Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nat Struct Biol 7: 602–608.
Vong QP, Cao K, Li HY, Iglesias PA, Zheng Y . (2005). Chromosome alignment and segregation regulated by ubiquitination of survivin. Science 310: 1499–1504.
Wang F, Dai J, Daum JR, Niedzialkowska E, Banerjee B, Stukenberg PT et al. (2010). Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis. Science 330: 231–235.
Wang Q, Greene MI . (2005). EGFR enhances Survivin expression through the phosphoinositide 3 (PI-3) kinase signaling pathway. Exp Mol Pathol 79: 100–107.
Wendt MD, Sun C, Kunzer A, Sauer D, Sarris K, Hoff E et al. (2007). Discovery of a novel small molecule binding site of human survivin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 3122–3129.
Xia W, Bisi J, Strum J, Liu L, Carrick K, Graham KM et al. (2006). Regulation of survivin by ErbB2 signaling: therapeutic implications for ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers. Cancer Res 66: 1640–1647.
Yamagishi Y, Honda T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y . (2010). Two histone marks establish the inner centromere and chromosome bi-orientation. Science 330: 239–243.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Robert L Margolis (the Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, La Jolla, CA, USA) for providing the pGEX-survivin plasmid. This work was supported by grants from the Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute of the University of Pennsylvania, The National Cancer Institute, the Breast Cancer Research Foundation and the Nidus Laboratories, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berezov, A., Cai, Z., Freudenberg, J. et al. Disabling the mitotic spindle and tumor growth by targeting a cavity-induced allosteric site of survivin. Oncogene 31, 1938–1948 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.377
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.377
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The survivin-ran inhibitor LLP-3 decreases oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis and growth of neuroblastoma cells
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Cancer therapeutics using survivin BIRC5 as a target: what can we do after over two decades of study?
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Survivin as a therapeutic target in Sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastoma
Oncogene (2015)
-
Loss of Survivin influences liver regeneration and is associated with impaired Aurora B function
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)
-
YAP modifies cancer cell sensitivity to EGFR and survivin inhibitors and is negatively regulated by the non-receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase 14
Oncogene (2013)