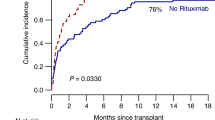
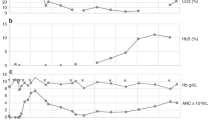
Summary:
ABO blood group antigens, of great importance in transplantation and transfusion, are present on virtually all cells, as well as in soluble form in plasma and body fluids. Naturally occurring plasma IgM and IgG antibodies against these antigens are ubiquitous. Nonetheless, the ABO blood group system is widely ignored by many transfusion services, except for purposes of red cell transfusion. We implemented a policy of transfusing only ABO identical platelets and red cells in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation or treatment for hematologic malignancies. Major bleeding episodes have occurred in about 5% of patients undergoing induction therapy for acute leukemia as compared with 15–20% in the literature. Overall survival times appear to be superior to that in historical cohorts. In 2002–2004, treatment-related mortality at 100 days in our Blood and Marrow Transplant Unit was 0.7% for autologous transplants (n=148), 13% for sibling allogeneic transplants (n=110), and 24% (n=62) for matched unrelated allogeneic transplants, suggesting that our approach is safe. We speculate that more rigorous efforts on the part of transfusion services to provide ABO identical blood components, and to remove incompatible supernatant plasma, when necessary, might yield reduced morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rydberg L . ABO-incompatibility in solid organ transplantation. Transfus Med 2001; 11: 325–342.
Stussi G, Seebach L, Muntwyler J et al. Graft-versus-host disease and survival after ABO-incompatible allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a single-centre experience. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 251–253.
Stussi G, Muntwyler J, Passweg JR et al. Consequences of ABO incompatibility in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 87–93.
Goldman J, Liesveld J, Nichols D et al. ABO incompatibility between donor and recipient and clinical outcomes in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leuk Res 2003; 27: 489–491.
Mehta J, Powles R, Sirohi B et al. Does donor–recipient ABO incompatibility protect against relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in first remission acute myeloid leukemia? Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 853–859.
Bolan CD, Leitman SF, Griffith LM et al. Delayed donor red cell chimerism and pure red cell aplasia following major ABO-incompatible nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2001; 98: 1687–1694.
Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim S et al. Anti-A isoagglutinin as a risk factor for the development of pure red cell aplasia after major ABO-incompatible allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 179–184.
Bolan CD, Childs RW, Procter JL et al. Massive immune haemolysis after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with minor ABO incompatibility. Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 787–795.
Duguid JKM, Minards J, Bolton-Maggs PHB . Incompatible plasma transfusions and haemolysis in children. Br Med J 1999; 318: 176–177.
McManigal S, Sims KL . Intravascular hemolysis secondary to ABO incompatible platelet products – an underrecognized transfusion reaction. Am J Clin Pathol 1999; 111: 202–206.
Lapierre V, Kuentz M, Tiberghien P . Allogeneic peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: guidelines for red blood cell immuno-hematological assessment and transfusion practice. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 507–512.
Schiffer CA . Prevention of alloimmunization against platelets. Blood 1991; 77: 1–4.
Slichter SJ . Platelet transfusion therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1990; 4: 291–311.
Rebulla P . Refractoriness to platelet transfusion. Curr Opin Hematol 2002; 9: 516–520.
Leukocyte reduction and ultraviolet B irradiation of platelets to prevent alloimmunization and refractoriness to platelet transfusions. The Trial to Reduce Alloimmunization to Platelets Study Group. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 1861–1869.
Carr R, Hutton JL, Jenkins JA et al. Transfusion of ABO-mismatched platelets leads to early platelet refractoriness. Br J Haematol 1990; 75: 408–413.
Heal JM, Rowe JM, McMican A et al. The role of ABO matching in platelet transfusion. Eur J Haematol 1993; 50: 110–117.
Heal JM, Rowe JM, Blumberg N . ABO and platelet transfusion revisited. Ann Hematol 1993; 66: 309–314.
Heal JM, Blumberg N, Masel D . An evaluation of crossmatching, HLA and ABO matching for platelet transfusions to refractory patients. Blood 1987; 70: 23–30.
Heal JM, Kenmotsu N, Rowe JM, Blumberg N . A possible survival advantage in adults with acute leukemia receiving ABO-identical platelet transfusions. Am J Hematol 1994; 45: 189–190.
Blumberg N, Heal JM, Hicks GL, Risher WH . Association of ABO-mismatched platelet transfusions with morbidity and mortality in cardiac surgery. Transfusion 2001; 41: 790–793.
Heckman KD, Weiner GJ, Davis CS et al. Randomized study of prophylactic platelet transfusion threshold during induction therapy for adult acute leukemia – 10 000/μl vs 20 000/μl. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 1143–1149.
Bernstein SH, Nademanee AP, Vose JM et al. A multicenter study of platelet recovery and utilization in patients after myeloablative therapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 1998; 91: 3509–3517.
Blumberg N, Heal JM, Rowe JM . A randomized trial of washed red blood cell and platelet transfusions in adult acute leukemia [ISRCTN76536440]. BMC Blood Disord 2004; 4: 6.
Heal JM, Blumberg N . The second century of ABO: and now for something completely different. Transfusion 1999; 39: 1155–1159.
Blumberg N, Heal JM, Kirkley SA et al. Leukodepleted-ABO-identical blood components in the treatment of hematologic malignancies: a cost analysis. Am J Hematol 1995; 48: 108–115.
Blumberg N, Heal JM, Gettings KF . WBC reduction of RBC transfusions is associated with a decreased incidence of RBC alloimmunization. Transfusion 2003; 43: 945–952.
Heal JM, Masel D, Blumberg N . Platelets coated with ABO immune complexes from refractory patients are associated with increased adhesion to monocytes. Transfusion 1993; 33 (Suppl.) 16S; abstract.
Heal JM, Masel D, Rowe JM, Blumberg N . Circulating immune complexes involving the ABO system after platelet transfusion. Br J Haematol 1993; 85: 566–572.
Heal JM, Masel D, Blumberg N . Interaction of platelet fc and complement receptors with circulating immune complexes involving the AB0 system. Vox Sang 1996; 71: 205–211.
Benjamin RJ, McGurk S, Ralston MS et al. ABO incompatibility as an adverse risk factor for survival after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transfusion 1999; 39: 179–187.
Benjamin RJ, Antin JH . ABO-incompatible bone marrow transplantation: the transfusion of incompatible plasma may exacerbate regimen-related toxicity. Transfusion 1999; 39: 1273–1274.
Blumberg N, Heal JM . The transfusion immunomodulation theory: the Th1/Th2 paradigm and an analogy with pregnancy as a unifying mechanism. Semin Hematol 1996; 33: 329–340.
Nielsen HJ, Hammer JH, Moesgaard F, Kehlet H . Comparison of the effects of SAG-M and whole-blood transfusions on postoperative suppression of delayed hypersensitivity. Canad J Surg 1991; 34: 146–150.
Jensen LS, Andersen AJ, Christiansen PM et al. Postoperative infection and natural killer cell function following blood transfusion in patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 1992; 79: 513–516.
Kirkley SA, Cowles J, Pellegrini Jr VD et al. Cytokine secretion after allogeneic or autologous blood transfusion. Lancet 1995; 345: 527.
Jensen LS, Hokland M, Nielsen HJ . A randomized controlled study of the effect of bedside leucocyte depletion on the immunosuppressive effect of whole blood transfusion in patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 1996; 83: 973–977.
Kirkley SA, Cowles J, Pellegrini Jr VD et al. Blood transfusion and total joint replacement surgery: T helper 2(Th2) cytokine secretion and clinical outcome. Transfus Med 1998; 8: 195–204.
Tartter PI, Mohandas K, Azar P et al. Randomized trial comparing packed red cell blood transfusion with and without leukocyte depletion for gastrointestinal surgery. Am J Surg 1998; 176: 462–466.
van de Watering LMG, Hermans J, Houbiers JGA et al. Beneficial effects of leukocyte depletion of transfused blood on postoperative complications in patients undergoing cardiac surgery – a randomized clinical trial. Circulation 1998; 97: 562–568.
Jensen LS, Kissmeyer-Nielsen P, Wolff B, Qvist N . Randomised comparison of leucocyte-depleted versus buffy-coat-poor blood transfusion and complications after colorectal surgery. Lancet 1996; 348: 841–845.
Heiss MM, Mempel W, Jauch K-W et al. Beneficial effect of autologous blood transfusion on infectious complications after colorectal cancer surgery. Lancet 1993; 342: 1328–1333.
Burrows L, Tartter P . Effect of blood transfusions on colonic malignancy recurrence rate (letter). Lancet 1982; 2: 660–662.
Blumberg N, Agarwal M, Chuang C . Relation between recurrence of cancer of the colon and blood transfusion. Br Med J 1985; 290: 1037–1039.
Habib RH, Zacharias A, Engoren M . Determinants of prolonged mechanical ventilation after coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thor Surg 1996; 62: 1164–1171.
Moore FA, Moore EE, Sauaia A . Blood transfusion – an independent risk factor for postinjury multiple organ failure. Arch Surg 1997; 132: 620–625.
Peerless JR, Alexander JJ, Pinchak AC et al. Oxygen delivery is an important predictor of outcome in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Surg 1998; 227: 726–734.
Money SR, Rice K, Crockett D et al. Risk of respiratory failure after repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms. Am J Surg 1994; 168: 152–155.
Tran DD, Van Onselen EB, Wensink AJ, Cuesta MA . Factors related to multiple organ system failure and mortality in a surgical intensive care unit. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1994; 9: 172–178.
Maetani S, Nishikawa T, Tobe T, Hirakawa A . Role of blood transfusion in organ system failure following major abdominal surgery. Ann Surg 1986; 203: 275–281.
Tadros T, Wobbes T, Hendriks T . Blood transfusion impairs the healing of experimental intestinal anastomoses. Ann Surg 1992; 215: 276–281.
Chiarugi M, Buccianti P, Disarli M et al. Association between perioperative blood transfusion and dehiscence of anastomosis after rectal resection for cancer. Acta Chir Belg 1996; 96: 108–111.
Golub R, Golub RW, Cantu R, Stein HD . A multivariate analysis of factors contributing to leakage of intestinal anastomoses. J Am College Surg 1997; 184: 364–372.
Virgin IV HW, Kurt-Jones EA, Wittenberg GF, Unanue ER . Immune complex effects on murine macrophages. II. Immune complex effects on activated macrohages cytotoxicity, membrane IL 1, and antigen presentation. J Immunol 1985; 135: 3744–3749.
Tripp CS, Beckerman KP, Unanue ER . Immune complexes inhibit antimicrobial responses through interleukin-10 production. Effects in severe combined immunodeficient mice during Listeria infection. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 1628–1634.
Gamberale R, Giordano M, Trevani AS et al. Modulation of human neutrophil apoptosis by immune complexes. J Immunol 1998; 161: 3666–3674.
Berger S, Chandra R, Ballo H et al. Immune complexes are potent inhibitors of interleukin-12 secretion by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol 1997; 27: 2994–3000.
Waymack JP, Gallon L, Barcelli U, Alexander JW . Effect of blood transfusions on macrophage function in a burned animal model. Curr Surg 1986; 43: 305–307.
Babcock GF, Alexander JW . The effects of blood transfusion on cytokine production by TH1 and TH2 lymphocytes in the mouse. Transplantation 1996; 61: 465–468.
Carpentier NA, Fiere DM, Schuh D et al. Circulating immune complexes and the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1982; 307: 1174–1180.
Peerschke EI, Ghebrehiwet B . C1q augments platelet activation in response to aggregated Ig. J Immunol 1997; 159: 5594–5598.
Birmingham DJ, Hebert LA, Shen XP et al. Effects of immune complex formation and complement activation on circulating platelets in the primate. Clin Immunol 1999; 91: 99–105.
Silliman CC, Ambruso DR, Boshkov LK . Transfusion-related acute lung injury. Blood 2005; 105: 2266–2273.
Nishimura M, Ishikawa Y, Satake M . Activation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils by immune complex: possible involvement in development of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Transfus Med 2004; 14: 359–367.
Kalmin ND, Brown DJ . Platelet washing with a blood cell processor. Transfusion 1982; 22: 125–127.
Vesilind GW, Simpson MB, Shifman MA et al. Evaluation of a centrifugal blood cell processor for washing platelet concentrates. Transfusion 1988; 28: 46–51.
Heal JM, Blumberg N, Kirkley SA et al. Leukocyte-reduced transfusions of ABO-identical platelets and clinical outcome in autologous bone marrow transplantation for lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 14: 943–948.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heal, J., Liesveld, J., Phillips, G. et al. What would Karl Landsteiner do? The ABO blood group and stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 36, 747–755 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705101
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705101
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Red blood cell-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2011)
-
Platelet transfusion and survival in adults with acute leukemia
Leukemia (2008)