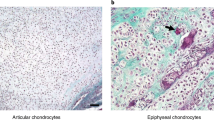
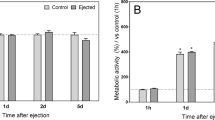
Abstract
Articular cartilage, the tissue that forms the gliding surface of joints, has a poor regenerative capacity. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) is a polypeptide that is anabolic and mitogenic for cartilage. Transfection of articular chondrocytes with an expression plasmid vector containing the cDNA for human IGF-I under the control of the cytomegalovirus promoter/enhancer led to expression of the transgene and synthesis of biologically relevant amounts of IGF-I protein. Transplantation of transfected articular chondrocytes on to the surface of articular cartilage explants led to the formation of a new tissue layer on the cartilage explant surface. The new tissue was characterized by the presence of type II collagen and proteoglycan and by the absence of type I collagen, consistent with hyaline-like cartilage. The tissue formed by the chondrocytes expressing IGF-I was thicker and contained more cells than controls transfected with an expression plasmid vector containing the Escherichia coli (E. coli) β-galactosidase (lacZ) gene. Transplantation of articular chondrocytes that overexpress human IGF-I also increased DNA synthesis and the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans by the underlying explant cartilage chondrocytes. These results identify a mechanism by which IGF-I may simultaneously promote chondrogenesis and shift cartilage homeostasis in an anabolic direction. The data further suggest that therapeutic growth factor gene transfer may be applicable to articular cartilage. Gene Therapy (2001) 8, 1443–1449.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trippel SB, Van Wyk JJ, Foster MB, Svoboda ME . Characterization of a specific somatomedin-c receptor on isolated bovine growth plate chondrocytes Endocrinology 1983 112: 2128–2136
Trippel SB . Growth factor actions on articular cartilage J Rheumatol Suppl 1995 43: 129–132
Trippel SB et al. Effect of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I and growth hormone on cultured growth plate and articular chondrocytes Pediatr Res 1989 25: 76–82
Rogachefsky RA, Dean DD, Howell DS, Altman RD . Treatment of canine osteoarthritis with insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and sodium pentosan polysulfate Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1993 1: 105–114
Nixon AJ, Fortier LA, Williams J, Mohammed H . Enhanced repair of extensive articular defects by insulin-like growth factor-I-laden fibrin composites J Orthop Res 1999 17: 475–487
Roessler BJ et al. Adenoviral-mediated gene transfer to rabbit synovium in vivo J Clin Invest 1993 92: 1085–1092
Yovandich J, O'Malley B, Sikes M, Ledley FD . Gene transfer to synovial cells by intra-articular administration of plasmid DNA Hum Gene Ther 1995 6: 603–610
Ghivizzani SC et al. Direct retrovirus-mediated gene transfer to the synovium of the rabbit knee: implications for arthritis gene therapy Gene Therapy 1997 4: 977–982
Ghivizzani SC et al. Direct adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha soluble receptors to rabbit knees with experimental arthritis has local and distal anti-arthritic effects Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 4613–4618
Baragi VM et al. Transplantation of transduced chondrocytes protects articular cartilage from interleukin 1-induced extracellular matrix degradation J Clin Invest 1995 96: 2454–2460
Kang R et al. Ex vivo gene transfer to chondrocytes in full-thickness articular cartilage defects: a feasibility study Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1997 5: 139–143
Doherty PJ et al. Resurfacing of articular cartilage explants with genetically-modified human chondrocytes in vitro Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1998 6: 153–159
Madry H, Trippel SB . Efficient lipid-mediated gene transfer to articular chondrocytes Gene Therapy 2000 7: 286–291
Smith P et al. Genetic enhancement of matrix synthesis by articular chondrocytes J Rheumatol 2000 43: 1156–1164
Honegger A, Humbel RE . Insulin-like growth factors I and II in fetal and adult bovine serum. Purification, primary structures, and immunological cross-reactivities J Biol Chem 1986 261: 569–575
Trippel SB et al. Regulation of growth-plate chondrocytes by insulin-like growth-factor I and basic fibroblast growth factor J Bone Joint Surg Am 1993 75: 177–189
Bonassar LJ, Trippel SB . Interaction of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-I in the regulation of growth plate chondrocytes Exp Cell Res 1997 234: 1–6
Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ . Articular cartilage repair and transplantation Arthritis Rheum 1998 41: 1331–1342
Romagnolo D et al. Overexpression of ovine insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates autonomous autocrine or paracrine growth in bovine mammary-derived epithelial cells Mol Endocrinol 1992 6: 1774–1780
Eming SA et al. Targeted expression of insulin-like growth factor to human keratinocytes: modification of the autocrine control of keratinocyte proliferation J Invest Dermatol 1996 107: 113–120
Matsumura T, Whelan MC, Li XQ, Trippel SB . Regulation by IGF-I and TGF-betal of swarm-rat chondrosarcoma chondrocytes J Orthop Res 2000 18: 351–355
von der Mark K, Gauss V, von der Mark H, Mueller P . Relationship between cell shape and type of collagen synthesis as chondrocytes lose their cartilage phenotype in culture Nature 1977 267: 531–532
Hunziker EB, Rosenberg LC . Repair of partial-thickness defects in articular cartilage: cell recruitment from the synovial membrane J Bone Joint Surg Am 1996 78: 721–733
Jansen M et al. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor Nature 1983 306: 609–611
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ . Nested analysis of variance Biometry 3rd edn: WH Freeman: New York 1995 pp 272–320
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was presented at the 46th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society in Orlando, FL, 12–15 March 2000. We thank AJ D'Ercole and B Moats-Staats for the human IGF-I cDNA, C Trahan for help with histological processing and M Cucchiarini and L Weissbach for valuable discussions. The work was supported by the German Academy for Natural Scientists Leopoldina (BMBF-LPD 9801–10, HM) and NIH grants AR 31068 and AR 45749 (SBT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madry, H., Zurakowski, D. & Trippel, S. Overexpression of human insulin-like growth factor-I promotes new tissue formation in an ex vivo model of articular chondrocyte transplantation. Gene Ther 8, 1443–1449 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301535
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301535
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 in articular cartilage repair for osteoarthritis treatment
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2021)
-
Where is human-based cellular pharmaceutical R&D taking us in cartilage regeneration?
3 Biotech (2020)
-
Hyaluronic acid-binding insulin-like growth factor-1: Creation of a gene encoding a bifunctional fusion protein
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Biomedical-grade, high mannuronic acid content (BioMVM) alginate enhances the proteoglycan production of primary human meniscal fibrochondrocytes in a 3-D microenvironment
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Tissue-Engineering Strategies to Repair Joint Tissue in Osteoarthritis: Nonviral Gene-Transfer Approaches
Current Rheumatology Reports (2014)