Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To determine the effect of weight loss and exercise interventions on serum leptin and to investigate the relationship of physical function and osteoarthritis (OA) severity with serum leptin in older overweight and obese adults with knee OA. In addition, the study examined if serum leptin predicts weight loss.
DESIGN: Longitudinal, controlled clinical trial of weight loss and exercise interventions.
SUBJECTS: Community dwelling, older, overweight and obese adults (n=316; >60 years of age; body mass index ≥28.0 kg m−2) with symptomatic knee OA and self-reported difficulty in performing selected physical activities were recruited.
INTERVENTIONS: Participants were randomized into one of four groups for the 18-month study duration: Healthy Lifestyle Controls, Dietary Weight Loss (Diet), Exercise Training (Exercise), and a combination of Dietary Weight Loss and Exercise Training (Diet+Exercise). The weight loss goal for the two Diet groups was 5% from baseline at 18 months. Participants in the Exercise groups were trained for 3 days week−1, 60 min day−1.
MEASUREMENTS: Body weight, body mass index, serum leptin, physical function, and OA severity were measured at baseline, 6 months, and 18 months.
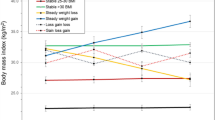
RESULTS: Diet and Diet+Exercise groups lost 5.3 and 6.1% of their weight, respectively, at 18 months with the Exercise group losing 2.9%. There was a significant main effect of weight loss on serum leptin with a decrease in serum leptin averaged across the 6- and 18-month time points for the Diet and Diet+Exercise groups compared to the other two groups (β=0.245; P<0.01). No main effect for exercise training was observed. Serum leptin was related to self-reported physical function. In all participants, a mixed model analysis demonstrated that lower levels of baseline serum leptin predict larger weight loss (β=−2.779; P=0.048).
CONCLUSION: Decreases in serum leptin may be one mechanism by which weight loss improves physical function and symptoms in OA patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994; 372: 425–432.
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Barley SK, Friedman JM . Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995; 269: 543–546.
Rosenbaum M, Nicolson M, Hirsch J, Murphy E, Chu F, Leibel RL . Effects of weight change on plasma leptin concentrations and energy expenditure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 3647–3654.
Berman DM, Rodrigues LM, Nicklas BJ, Ryan AS, Dennis KE, Goldberg AP . Racial disparities in metabolism, central obesity, and sex hormone-binding globulin in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 97–103.
Olive JL, Miller GD . Differential effects of maximal- and moderate-intensity runs on plasma leptin in healthy trained subjects. Nutrition 2001; 17: 365–369.
Rissanen P, Makimattila S, Vehmas T, Taavitsainen M, Rissanen A . Effect of weight loss and regional fat distribution on plasma leptin concentration in obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23: 645–649.
Nicklas BJ, Katzel LI, Ryan AS, Dennis KE, Goldberg AP . Gender differences in the response of plasma leptin concentrations to weight loss in obese older individuals. Obes Res 1997; 5: 62–68.
Moller N, O'Brien P, Nair KS . Disruption of the relationship between fat content and leptin levels with aging in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 931–934.
Reseland JE, Anderssen SA, Solvoll K, Hjermann I, Urdal P, Holme I, Drevon CA . Effect of long-term changes in diet and exercise on plasma leptin concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr 2001; 73: 240–245.
Carantoni M, Abbasi F, Azhar S, Schaaf P, Reaven GM . Can changes in plasma insulin concentration explain the variability in leptin response to weight loss in obese women with normal glucose tolerance? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 869–872.
Loeser RF . Systemic and local regulation of articular cartilage metabolism: where does leptin fit in the puzzle? Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 3009–3012.
Figenschau Y, Knutsen G, Shahazeydi S, Johansen O, Sveinbjornsson B . Human articular chondrocytes express functional leptin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 287: 190–197.
Otero M, Gomez Reino JJ, Gualillo O . Synergistic induction of nitric oxide synthase type II: in vitro effect of leptin and interferon-gamma in human chondrocytes and ATDC5 chondrogenic cells. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 404–409.
Dumond H, Presle N, Terlain B, Mainard D, Loeuille D, Netter P, Pottie P . Evidence for a key role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 3118–3129.
Schaffler A, Ehling A, Neumann E, Herfarth H, Tarner I, Scholmerich J, Muller-Ladner U, Gay S . Adipocytokines in synovial fluid. JAMA 2003; 290: 1709–1710.
Bokarewa M, Bokarew D, Hultgren O, Tarkowski A . Leptin consumption in the inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62: 952–956.
Scharstuhl A, Glansbeek HL, van Beuningen HM, Vitters EL, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB . Inhibition of endogenous TGF-beta during experimental osteoarthritis prevents osteophyte formation and impairs cartilage repair. J Immunol 2002; 169: 507–514.
Taaffe DR, Harris TB, Ferrucci L, Rowe J, Seeman TE . Cross-sectional and prospective relationships of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein with physical performance in elderly persons: MacArthur studies of successful aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2000; 55: M709–M715.
Ferrucci L, Penninx BW, Volpato S, Harris TB, Bandeen-Roche K, Balfour J, Leveille SG, Fried LP, Md JM . Change in muscle strength explains accelerated decline of physical function in older women with high interleukin-6 serum levels. J Am Geriatr Soc 2002; 50: 1947–1954.
Cappola AR, Xue QL, Ferrucci L, Guralnik JM, Volpato S, Fried LP . Insulin-like growth factor I and interleukin-6 contribute synergistically to disability and mortality in older women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 2019–2025.
Ferrucci L, Harris TB, Guralnik JM, Tracy RP, Corti MC, Cohen HJ, Penninx B, Pahor M, Wallace R, Havlik RJ . Serum IL-6 level and the development of disability in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 1999; 47: 639–646.
Mokdad AH, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, Bowman BA, Marks JS, Koplan JP . The spread of the obesity epidemic in the United States, 1991–1998. JAMA 1999; 282: 1519–1522.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of disabilities and associated health conditions among adults— United States, 1999, 2001 Morbidity Mortality Week Rep 50: 120–125.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of arthritis—United States, 1997, 2001 Morbidity Mortality Week Rep 50: 334–336.
Messier SP, Loeser RF, Mitchell MN, Valle G, Morgan TP, Rejeski WJ, Ettinger WH . Exercise and weight loss in obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis: a preliminary study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2000; 48: 1062–1072.
Ettinger Jr WH, Burns R, Messier SP, Applegate W, Rejeski WJ, Morgan T, Shumaker S, Berry MJ, O'Toole M, Monu J, Craven T . A randomized trial comparing aerobic exercise and resistance exercise with a health education program in older adults with knee osteoarthritis. The Fitness Arthritis and Seniors Trial (FAST). JAMA 1997; 277: 25–31.
Messier SP, Loeser RF, Miller GD, Morgan T, Rejeski WJ, Sevick MA, Ettinger W, Pahor M, Williamson JD . Exercise and dietary weight loss in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 1501–1510.
Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Maffei M, Wang H, Friedman JM, Bennett PH, Bogardus C . Relatively low plasma leptin concentrations precede weight gain in Pima Indians. Nat Med 1997; 3: 238–240.
Di Stefano G, Bini V, Papi F, Celi F, Contessa G, Berioli MG, Bacosi ML, Falorni A . Leptin serum concentrations predict the responsiveness of obese children and adolescents to weight excess reduction program. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000; 24: 1586–1591.
Verdich C, Toubro S, Buemann B, Holst JJ, Bulow J, Simonsen L, Sondergaard SB, Christensen NJ, Astrup A . Leptin levels are associated with fat oxidation and dietary-induced weight loss in obesity. Obes Res 2001; 9: 452–461.
Torgerson JS, Carlsson B, Stenlof K, Carlsson LM, Bringman E, Sjostrom L . A low serum leptin level at baseline and a large early decline in leptin predict a large 1-year weight reduction in energy-restricted obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 4197–4203.
Naslund E, Andersson I, Degerblad M, Kogner P, Kral JG, Rossner S, Hellsrom PM . Associations of leptin, insulin resistance and thyroid function with long-term weight loss in dieting obese men. J Intern Med 2000; 248: 299–308.
Miller GD, Rejeski WJ, Williamson JD, Morgan T, Sevick MA, Loeser RF, Ettinger WH, Messier SP, ADAPT Investigators. The Arthritis, Diet and Activity Promotion Trial (ADAPT): design, rationale, and baseline results. Control Clin Trials 2003; 24: 462–480.
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW . Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 1988; 15: 1833–1840.
Altman RD, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Carstens J, Cooke TD, Genant H, Gofton P, Groth H, McShane DJ, Murphy WA . Radiographic assessment of progression in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1987; 30: 1214–1225.
Xiao E, Xia-Zhang L, Vulliemoz NR, Ferin M, Wardlaw SL . Leptin modulates inflammatory cytokine and neuroendocrine responses to endotoxin in the primate. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 4350–4353.
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI . Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature 1998; 394: 897–901.
Moore SE, Morgan G, Collinson AC, Swain JA, O'Connell MA, Prentice AM . Leptin, malnutrition, and immune response in rural Gambian children. Arch Dis Child 2002; 87: 192–197.
Prentice AM, Moore SE, Collinson AC, O'Connell MA . Leptin and undernutrition. Nutr Rev 2002; 60: S56–S67.
Harris RB, Zhou J, Redmann Jr SM, Smagin GN, Smith SR, Rodgers E, Zachwieja JJ . A leptin dose–response study in obese (ob/ob) and lean (+/?) mice. Endocrinology 1998; 139: 8–19.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL . Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 292–295.
Oliveria SA, Felson DT, Cirillo PA, Reed JI, Walker AM . Body weight, body mass index, and incident symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Epidemiology 1999; 10: 161–166.
Felson DT, Zhang Y, Anthony JM, Naimark A, Anderson JJ . Weight loss reduces the risk for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in women. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med 1992; 116: 535–539.
Sturmer T, Gunther KP, Brenner H . Obesity, overweight and patterns of osteoarthritis: the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study. J Clin Epidemiol 2000; 53: 307–313.
Wing RR, Sinha MK, Considine RV, Lang W, Caro JF . Relationship between weight loss maintenance and changes in serum leptin levels. Horm Metab Res 1996; 28: 698–703.
Wadden TA, Considine RV, Foster GD, Anderson DA, Sarwer DB, Caro JS . Short- and long-term changes in serum leptin dieting obese women: effects of caloric restriction and weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 214–218.
Wisse BE, Campfield LA, Marliss EB, Morais JA, Tenenbaum R, Gougeon R . Effect of prolonged moderate and severe energy restriction and refeeding on plasma leptin concentrations in obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 70: 321–330.
Xenachis C, Samojlik E, Raghuwanshi MP, Kirschner MA . Leptin, insulin and TNF-alpha in weight loss. J Endocrinol Invest 2001; 24: 865–870.
Thong FS, Hudson R, Ross R, Janssen I, Graham TE . Plasma leptin in moderately obese men: independent effects of weight loss and aerobic exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2000; 279: E307–E313.
Chu NF, Stampfer MJ, Spiegelman D, Rifai N, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB . Dietary and lifestyle factors in relation to plasma leptin concentrations among normal weight and overweight men. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 106–114.
Hassink SG, Sheslow DV, deLancey E, Opentanova I, Considine RV, Caro JF . Serum leptin in children with obesity: relationship to gender and development. Pediatrics 1996; 98: 201–203.
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Miettinen H, Wei M, Gingerich RL . Leptin concentrations in diabetic and nondiabetic Mexican-Americans. Diabetes 1996; 45: 822–824.
Chu NF, Spiegelman D, Yu J, Rifai N, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB . Plasma leptin concentrations and four-year weight gain among US men. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 346–353.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Claude D Pepper Older Americans (Grant 5P60AG10484-00) and the General Clinical Research Center (Grant M01-RR07122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, G., Nicklas, B., Davis, C. et al. Is serum leptin related to physical function and is it modifiable through weight loss and exercise in older adults with knee osteoarthritis?. Int J Obes 28, 1383–1390 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802737
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802737
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Effect of Chronic Exercise Training on Leptin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Sports Medicine (2018)
-
Scoping review report: obesity in older adults
International Journal of Obesity (2012)
-
Effects of diet type and supplementation of glucosamine, chondroitin, and MSM on body composition, functional status, and markers of health in women with knee osteoarthritis initiating a resistance-based exercise and weight loss program
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (2011)
-
The impact of obesity on the musculoskeletal system
International Journal of Obesity (2008)