Abstract
Objective: To assess trends in prevalence and detection, treatment and control of hypertension in a German population between 1984 and 1995.
Setting and participants: Independent random samples of the population were examined in cross-sectional surveys with identical methods in 1984/85 (age range 25 to 64 years, n = 4022 participants), 1989/90 (age range 25 to 74 years, n = 4940) and 1994/95 (age range 25 to 74 years, n = 4856).
Main outcome measures: Prevalence of hypertension and proportions of hypertensives detected, treated and controlled. Hypertension was defined as blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive medication.
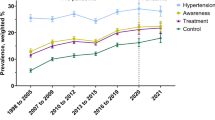
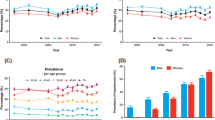
Results: The prevalence of hypertension did not change significantly over the 10 years (25–64 years, age-standardised 1984/85: 37.8% in men and 24.6% in women; 1994/95: 39.3% and 24.8%, respectively). Rates of detection, treatment and control of hypertension did not change much either. Of all hypertensives in 1994/95, 54% were detected in men and 64% in women, the treatment rates were 23% and 32%, and the proportions of those with controlled hypertension (below 140/90 mm Hg with treatment) were as low as 7% and 13%, respectively. Rates were higher in the older age groups, however, control rates never exceeded 20% at any age.
Conclusions: Despite considerable changes in the pharmacological treatment of hypertension there was a disappointing stagnation with regard to the management of this important risk factor in the community. The reasons for this unfavourable trend need clarification and appropriate public health action.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasse, C., Hense, HW., Stieber, J. et al. Assessing hypertension management in the community: trends of prevalence, detection, treatment, and control of hypertension in the MONICA Project, Augsburg 1984–1995. J Hum Hypertens 15, 27–36 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Trend and projection of non-communicable diseases risk factors in Iran from 2001 to 2030
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
The Risk Factors of Hypertension and Their Predictive Power in Identifying Patients Using a Decision Tree
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine (2024)
-
Role of gender in explaining metabolic syndrome risk factors in an Iranian rural population using structural equation modelling
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Frauen sind einfach anders!?
Gefässchirurgie (2023)
-
‘Inequalities in prevalence of hypertension, prehypertension, anti-hypertensive coverage, awareness, and effective treatment in 429 districts of Iran; a population-based STEPS 2016 small area spatial estimation model’
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2023)