Abstract
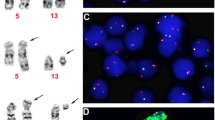
Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (IHES) is a disease that is difficult to classify, and diagnosis is one of exclusion. The identification of a cytogenetically invisible interstitial deletion resulting in the fusion of FIP1-Like-1 (FIP1L1) to platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) has enabled many IHES cases to be reclassified as chronic eosinophilic leukemia. As it is likely that PDGFRA may fuse to other partner genes, we established a reverse transcriptase-PCR test to detect specific overexpression of the PDGFRA kinase domain as an indicator of the presence of a fusion gene. Overexpression was detected in 12/12 FIP1L1-PDGFRA-positive patients, plus 9/217 (4%) patients with hypereosinophilia who had tested negative for FIP1L1-PDGFRA. One of the positive cases was investigated in detail and found to have a complex karyotype involving chromosomes 3, 4 and 10. Amplification of the genomic breakpoint by bubble PCR revealed a novel fusion between KIF5B at 10p11 and PDGFRA at 4q12. Imatinib, a known inhibitor of PDGFRα, produced a complete cytogenetic response and disappearance of the KIF5B-PDGFRA fusion by PCR, from both genomic DNA and mRNA. This study demonstrates the utility of screening for PDGFRA kinase domain overexpression in patients with IHES and has identified a third PDGFRA fusion partner in chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD . The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2002; 100: 2292–2302.
Bain BJ . Cytogenetic and molecular genetic aspects of eosinophilic leukaemias. Br J Haematol 2003; 122: 173–179.
Brito-Babapulle F . The eosinophilias, including the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Br J Haematol 2003; 121: 203–223.
Chang HW, Leong KH, Koh DR, Lee SH . Clonality of isolated eosinophils in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood 1999; 93: 1651–1657.
Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J et al. A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1201–1214.
Griffin JH, Leung J, Bruner RJ, Caligiuri MA, Briesewitz R . Discovery of a fusion kinase in EOL-1 cells and idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 7830–7835.
Klion AD, Robyn J, Akin C, Noel P, Brown M, Law M et al. Molecular remission and reversal of myelofibrosis in response to imatinib mesylate treatment in patients with the myeloproliferative variant of hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood 2004; 103: 473–478.
Pardanani A, Ketterling RP, Brockman SR, Flynn HC, Paternoster SF, Shearer BM et al. CHIC2 deletion, a surrogate for FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion, occurs in systemic mastocytosis associated with eosinophilia and predicts response to imatinib mesylate therapy. Blood 2003; 102: 3093–3096.
Apperley JF, Gardembas M, Melo JV, Russell-Jones R, Bain BJ, Baxter EJ et al. Response to imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic myeloproliferative diseases with rearrangements of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 481–487.
Jones AV, Cross NCP . Oncogenic derivatives of platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 2004; 61: 2912–2923.
Gotlib J . Molecular classification and pathogenesis of eosinophilic disorders: 2005 update. Acta Haematol 2005; 114: 7–25.
Chung KF, Hew M, Score J, Jones AV, Reiter A, Cross NCP et al. Cough and hypereosinophilia due to FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene with tyrosine kinase activity. Eur Respir J 2006; 27: 230–232.
Cross NCP, Melo JV, Feng L, Goldman JM . An optimized multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of BCR-ABL fusion mRNAs in haematological disorders. Leukemia 1994; 8: 186–189.
Xie JF, Stroumza J, Graves DT . IL-1 down-regulates platelet-derived growth factor-alpha receptor gene expression at the transcriptional level in human osteoblastic cells. J Immunol 1994; 153: 378–383.
Zhang JG, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Characterization of genomic BCR-ABL breakpoints in chronic myeloid leukaemia by PCR. Br J Haematol 1995; 90: 138–146.
Baxter EJ, Kulkarni S, Vizmanos JL, Jaju R, Martinelli G, Testoni N et al. Novel translocations that disrupt the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRB) gene in BCR-ABL-negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 251–256.
Baxter EJ, Hochhaus A, Bolufer P, Reiter A, Fernandez JM, Senent L et al. The t(4;22)(q12;q11) in atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia fuses BCR to PDGFRA. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 1391–1397.
Pardanani A, Brockman SR, Paternoster SF, Flynn HC, Ketterling RP, Lasho TL et al. FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion: prevalence and clinicopathologic correlates in 89 consecutive patients with moderate to severe eosinophilia. Blood 2004; 104: 3038–3045.
Roche-Lestienne C, Lepers S, Soenen-Cornu V, Kahn JE, Lai JL, Hachulla E et al. Molecular characterization of the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) in 35 French patients with normal conventional cytogenetics. Leukemia 2005; 19: 792–798.
Tanaka Y, Kanai Y, Okada Y, Nonaka S, Takeda S, Harada A et al. Targeted disruption of mouse conventional kinesin heavy chain, kif5B, results in abnormal perinuclear clustering of mitochondria. Cell 1998; 93: 1147–1158.
Cross NCP, Reiter A . Tyrosine kinase fusion genes in chronic myeloproliferative diseases. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1207–1212.
De Keersmaecker K, Cools J . Chronic myeloproliferative disorders: a tyrosine kinase tale. Leukemia 2006; 20: 200–205.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Leukaemia Research Fund. We are grateful to Drs Valérie Parlier and Dominique Mühlematter of the Unité de Cytogénétique du Cancer, Lausanne for cytogenetic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Score, J., Curtis, C., Waghorn, K. et al. Identification of a novel imatinib responsive KIF5B-PDGFRA fusion gene following screening for PDGFRA overexpression in patients with hypereosinophilia. Leukemia 20, 827–832 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404154
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404154
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of CARM1 promotes its enzymatic activity and alters its target specificity
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Kinesins and cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2012)
-
The t(4;9)(q11;q33) fuses CEP110 to KIT in a case of acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2011)