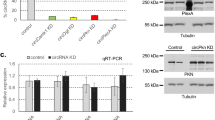
Abstract
RNA interference (RNAi) is a gene silencing mechanism that can be triggered by introducing double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) into cells expressing the appropriate molecular machinery, which then degrades the corresponding endogenous mRNA. RNAi can be used for determining gene function and creating functional ‘knockout’ organisms. Here we show for the first time that RNAi can be induced in adult fruit flies by injecting dsRNA into the abdomen of anesthetized Drosophila, and that this method can also target genes expressed in the central nervous system (CNS). Two genes were targeted to investigate the effects of dsRNA injection on their mRNA content; lacZ transgene (expressed either in the gut or in the CNS), and GM06434, the Drosophila homologue of the C. elegans gene nrf (nose resistant to fluoxetine). Both the transgene and the endogenous gene were successfully silenced in adult Drosophila by intra-abdominal injection of their respective dsRNA. We propose that our method of RNAi in adult flies can be used to characterize gene functioning in the CNS without the typical interference in development found in most gene mutation studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fire A . RNA-triggered gene silencing Trends Genet 1999 15: 358–363
Carthew RW . Gene silencing by double-stranded RNA Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001 13: 244–248
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP . RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals Cell 2000 101: 25–33
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs Genes Dev 2001 15: 188–200
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ . Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference Nature 2001 409: 363
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ . An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells Nature 2000 404: 293–296
Smalheiser NR, Manev H, Costa E . RNAi and brain function: was McConnell on the right track? Trends Neurosci 2001 24: 216–218
Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Zipperlen P, Martinez-Campos M, Sohrmann M, Ahringer J . Functional genomic analysis of C. elegans chromosome I by systematic RNA interference Nature 2000 408: 325–330
Gonczy P, Echeverri G, Oegema K, Coulson A, Jones SJ, Copley RR et al. Functional genomic analysis of cell division in C. elegans using RNAi of genes on chromosome III Nature 2000 408: 331–336
Marx J . Interfering with gene expression Science 2000 288: 1370–1372
Wianny F, Zernicka-Goetz M . Specific interference with gene function by double-stranded RNA in early mouse development Nat Cell Biol 2000 2: 70–75
Chan HY, Bonini NM . Drosophila models of human neurodegenerative disease Cell Death Differ 2000 7: 1075–1080
Kennerdell JR, Carthew RW . Heritable gene silencing in Drosophila using double-stranded RNA Nat Biotechnol 2000 18: 896–898
Fortier E, Belote JM . Temperature-dependent gene silencing by an expressed inverted repeat in Drosophila Genesis 2000 26: 240–244
Choy RK, Thomas JH . Fluoxetine-resistant mutants in C. elegans define a novel family of transmembrane proteins Mol Cell 1999 4: 143–152
Sullivan W, Ashburner M, Scott Hawley R (eds) . Drosophila Protocols Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York 2000
Schnetzer JW, Tyler MS . Endogenous beta-galactosidase activity in the larval, pupal, and adult stages of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, indicates need for caution in lacZ fusion-gene studies Biol Bull 1996 190: 173–187
Tuschl T, Zamore PD, Lehmann R, Bartel DP, Sharp PA . Targeted mRNA degradation by double-stranded RNA in vitro Genes Dev 1999 13: 3191–3197
Yang D, Lu H, Erickson JW . Evidence that processed small dsRNAs may mediate sequence-specific mRNA degradation during RNAi in Drosophila embryos Curr Biol 2000 10: 1191–1200
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans Nature 1998 391: 806–811
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Erminio Costa for his support and encouragement of our project, the UIC Psychiatric Institute for financial support, and Dr Tolga Uz for help in preparing the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dzitoyeva, S., Dimitrijevic, N. & Manev, H. Intra-abdominal injection of double-stranded RNA into anesthetized adult Drosophila triggers RNA interference in the central nervous system. Mol Psychiatry 6, 665–670 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000955
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000955
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Plant and animal small RNA communications between cells and organisms
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2022)
-
Biotic stress triggered small RNA and RNAi defense response in plants
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Chronic dysfunction of Stromal interaction molecule by pulsed RNAi induction in fat tissue impairs organismal energy homeostasis in Drosophila
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Small interfering RNA-mediated regulation of gene expression and its role as a plant reverse genetic tool
Indian Journal of Plant Physiology (2017)
-
Ingestion of genetically modified yeast symbiont reduces fitness of an insect pest via RNA interference
Scientific Reports (2016)