Abstract
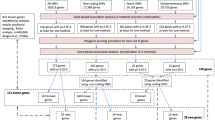
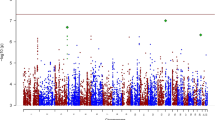
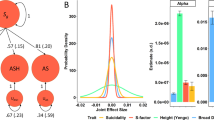
We describe a multistage approach to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with neuroticism, a personality trait that shares genetic determinants with major depression and anxiety disorders. Whole genome association with 452 574 SNPs was performed on DNA pools from ∼2000 individuals selected on extremes of neuroticism scores from a cohort of 88 142 people from southwest England. The most significant SNPs were then genotyped on independent samples to replicate findings. We were able to replicate association of one SNP within the PDE4D gene in a second sample collected by our laboratory and in a family-based test in an independent sample; however, the SNP was not significantly associated with neuroticism in two other independent samples. We also observed an enrichment of low P-values in known regions of copy number variations. Simulation indicates that our study had ∼80% power to identify neuroticism loci in the genome with odds ratio (OR)>2, and ∼50% power to identify small effects (OR=1.5). Since we failed to find any loci accounting for more than 1% of the variance, the heritability of neuroticism probably arises from many loci each explaining much less than 1%. Our findings argue the need for much larger samples than anticipated in genetic association studies and that the biological basis of emotional disorders is extremely complex.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eysenck HJ . The Biological Basis of Personality. Thomas: Springfield, IL, 1967.
Angst J, Clayton P . Premorbid personality of depressive, bipolar and schizophrenic patients with special reference to suicidal issues. Compr Psychiatry 1986; 27: 511–532.
Boyce P, Parker G, Barnett B, Cooney M, Smith F . Personality as a vulnerability factor to depression. Br J Psychiatry 1991; 159: 106–114.
Hirschfeld RM, Klerman GL, Lavori P, Keller MB, Griffith P, Coryell W . Premorbid personality assessments of first onset of major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1989; 46: 345–350.
Kendler KS, Neale MC, Kessler RC, Heath AC, Eaves LJ . A longitudinal twin study of personality and major depression in women. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50: 853–862.
Bienvenu OJ, Samuels JF, Costa PT, Reti IM, Eaton WW, Nestadt G . Anxiety and depressive disorders and the five-factor model of personality: a higher- and lower-order personality trait investigation in a community sample. Depress Anxiety 2004; 20: 92–97.
Cox BJ, MacPherson PS, Enns MW, McWilliams LA . Neuroticism and self-criticism associated with posttraumatic stress disorder in a nationally representative sample. Behav Res Ther 2004; 42: 105–114.
Jylha P, Isometsa E . The relationship of neuroticism and extraversion to symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general population. Depress Anxiety 2006; 23: 281–289.
Jylha P, Isometsa E . Temperament, character and symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general population. Eur Psychiatry 2006; 21: 389–395.
Hettema JM, Neale MC, Myers JM, Prescott CA, Kendler KS . A population-based twin study of the relationship between neuroticism and internalizing disorders. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 857–864.
Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Prescott CA . Toward a comprehensive developmental model for major depression in women. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 1133–1145.
Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Prescott CA . Toward a comprehensive developmental model for major depression in men. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 115–124.
Kendler KS, Gatz M, Gardner CO, Pedersen NL . Personality and major depression: a Swedish longitudinal, population-based twin study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006; 63: 1113–1120.
Fullerton J, Cubin M, Tiwari H, Wang C, Bomhra A, Davidson S et al. Linkage analysis of extremely discordant and concordant sibling pairs identifies quantitative-trait loci that influence variation in the human personality trait neuroticism. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 879–890.
Nash MW, Huezo-Diaz P, Williamson RJ, Sterne A, Purcell S, Hoda F et al. Genome-wide linkage analysis of a composite index of neuroticism and mood-related scales in extreme selected sibships. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 2173–2182.
Neale BM, Sullivan PF, Kendler KS . A genome scan of neuroticism in nicotine dependent smokers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 132: 65–69.
Ioannidis JP, Trikalinos TA, Khoury MJ . Implications of small effect sizes of individual genetic variants on the design and interpretation of genetic association studies of complex diseases. Am J Epidemiol 2006; 164: 609–614.
Darvasi A, Soller M . Selective DNA pooling for determination of linkage between a molecular marker and a quantitative trait locus. Genetics 1994; 138: 1365–1373.
Butcher LM, Meaburn E, Liu L, Fernandes C, Hill L, Al-Chalabi A et al. Genotyping pooled DNA on microarrays: a systematic genome screen of thousands of SNPs in large samples to detect QTLs for complex traits. Behav Genet 2004; 34: 549–555.
Craig I, Meaburn E, Butcher L, Hill L, Plomin R . Single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping in DNA pools. Methods Mol Biol 2005; 311: 147–164.
Kirov G, Nikolov I, Georgieva L, Moskvina V, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC . Pooled DNA genotyping on Affymetrix SNP genotyping arrays. BMC Genomics 2006; 7: 27.
Macgregor S, Visscher PM, Montgomery G . Analysis of pooled DNA samples on high density arrays without prior knowledge of differential hybridization rates. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: e55.
Meaburn E, Butcher LM, Schalkwyk LC, Plomin R . Genotyping pooled DNA using 100K SNP microarrays: a step towards genomewide association scans. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: e27.
Willis-Owen SA, Turri MG, Munafo MR, Surtees PG, Wainwright NW, Brixey RD et al. The serotonin transporter length polymorphism, neuroticism, and depression: a comprehensive assessment of association. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 58: 451–456.
Willis-Owen SA, Shifman S, Copley RR, Flint J . DCNP1: a novel candidate gene for major depression. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 121–122.
Willis-Owen SA, Fullerton J, Surtees PG, Wainwright NW, Miller S, Flint J . The Val66Met coding variant of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene does not contribute toward variation in the personality trait neuroticism. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 58: 738–742.
Martin N, Goodwin G, Fairburn C, Wilson R, Allison D, Cardon LR et al. A population based study of personality in 34 000 sib-pairs. Twin Res 2000; 3: 310–315.
Eysenck HJ, Eysenck SBG (eds). Manual of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire. Educational and Industrial Testing Service: San Diego, CA, 1975.
Aluja A, García O, Garcia LF . A comparative study of Zuckerman's three structural models for personality through the NEO-PI-R: ZKPQ-III-R, EPQ-RS and Goldberg's 50-bipolar adjectives. Pers Individ Dif 2002; 33: 713–725.
De Fruyt F, Van De Wiele L, Van Heeringen C . Cloninger's psychobiological model of temperament and character and the five-factor model of personality. Pers Individ Dif 2000; 29: 441–452.
Shifman S, Pisante-Shalom A, Yakir B, Darvasi A . Quantitative technologies for allele frequency estimation of SNPs in DNA pools. Mol Cell Probes 2002; 16: 429–434.
Meaburn E, Butcher LM, Liu L, Fernandes C, Hansen V, Al-Chalabi A et al. Genotyping DNA pools on microarrays: tackling the QTL problem of large samples and large numbers of SNPs. BMC Genomics 2005; 6: 52.
Altshuler D, Brooks LD, Chakravarti A, Collins FS, Daly MJ, Donnelly P . A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 2005; 437: 1299–1320.
Schaid DJ, Rowland CM, Tines DE, Jacobson RM, Poland GA . Score tests for association between traits and haplotypes when linkage phase is ambiguous. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 425–434.
Schaid DJ . Evaluating associations of haplotypes with traits. Genet Epidemiol 2004; 27: 348–364.
Redon R, Ishikawa S, Fitch KR, Feuk L, Perry GH, Andrews TD et al. Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature 2006; 444: 444–454.
Kirk KM, Birley AJ, Statham DJ, Haddon B, Lake RI, Andrews JG et al. Anxiety and depression in twin and sib pairs extremely discordant and concordant for neuroticism: prodromus to a linkage study. Twin Res 2000; 3: 299–309.
Hettema JM, An SS, Neale MC, Bukszar J, van den Oord EJ, Kendler KS et al. Association between glutamic acid decarboxylase genes and anxiety disorders, major depression, and neuroticism. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 752–762.
Boomsma DI, Beem AL, van den Berg M, Dolan CV, Koopmans JR, Vink JM et al. Netherlands twin family study of anxious depression (NETSAD). Twin Res 2000; 3: 323–334.
Middeldorp CM, Birley AJ, Cath DC, Gillespie NA, Willemsen G, Statham DJ et al. Familial clustering of major depression and anxiety disorders in Australian and Dutch twins and siblings. Twin Res Hum Genet 2005; 8: 609–615.
Rettew DC, Vink JM, Willemsen G, Doyle A, Hudziak JJ, Boomsma DI . The genetic architecture of neuroticism in 3301 Dutch adolescent twins as a function of age and sex: a study from the Dutch twin register. Twin Res Hum Genet 2006; 9: 24–29.
Jardine R, Martin NG, Henderson AS . Genetic covariation between neuroticism and the symptoms of anxiety and depression. Genet Epidemiol 1984; 1: 89–107.
Kessler R, Mroczek D . Final Version of the Psychological Distress Scale. Technical Note. Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, 1994.
Sham P, Bader JS, Craig I, O'Donovan M, Owen M . DNA pooling: a tool for large-scale association studies. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 862–871.
Mohlke KL, Erdos MR, Scott LJ, Fingerlin TE, Jackson AU, Silander K et al. High-throughput screening for evidence of association by using mass spectrometry genotyping on DNA pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 16928–16933.
Barratt BJ, Payne F, Rance HE, Nutland S, Todd JA, Clayton DG . Identification of the sources of error in allele frequency estimations from pooled DNA indicates an optimal experimental design. Ann Hum Genet 2002; 66: 393–405.
Norton N, Williams HJ, Williams NM, Spurlock G, Zammit S, Jones G et al. Mutation screening of the Homer gene family and association analysis in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2003; 120: 18–21.
Shifman S, Bronstein M, Sternfeld M, Pisante-Shalom A, Lev-Lehman E, Weizman A et al. A highly significant association between a COMT haplotype and schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1296–1302.
Sawcer S, Maranian M, Setakis E, Curwen V, Akesson E, Hensiek A et al. A whole genome screen for linkage disequilibrium in multiple sclerosis confirms disease associations with regions previously linked to susceptibility. Brain 2002; 125: 1337–1347.
Bansal A, van den Boom D, Kammerer S, Honisch C, Adam G, Cantor CR et al. Association testing by DNA pooling: an effective initial screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 16871–16874.
Hinds DA, Seymour AB, Durham LK, Banerjee P, Ballinger DG, Milos PM et al. Application of pooled genotyping to scan candidate regions for association with HDL cholesterol levels. Hum Genomics 2004; 1: 421–434.
Papassotiropoulos A, Stephan DA, Huentelman MJ, Hoerndli FJ, Craig DW, Pearson JV et al. Common Kibra alleles are associated with human memory performance. Science 2006; 314: 475–478.
Butcher LM, Meaburn E, Knight J, Sham PC, Schalkwyk LC, Craig IW et al. SNPs, microarrays and pooled DNA: identification of four loci associated with mild mental impairment in a sample of 6000 children. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 1315–1325.
Ioannidis JP, Trikalinos TA, Khoury MJ . Implications of small effect sizes of individual genetic variants on the design and interpretation of genetic association studies of complex diseases. Am J Epidemiol 2006; 164: 609–614.
Lee JA, Lupski JR . Genomic rearrangements and gene copy-number alterations as a cause of nervous system disorders. Neuron 2006; 52: 103–121.
Wilson GM, Flibotte S, Chopra V, Melnyk BL, Honer WG, Holt RA . DNA copy-number analysis in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia reveals aberrations in genes involved in glutamate signaling. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 743–749.
Smith GW, Aubry JM, Dellu F, Contarino A, Bilezikjian LM, Gold LH et al. Corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1-deficient mice display decreased anxiety, impaired stress response, and aberrant neuroendocrine development. Neuron 1998; 20: 1093–1102.
Benbrook DM, Jones NC . Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene 1990; 5: 295–302.
Benbrook DM, Jones NC . Different binding specificities and transactivation of variant CRE's by CREB complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 1994; 22: 1463–1469.
Le Jeune IR, Shepherd M, Van Heeke G, Houslay MD, Hall IP . Cyclic AMP-dependent transcriptional up-regulation of phosphodiesterase 4D5 in human airway smooth muscle cells. Identification and characterization of a novel PDE4D5 promoter. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 35980–35989.
Fleischhacker WW, Hinterhuber H, Bauer H, Pflug B, Berner P, Simhandl C et al. A multicenter double-blind study of three different doses of the new cAMP-phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram in patients with major depressive disorder. Neuropsychobiology 1992; 26: 59–64.
Scott AI, Perini AF, Shering PA, Whalley LJ . In-patient major depression: is rolipram as effective as amitriptyline? Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1991; 40: 127–129.
Zhang HT, Huang Y, Jin SL, Frith SA, Suvarna N, Conti M et al. Antidepressant-like profile and reduced sensitivity to rolipram in mice deficient in the PDE4D phosphodiesterase enzyme. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002; 27: 587–595.
Wong ML, Whelan F, Deloukas P, Whittaker P, Delgado M, Cantor RM et al. Phosphodiesterase genes are associated with susceptibility to major depression and antidepressant treatment response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 15124–15129.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this work was provided by the Wellcome Trust. SS is supported by the European Molecular Biology Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shifman, S., Bhomra, A., Smiley, S. et al. A whole genome association study of neuroticism using DNA pooling. Mol Psychiatry 13, 302–312 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002048
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002048
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Variants in regulatory elements of PDE4D associate with major mental illness in the Finnish population
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Meta-analysis of genome-wide SNP- and pathway-based associations for facets of neuroticism
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
-
GWA meta-analysis of personality in Korean cohorts
Journal of Human Genetics (2015)
-
An efficient and cost-effective approach for genic microsatellite marker-based large-scale trait association mapping: identification of candidate genes for seed weight in chickpea
Molecular Breeding (2014)
-
Harmonization of Neuroticism and Extraversion phenotypes across inventories and cohorts in the Genetics of Personality Consortium: an application of Item Response Theory
Behavior Genetics (2014)