Abstract
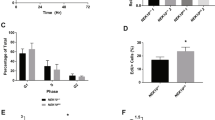
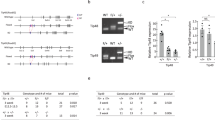
Neoplastic transformation sensitizes many cells to apoptosis. This phenomenon may underlie the therapeutic benefit of many anticancer drugs, but its molecular basis is poorly understood. We have used a selective and potent farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) to probe a mechanism of apoptosis that is peculiarly linked to neoplastic transformation. While nontoxic to untransformed mouse cells, FTI triggers a massive RhoB-dependent, p53-independent apoptosis in mouse cells that are neoplastically transformed. Here we offer evidence that the BAR adapter-encoding tumor suppressor gene Bin1 is required for this transformation-selective death program. Targeted deletion of Bin1 in primary mouse embyro fibroblasts (MEFs) transformed by E1A+Ras did not affect FTI-induced reversion, actin fiber formation, or growth inhibition, but it abolished FTI-induced apoptosis. The previously defined requirement for RhoB in these effects suggests that Bin1 adapter proteins act downstream or in parallel to RhoB in cell death signaling. The death defect in Bin1 null cells was significant insofar as it abolished FTI efficacy in tumor xenograft assays. p53 deletion did not phenocopy the effects of Bin1 deletion. However, MEFs transformed by SV40 large T antigen+Ras were also resistant to apoptosis by FTI, consistent with other evidence that large T inhibits Bin1-dependent cell death by a p53-independent mechanism. Taken together, the results define a function for Bin1 in apoptosis that is conditional on transformation stress. This study advances understanding of the functions of BAR adapter proteins, which are poorly understood, by revealing genetic interactions with an Rho small GTPase that functions in stress signaling. The frequent losses of Bin1 expression that occur in human breast and prostate cancers may promote tumor progression and limit susceptibility to FTI or other therapeutic agents that exploit the heightened sensitivity of neoplastic cells to apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson P, Paterson HF and Hall A . (1992). J. Cell Biol., 119, 617–627.
Amberg DC, Basart E and Botstein D . (1995). Nat. Struc. Biol., 2, 28–35.
Balguerie A, Sivadon P, Bonneu M and Aigle M . (1999). J. Cell Sci., 112, 2529–2537.
Barrington RE, Subler MA, Rands E, Omer CA, Miller PJ, Hundley JE, Koester SK, Troyer DA, Bearss DJ, Conner MW, Gibbs JB, Hamilton K, Koblan KS, Mosser SD, O'Neill TJ, Schaber MD, Senderak ET, Windle JJ, Oliff A and Kohl NE . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 85–92.
Bauer F, Urdaci M, Aigle M and Crouzet M . (1993). Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 5070–5084.
Bon E, Recordon-Navarro P, Durrens P, Iwase M, Toh-E A and Aigle M . (2000). Yeast, 16, 1229–1241.
Breton AM and Aigle M . (1998). Curr. Genet., 34, 280–286.
Colwill K, Field D, Moore L, Friesen J and Andrews B . (1999). Genetics, 152, 881–893.
Cox A . (2001). Drugs, 61, 723–732.
Cryns VL, Byun Y, Rana A, Mellor H, Lustig KD, Ghanem L, Parker PJ, Kirschner MW and Yuan J . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 29449–29453.
Du W, Lebowitz P and Prendergast GC . (1999a). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 1831–1840.
Du W, Liu A and Prendergast GC . (1999b). Cancer Res., 59, 4808–4812.
Du W and Prendergast GC . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 5924–5928.
DuHadaway JB, Sakamuro D, Ewert DL and Prendergast GC . (2001). Cancer Res., 16, 3151–3156.
Elliott K, Ge K, Du W and Prendergast GC . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 4669–4684.
Elliott K, Sakamuro D, Basu A, Du W, Wunner W, Staller P, Gaubatz S, Zhang H, Prochownik E, Eilers M and Prendergast GC . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3564–3573.
Galderisi U, Di Bernardo G, Cipollaro M, Jori FP, Piegari E, Cascino A, Peluso G and Melone MAB . (1999). J. Cell. Biochem., 74, 313–322.
Gampel A, Parker PJ and Mellor H . (1999). Curr. Biol., 9, 955–958.
Ge K, DuHadaway J, Du W, Herlyn M, Rodeck U and Prendergast GC . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 9689–9694.
Ge K, DuHadaway J, Sakamuro D, Wechsler-Reya R, Reynolds C and Prendergast GC . (2000a). Int. J. Cancer, 85, 376–383.
Ge K, Minhas F, DuHadaway J, Mao N-C, Wilson D, Sakamuro D, Buccafusca R, Nelson P, Malkowicz SB, Tomaszewski JT and Prendergast GC . (2000b). Int. J. Cancer, 86, 155–161.
Hogarty MD, Liu X, Thompson PM, White PS, Sulman EP, Maris JM and Brodeur GM . (2000). Med. Pediatr. Oncol., 35, 559–562.
Huang H, Colella S, Kurrer M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P and Ohgaki H . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 6868–6874.
Kadlec L and Pendergast A-M . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12390–12395.
Koh H, Lee KH, Kim D, Kim S, Kim JW and Chung J . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 34451–34458.
Kohl NE, Omer CA, Conner MW, Anthony NJ, Davide JP, deSolms SJ, Giuliani EA, Gomez RP, Graham SL, Hamilton K, Handt LK, Hartman GD, Koblan KS, Kral AM, Miller PJ, Mosser SD, O'Neill TJ, Rands E, Schaber MD, Gibbs JB and Oliff A . (1995). Nat. Med., 1, 792–797.
Lebowitz P and Prendergast GC . (1998). Cell Adhes. CommUN., 4, 1–11.
Lebowitz PF, Davide JP and Prendergast GC . (1995). Mol. Cell. Biol., 15, 6613–6622.
Lebowitz PF, Sakamuro D and Prendergast GC . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 708–713.
Lee E, Marcucci M, Daniell L, Pypaert M, Weiss OA, Ochoa GC, Farsad K, Wenk MR and De Camilli P . (2002). Science, 297, 1193–1196.
Lee J, Colwill K, Aneuliunas V, Tennyson C, Moore L, Ho Y and Andrews B . (1998). Curr. Biol., 8, 1310–1321.
Liu A-X, Cerniglia GJ, Bernhard EJ and Prendergast GC . (2001a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 6192–6197.
Liu A-X, Du W, Liu J-P, Jessell TM and Prendergast GC . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 6105–6113.
Liu A-X, Rane N, Liu J-P and Prendergast GC . (2001b). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 6906–6912.
Mangues R, Corral T, Kohl NE, Symmans WF, Lu S, Malumbres M, Gibbs JB, Oliff A and Pellicer A . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 1253–1259.
Mellor J, Flynn P, Nobes CD, Hall A and Parker PJ . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 4811–4814.
Michaelson D, Silletti J, Murphy G, D'Eustachio P, Rush M and Philips MR . (2001). J. Cell Biol., 152, 111–126.
Prendergast GC . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 2966–2986.
Prendergast GC . (2000). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 12, 166–173.
Prendergast GC . (2001). Nature Rev. Cancer, 1, 162–168.
Prendergast GC and Cole MD . (1989). Mol. Cell. Biol., 9, 124–134.
Prendergast GC, Davide JP, deSolms SJ, Giuliani E, Graham S, Gibbs JB, Oliff A and Kohl NE . (1994). Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 4193–4202.
Prendergast GC, Lawe D and Ziff EB . (1991). Cell, 65, 395–407.
Routhier EL, Donover PS and Prendergast GC . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 637–647.
Sakamuro D, Elliott K, Wechsler-Reya R and Prendergast GC . (1996). Nature Genet., 14, 69–77.
Sakamuro D, Eviner V, Elliott K, Showe L, White E and Prendergast GC . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 2411–2418.
Sepp-Lorenzino L, Ma Z, Rands E, Kohl NE, Gibbs JB, Oliff A and Rosen N . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 5302–5309.
Suzuki N, Urano J and Tamanoi F . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 15356–15361.
Takahashi M, Mukai H, Toshimori M, Miyamoto M and Ono Y . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 11566–11571.
Wechsler-Reya R, Elliott K, Herlyn M and Prendergast GC . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 3258–3263.
Wechsler-Reya R, Elliott K and Prendergast GC . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 566–575.
Wigge P and McMahon HT . (1998). Trends Neurosci., 21, 339–344.
Zalcman G, Closson V, Linares-Cruz G, Leregours F, Honore N, Tavitian A and Olofsson B . (1995). Oncogene, 10, 1935–1945.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of our laboratory for criticizing the manuscript. This work was sustained in part by grants to GCP from the NIH (CA82222) and the US Army Breast and Prostate Cancer Research Programs (DAMD17-96-1-6324 and PC970326).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DuHadaway, J., Du, W., Donover, S. et al. Transformation-selective apoptotic program triggered by farnesyltransferase inhibitors requires Bin1. Oncogene 22, 3578–3588 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206481
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206481
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BIN1 in cancer: biomarker and therapeutic target
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
The c-MYC-interacting proapoptotic tumor suppressor BIN1 is a transcriptional target for E2F1 in response to DNA damage
Cell Death & Differentiation (2009)
-
Immune escape as a fundamental trait of cancer: focus on IDO
Oncogene (2008)
-
Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1, potentiates cancer chemotherapy
Nature Medicine (2005)