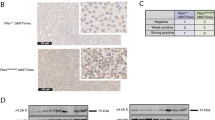
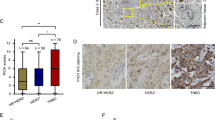
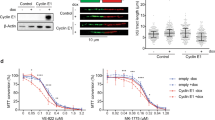
Abstract
The rapid cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage is mediated by degradation of the Cdc25A phosphatase, a proto-oncogene whose mRNA is frequently overexpressed in human tumours. Here, we study the occurrence and mechanisms of Cdc25A deregulation in human breast cancer cell lines. We demonstrate aberrantly elevated Cdc25A protein abundance and phosphatase activity in eight out of 15 cell lines, in some cases resulting in abrogation of the Cdc25A-mediated checkpoint response to ionizing radiation (IR), and this defect correlated with hypersensitivity to IR. Furthermore, we present evidence that deregulation of Cdc25A occurs predominantly on the post-transcriptional level, as overabundant Cdc25A protein was usually not accompanied by adequate mRNA overexpression. Instead, we demonstrate that aberrantly enhanced protein stability is an important mechanism underlying Cdc25A overabundance in a subset of breast cancer cell lines. Given the frequency of this mechanism, we propose that the DNA integrity checkpoint controlling Cdc25A protein stability might be a common target for deregulation in breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham RT . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2177–2196.
Bartek J, Falck J and Lukas J . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2, 877–886.
Bartek J and Lukas J . (2001a). Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol., 13, 738–747.
Bartek J and Lukas J . (2001b). FEBS Lett., 490, 117–122.
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Strauss M and Bartek J . (1994). J. Pathol., 172, 237–245.
Cangi MG, Cukor B, Soung P, Signoretti S, Moreira Jr G, Ranashinge M, Cady B, Pagano M and Loda M . (2000). J. Clin. Invest., 106, 753–761.
D'Amours D and Jackson SP . (2002). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 3, 317–327.
Donzelli M, Squatrito M, Ganoth D, Hershko A, Pagano M and Draetta GF . (2002). EMBO J., 21, 4875–4884.
Falck J, Mailand N, Syljuåsen RG, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2001). Nature, 410, 842–847.
Galaktionov K, Chen X and Beach D . (1996). Nature, 382, 511–517.
Galaktionov K, Lee AK, Eckstein J, Draetta G, Meckler J, Loda M and Beach D . (1995). Science, 269, 1575–1577.
Gasparotto D, Maestro R, Piccinin S, Vukosavljevic T, Barzan L, Sulfaro S and Boiocchi M . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 2366–2368.
Hoeijmakers JH . (2001). Nature, 411, 366–374.
Jiang XR, Jimenez G, Chang E, Frolkis M, Kusler B, Sage M, Beeche M, Bodnar AG, Wahl GM, Tlsty TD and Chiu CP . (1999). Nat. Genet., 21, 111–114.
Jinno S, Suto K, Nagata A, Igarashi M, Kanaoka Y, Nojima H and Okayama H . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 1549–1556.
Lengauer C, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1998). Nature, 396, 643–649.
Lukas J, Bartkova J, Rohde M, Strauss M and Bartek J . (1995). Mol. Cell. Biol., 15, 2600–2611.
Mailand N, Falck J, Lukas C, Syljuåsen RG, Welcker M, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000). Science, 288, 1425–1429.
Mailand N, Podtelejnikov AV, Groth A, Mann M, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2002). EMBO J., 21, 5911–5920.
May P and May E . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 7621–7636.
Meijers-Heijboer H, van den Ouweland A, Klijn J, Wasielewski M, de Snoo A, Oldenburg R, Hollestelle A, Houben M, Crepin E, van Veghel-Plandsoen M, Elstrodt F, van Duijn C, Bartels C, Meijers C, Schutte M, McGuffog L, Thompson D, Easton D, Sodha N, Seal S, Barfoot R, Mangion J, Chang-Claude J, Eccles D, Eeles R, Evans DG, Houlston R, Murday V, Narod S, Peretz T, Peto J, Phelan C, Zhang HX, Szabo C, Devilee P, Goldgar D, Futreal PA, Nathanson KL, Weber B, Rahman N and Stratton MR . (2002). Nat. Genet., 31, 55–59.
Mondesert O, Ducommun B and Bugler B . (2002). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 295, 673–677.
Moynahan ME . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 8994–9007.
Nilsson I and Hoffmann I . (2000). Prog. Cell Cycle Res., 4, 107–114.
Nishioka K, Doki Y, Shiozaki H, Yamamoto H, Tamura S, Yasuda T, Fujiwara Y, Yano M, Miyata H, Kishi K, Nakagawa H, Shamma A and Monden M . (2001). Br. J. Cancer, 85, 412–421.
Rotman G and Shiloh Y . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6135–6144.
Rouse J and Jackson SP . (2002). Science, 297, 547–551.
Santoni-Rugiu E, Falck J, Mailand N, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3497–3509.
Shiloh Y . (2003). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 3, 155–168.
Sørensen CS, Lukas C, Kramer ER, Peters JM, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 7613–7623.
Sørensen CS, Syljuåsen RG, Falck J, Schroeder T, Rönnstrand L, Khanna KK, Zhou BB, Bartek J and Lukas J . (2003). Cancer Cell, 3, 247–248.
Soussi T and Beroud C . (2001). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 1, 233–240.
Taniguchi T, Garcia-Higuera I, Xu B, Andreassen PR, Gregory RC, Kim ST, Lane WS, Kastan MB and D’Andrea AD . (2002). Cell, 109, 459–472.
Tassan JP, Schultz SJ, Bartek J and Nigg EA . (1994). J. Cell Biol., 127, 467–478.
Tauchi H, Matsuura S, Kobayashi J, Sakamoto S and Komatsu K . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 8967–8980.
Vahteristo P, Bartkova J, Eerola H, Syrjäkoski K, Ojala S, Kilpivaara O, Tamminen A, Kononen J, Aittomäki K, Heikkilä P, Holli K, Blomqvist C, Bartek J, Kallioniemi OP and Nevanlinna H . (2002). Am. J. Hum. Genet., 71, 432–438.
Varley JM, Evans DG and Birch JM . (1997). Br. J. Cancer, 76, 1–14.
Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC and Helin K . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 6379–6395.
Wu W, Fan YH, Kemp BL, Walsh G and Mao L . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 4082–4085.
Zhou BB and Elledge SJ . (2000). Nature, 408, 433–439.
Acknowledgements
We thank P Guldberg for help with the real-time PCR, AE Lykkesfeldt and PE Lønning for some of the cell lines, and current and former members of the Department of Cell Cycle and Cancer for generously sharing expertise and ideas. This work was supported by the Danish Cancer Society, the European Commission, the Dr Mildred Scheel Stiftung für Krebsforschung, Bonn, Germany, the Danish Medical Research Council, and the Alfred Benzon's Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Löffler, H., Syljuåsen, R., Bartkova, J. et al. Distinct modes of deregulation of the proto-oncogenic Cdc25A phosphatase in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 22, 8063–8071 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206976
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206976
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mechanisms and function of substrate recruitment by F-box proteins
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2013)
-
Identification of differential expressed transcripts in cervical cancer of Mexican patients
Tumor Biology (2011)
-
Casein kinase 1 functions as both penultimate and ultimate kinase in regulating Cdc25A destruction
Oncogene (2010)
-
Ubiquitin hydrolase Dub3 promotes oncogenic transformation by stabilizing Cdc25A
Nature Cell Biology (2010)
-
Cdc25A and Dub3 in a high-stakes balancing act
Nature Cell Biology (2010)