Abstract
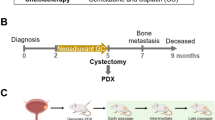
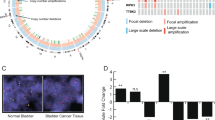
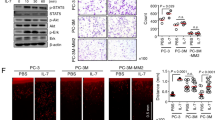
Recent studies have found a higher frequency of the PTEN tumor-suppressor gene alterations in invasive bladder carcinoma than in superficial disease, suggesting that PTEN is important in this process. A role of PTEN in bladder cancer invasion is further suggested by the fact that PTEN is a regulator of cell motility, a necessary component of tumor invasion. However, it is unknown whether PTEN is mechanistically involved in ‘in vivo’ tumor invasion or merely an epiphenomenon and, if the former is true, whether this process is dependent on its protein or lipid phosphatase activities. To address these issues, we stably transfected several commonly used human bladder cancer cell lines with known invasive phenotypes with either wild-type PTEN constructs or those deficient in the lipid phosphatase (G129E) or both protein and lipid phosphatase (G129R) activities. Here we show that chemotaxis was inhibited by both the wild-type and G129E mutant of PTEN but not by G129R-transfected cells. Using a novel organotypic in vitro invasion assay, we evaluated the impact of wild-type and mutant PTEN transgene expression on the invasive ability of T24T, a human bladder cancer cell line with a functionally impaired PTEN. Results indicate that the G129E mutant blocks invasion as efficiently as wild-type PTEN transfection. In contrast to the wild-type gene, this mutant has no effect on cell clonogenicity in agar. To further establish the role of PTEN in tumor invasion, we evaluated vector- and PTEN-transfected T24T cells in an orthotopic in vivo assay that faithfully reproduces human disease. Microscopic examination of murine bladders at the completion of this experiment parallels the results obtained with the organotypic assay. Our results are the first demonstration: (1) that the inhibitory effects of PTEN on cell motility translate into suppression of in vivo invasion; (2) that PTEN can inhibit tumor invasion even in the absence of its lipid phosphatase activity; (3) how organotypic in vitro approaches can be used as surrogates of in vivo invasion allowing rapid dissection of molecular processes leading to this phenotype while reducing the number of animals used in research.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlering TE, Dubeau L and Jones PA . (1987). Cancer Res., 47, 6660–6665.
Aveyard JS, Skilleter A, Habuchi T and Knowles MA . (1999). Br. J. Cancer, 80, 904–908.
Cairns P, Evron E, Okami K, Halachmi N, Esteller M, Herman JG, Bose S, Wang SI, Parsons R and Sidransky D . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 3215–3218.
Cappellen D, Gil Diez de Medina S, Chopin D, Thiery JP and Radvanyi F . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 3059–3066.
Fontana D, Bellina M, Scoffone C, Cagnazzi E, Cappia S, Cavallo F, Russo R and Leonardo E . (1996). Eur. Urol., 29, 470–476.
Furnari FB, Huang HJ and Cavenee WK . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5002–5008.
Furnari FB, Lin H, Huang HS and Cavenee WK . (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 12479–12484.
Gildea JJ, Golden WL, Harding MA and Theodorescu D . (2000a). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 27, 252–263.
Gildea JJ, Harding MA, Gulding KM and Theodorescu D . (2000b). Biotechniques, 29, 81–86.
Gildea JJ, Harding MA, Seraj MJ, Gulding KM and Theodorescu D . (2002a). Cancer Res., 62, 982–985.
Gildea JJ, Seraj MJ, Oxford G, Harding MA, Hampton GM, Moskaluk CA, Frierson HF, Conaway MR and Theodorescu D . (2002b). Cancer Res., 62, 6418–6423.
Heney NM, Ahmed S, Flanagan MJ, Frable W, Corder MP, Hafermann MD and Hawkins IR . (1983). J. Urol., 130, 1083–1086.
Kulik G, Klippel A and Weber MJ . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 1595–1606.
Li DM and Sun H . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 15406–15411.
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, Bigner SH, Giovanella BC, Ittmann M, Tycko B, Hibshoosh H, Wigler MH and Parsons R . (1997). Science, 275, 1943–1947.
Lianes P, Charytonowicz E, Cordon-Cardo C, Fradet Y, Grossman HB, Hemstreet GP, Waldman FM, Chew K, Wheeless LL and Faraggi D . (1998). Clin. Cancer Res., 4, 1267–1271.
Lipponen P and Eskelinen M . (1994). Br. J. Cancer, 69, 1120–1125.
Liu J, Babaian DC, Liebert M, Steck PA and Kagan J . (2000). Mol. Carcinogen., 29, 143–150.
Ludbrook J . (1998). Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 25, 1032–1037.
Maehama T and Dixon JE . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 13375–13378.
Maehama T and Dixon JE . (1999). Trends Cell Biol., 9, 125–128.
Maier D, Jones G, Li X, Schonthal AH, Gratzl O, Van Meir EG and Merlo A . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 5479–5482.
Myers MP, Pass I, Batty IH, Van der Kaay J, Stolarov JP, Hemmings BA, Wigler MH, Downes CP and Tonks NK . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 13513–13518.
Seraj MJ, Thomas AR, Chin JL and Theodorescu D . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 1516–1522.
Simpson L and Parsons R . (2001). Exp. Cell Res., 264, 29–41.
Skinner DG, Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Skinner EC, Boyd SD, Figueroa A, Jones P, Cote R and Groshen S . (1998). Eur. Urol., 33, 25–26.
Steck PA, Pershouse MA, Jasser SA, Yung WK, Lin H, Ligon AH, Langford LA, Baumgard ML, Hattier T, Davis T, Frye C, Hu R, Swedlund B, Teng DH and Tavtigian SV . (1997). Nat. Genet., 15, 356–362.
Tamura M, Gu J, Danen EH, Takino T, Miyamoto S and Yamada KM . (1999a). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 20693–20703.
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K, Aota S, Parsons R and Yamada KM . (1998). Science, 280, 1614–1617.
Tamura M, Gu J, Takino T and Yamada KM . (1999b). Cancer Res., 59, 442–449.
Tanaka M, Koul D, Davies MA, Liebert M, Steck PA and Grossman HB . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5406–5412.
Theodorescu D, Cornil I, Fernandez BJ and Kerbel RS . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 9047–9051.
Theodorescu D, Laderoute KR and Gulding KM . (1998). Cell Growth Differ., 9, 919–928.
Upchurch Jr GR, Welch GN, Fabian AJ, Freedman JE, Johnson JL, Keaney Jr JF and Loscalzo J . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 17012–17017.
Vazquez F and Sellers WR . (2000). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1470, M21–M35.
Wang DS, Rieger-Christ K, Latini JM, Moinzadeh A, Stoffel J, Pezza JA, Saini K, Libertino JA and Summerhayes IC . (2000). Int. J. Cancer, 88, 620–625.
Weng LP, Smith WM, Dahia PL, Ziebold U, Gil E, Lees JA and Eng C . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 5808–5814.
Wolf Jr JS and Smith DS . (1996). Urology, 47, 2–13.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr A Klippel for the generous gift of dominant-negative PI3K p85 subunit, Drs Frank Furnari and Webster Cavenee for the PTEN constructs and PBABE vector used for generation of both transient and stable transfections and Kathryn M Gulding for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by an NIH training grant DK007766 to JJG and NIH R01CA085329 awards to DT JJG is an American Foundation for Urologic Disease (AFUD) scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gildea, J., Herlevsen, M., Harding, M. et al. PTEN can inhibit in vitro organotypic and in vivo orthotopic invasion of human bladder cancer cells even in the absence of its lipid phosphatase activity. Oncogene 23, 6788–6797 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207599
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207599
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity
Nature Reviews Cancer (2015)
-
Identification of nucleolus-localized PTEN and its function in regulating ribosome biogenesis
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Suppression of human lung cancer cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro by the transducer of ErbB-2.1 (TOB1)
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2012)
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase, mTOR, and Glycogen synthase kinase-3β mediated regulation of p21 in human urothelial carcinoma cells
BMC Urology (2011)
-
Suppression of cellular proliferation and invasion by the concerted lipid and protein phosphatase activities of PTEN
Oncogene (2010)