Abstract
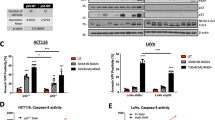
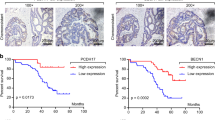
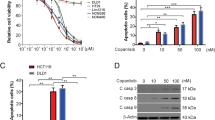
c-FLIP inhibits caspase 8 activation and apoptosis mediated by death receptors such as Fas and DR5. We studied the effect of c-FLIP on the apoptotic response to chemotherapies used in colorectal cancer (CRC) (5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin and irinotecan). Simultaneous downregulation of both c-FLIP splice forms c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS with siRNA synergistically enhanced chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in p53 wild-type (HCT116p53+/+, RKO), null (HCT116p53−/−) and mutant (H630) CRC cell lines. Furthermore, overexpression of c-FLIPL, but not c-FLIPS, potently inhibited apoptosis induced by chemotherapy in HCT116p53+/+ cells, suggesting that c-FLIPL was the more important splice form in mediating chemoresistance. In support of this, siRNA specifically targeted against c-FLIPL synergistically enhanced chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in a manner similar to the siRNA targeted against both splice forms. Inhibition of caspase 8 blocked the enhanced apoptosis induced by c-FLIP-targeted (FT) siRNA and chemotherapy. Furthermore, we found that downregulating cell surface DR5, but not Fas, also inhibited apoptosis induced by FT siRNA and chemotherapy. Interestingly, these effects were not dependent on activation of DR5 by its ligand TRAIL. These results indicate that c-FLIP inhibits TRAIL-independent, DR5- and caspase 8-dependent apoptosis in response to chemotherapy in CRC cells. Moreover, targeting c-FLIP in combination with existing chemotherapies may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J and Hickish T et al. (2004). N Engl J Med, 350, 2343–2351.
Aragane Y, Kulms D, Metze D, Wilkes G, Poppelmann B and Luger TA et al. (1998). J Cell Biol, 140, 171–182.
Beltinger C, Fulda S, Kammertoens T, Meyer E, Uckert W and Debatin KM . (1999). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96, 8699–8704.
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV and Wallach D . (1996). Cell, 85, 803–815.
Chan FK, Chun HJ, Zheng L, Siegel RM, Bui KL and Lenardo MJ . (2000). Science, 288, 2351–2354.
Chinnaiyan AM, O'Rourke K, Tewari M and Dixit VM . (1995). Cell, 81, 505–512.
Chou TC and Talalay P . (1984). Adv Enzyme Regul, 22, 27–55.
Conticello C, Pedini F, Zeuner A, Patti M, Zerilli M and Stassi G et al. (2004). J Immunol, 172, 5467–5477.
Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD and Karasek P et al. (2000). Lancet, 355, 1041–1047.
Fulda S, Meyer E and Debatin KM . (2000). Cancer Res, 60, 3947–3956.
Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, Le Bail N, Faggiuolo R and Focan C et al. (2000). J Clin Oncol, 18, 136–147.
Gniadecki R . (2004). Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 320, 165–169.
Griffith TS and Lynch DH . (1998). Curr Opin Immunol, 10, 559–563.
Iordanov MS, Kirsch JD, Ryabinina OP, Wong J, Spitz PN and Korcheva VB et al. (2005). Apoptosis, 10, 167–176.
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K and Steiner V et al. (1997). Nature, 388, 190–195.
Jin TG, Kurakin A, Benhaga N, Abe K, Mohseni M and Sandra F et al. (2004). J Biol Chem, 279, 55594–55601.
Kamarajan P, Sun NK and Chao CC . (2003). Biochem J, 376, 253–260.
Kataoka T, Schroter M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Irmler M and Thome M et al. (1998). J Immunol, 161, 3936–3942.
Kataoka T and Tschopp J . (2004). Mol Cell Biol, 24, 2627–2636.
Kim SG, Jong HS, Kim TY, Lee JW, Kim NK and Hong SH et al. (2004). Mol Biol Cell, 15, 420–434.
Krueger A, Baumann S, Krammer PH and Kirchhoff S . (2001). Mol Cell Biol, 21, 8247–8254.
Longley DB, Boyer J, Allen WL, Latif T, Ferguson PR and Maxwell PJ et al. (2002). Cancer Res, 62, 2644–2649.
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG . (2003). Nat Rev Cancer, 3, 330–338.
Mathas S, Lietz A, Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel F, Wiesner B and Janz M et al. (2004). J Exp Med, 199, 1041–1052.
Matta H, Eby MT, Gazdar AF and Chaudhary PM . (2002). Cancer Biol Ther, 1, 652–660.
Maxwell PJ, Longley DB, Latif T, Boyer J, Allen W and Lynch M et al. (2003). Cancer Res, 63, 4602–4606.
Micheau O, Solary E, Hammann A and Dimanche-Boitrel MT . (1999). J Biol Chem, 274, 7987–7992.
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P, Holler N, Tschopp J and Nicholson DW et al. (2002). J Biol Chem, 277, 45162–45171.
Mosmann T . (1983). J Immunol Methods, 65, 55–63.
Nagata S . (1999). Annu Rev Genet, 33, 29–55.
Nam SY, Jung GA, Hur GC, Chung HY, Kim WH and Seol DW et al. (2003). Cancer Sci, 94, 1066–1073.
Park SJ, Kim YY, Ju JW, Han BG, Park SI and Park BJ . (2001). Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 289, 1205–1210.
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, Kotoula V, Tseleni-Balafouta S, Ashkenazi A and Koutras DA et al. (2002). Am J Pathol, 161, 643–654.
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW and Park JH . (2001). J Pathol, 194, 15–19.
Santiago B, Galindo M, Palao G and Pablos JL . (2004). J Immunol, 172, 560–566.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH and Peter ME . (1999). J Biol Chem, 274, 1541–1548.
Wang S and El-Deiry WS . (2004). Cancer Res, 64, 6666–6672.
Yeh WC, Itie A, Elia AJ, Ng M, Shu HB and Wakeham A et al. (2000). Immunity, 12, 633–642.
Zhou XD, Yu JP, Liu J, Luo HS, Chen HX and Yu HG . (2004). Clin Sci (London), 106, 397–405.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by: Cancer Research UK, the Medical Research Council, the Research and Development Office and the Department of Health and Social Services, Northern Ireland and the Ulster Cancer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longley, D., Wilson, T., McEwan, M. et al. c-FLIP inhibits chemotherapy-induced colorectal cancer cell death. Oncogene 25, 838–848 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209122
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cut-like homeobox 1 (CUX1) tumor suppressor gene haploinsufficiency induces apoptosis evasion to sustain myeloid leukemia
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Pevonedistat (MLN4924): mechanism of cell death induction and therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2020)
-
The pro-survival function of DLEC1 and its protection of cancer cells against 5-FU-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of BCL-XL
Cytotechnology (2019)
-
Cytoplasmic FLIP(S) and nuclear FLIP(L) mediate resistance of castrate-resistant prostate cancer to apoptosis induced by IAP antagonists
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Negative regulators of cell death pathways in cancer: perspective on biomarkers and targeted therapies
Apoptosis (2018)