Abstract
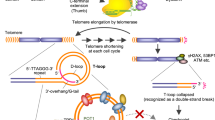
Inhibition of telomerase activity by telomerase inhibitors induces a gradual loss of telomeres, and this in turn causes cancer cells to enter to a crisis stage. Here, we report the telomerase inhibitor telomestatin, which is known to stabilize G-quadruplex structures at 3′ single-stranded telomeric overhangs (G-tails), rapidly dissociates TRF2 from telomeres in cancer cells within a week, when given at a concentration that does not cause normal cells to die. The G-tails were dramatically reduced upon short-term treatment with the drug in cancer cell lines, but not in normal fibroblasts and epithelial cells. In addition, telomestatin also induced anaphase bridge formation in cancer cell lines. These effects of telomestatin were similar to those of dominant negative TRF2, which also causes a prompt loss of the telomeric G-tails and induces an anaphase bridge. These results indicate that telomestatin exerts its anticancer effect not only through inhibiting telomere elongation, but also by rapidly disrupting the capping function at the very ends of telomeres. Unlike conventional telomerase inhibitors that require long-term treatments, the G-quadruplex stabilizer telomestatin induced prompt cell death, and it was selectively effective in cancer cells. This study also identifies the TRF2 protein as a therapeutic target for treating many types of cancer which have the TRF2 protein at caps of the telomere DNA of each chromosome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama M, Hideshima T, Shammas MA, Hayashi T, Hamasaki M, Tai YT et al. (2003). Cancer Res 63: 6187–6194.
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB et al. (1998). Science 279: 349–352.
Broccoli D, Smogorzewska A, Chong L, de Lange T . (1997). Nat Genet 17: 231–235.
Carney SA, Tahara H, Swartz CD, Risinger JI, He H, Moore AB et al. (2002). Lab Invest 82: 719–728.
Fang G, Cech TR . (1993a). Biochemistry 32: 11646–11657.
Fang G, Cech TR . (1993b). Cell 74: 875–885.
Giraldo R, Suzuki M, Chapman L, Rhodes D . (1994). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7658–7662.
Gomez D, Paterski R, Lemarteleur T, Shin-Ya K, Mergny JL, Riou JF . (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 41487–41494.
Gowan SM, Harrison JR, Patterson L, Valenti M, Read MA, Neidle S et al. (2002). Mol Pharmacol 61: 1154–1162.
Gowan SM, Heald R, Stevens MF, Kelland LR . (2001). Mol Pharmacol 60: 981–988.
Griffith JD, Comeau L, Rosenfield S, Stansel RM, Bianchi A, Moss H et al. (1999). Cell 97: 503–514.
Gu J, Spitz MR, Zhao H, Lin J, Grossman HB, Dinney CP et al. (2005). Carcinogenesis 26: 1741–1747.
Hahn WC, Stewart SA, Brooks MW, York SG, Eaton E, Kurachi A et al. (1999). Nat Med 5: 1164–1170.
Han H, Hurley LH . (2000). Trends Pharmacol Sci 21: 136–142.
Hanaoka S, Nagadoi A, Nishimura Y . (2005). Protein Sci 14: 119–130.
Hirose M, Abe-Hashimoto J, Ogura K, Tahara H, Ide T, Yoshimura T . (1997). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 123: 337–344.
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Dai Y, Hardy S, de Lange T . (1999). Science 283: 1321–1325.
Kim MY, Gleason-Guzman M, Izbicka E, Nishioka D, Hurley LH . (2003). Cancer Res 63: 3247–3256.
Kim MY, Vankayalapati H, Shin-Ya K, Wierzba K, Hurley LH . (2002). J Am Chem Soc 124: 2098–2099.
Kondo S, Tanaka Y, Kondo Y, Hitomi M, Barnett GH, Ishizaka Y et al. (1998). Faseb J 12: 801–811.
Makarov VL, Hirose Y, Langmore JP . (1997). Cell 88: 657–666.
Mergny JL, Helene C . (1998). Nat Med 4: 1366–1367.
Nakamura Y, Hirose M, Matsuo H, Tsuyama N, Kamisango K, Ide T . (1999). Clin Chem 45: 1718–1724.
Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Kumaki F, Hiroi S, Mukai M, Ikeda E et al. (2003). Clin Cancer Res 9: 1105–1111.
Nakayama J, Tahara H, Tahara E, Saito M, Ito K, Nakamura H et al. (1998). Nat Genet 18: 65–68.
Nijjar T, Bassett E, Garbe J, Takenaka Y, Stampfer MR, Gilley D et al. (2005). Oncogene 24: 3369–3376.
Parkinson GN, Lee MP, Neidle S . (2002). Nature 417: 876–880.
Riou JF, Guittat L, Mailliet P, Laoui A, Renou E, Petitgenet O et al. (2002). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 2672–2677.
Rosu F, Gabelica V, Shin-ya K, De Pauw E . (2003). Chem Commun (Camb): 2702–2703.
Seimiya H, Muramatsu Y, Ohishi T, Tsuruo T . (2005). Cancer Cell 7: 25–37.
Seimiya H, Muramatsu Y, Smith S, Tsuruo T . (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 1944–1955.
Seimiya H, Oh-hara T, Suzuki T, Naasani I, Shimazaki T, Tsuchiya K et al. (2002). Mol Cancer Ther 1: 657–665.
Shay JW, Wright WE . (2005). Cancer Cell 7: 1–2.
Shin-ya K, Wierzba K, Matsuo K, Ohtani T, Yamada Y, Furihata K et al. (2001). J Am Chem Soc 123: 1262–1263.
Smogorzewska A, van Steensel B, Bianchi A, Oelmann S, Schaefer MR, Schnapp G et al. (2000). Mol Cell Biol 20: 1659–1668.
Stansel RM, de Lange T, Griffith JD . (2001). Embo J 20: 5532–5540.
Tahara H, Kusunoki M, Yamada Y, Matsumura S, Ide T . (2005). Nat Meth 2: 829–831.
Tahara H, Nakanishi T, Kitamoto M, Nakashio R, Shay JW, Tahara E et al. (1995). Cancer Res 55: 2734–2736.
Takai H, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T . (2003). Curr Biol 13: 1549–1556.
Tauchi T, Shin-Ya K, Sashida G, Sumi M, Nakajima A, Shimamoto T et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 5338–5347.
van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T . (1998). Cell 92: 401–413.
Williamson JR, Raghuraman MK, Cech TR . (1989). Cell 59: 871–880.
Wright WE, Tesmer VM, Huffman KE, Levene SD, Shay JW . (1997). Genes Dev 11: 2801–2809.
Zahler AM, Williamson JR, Cech TR, Prescott DM . (1991). Nature 350: 718–720.
Zhang X, Mar V, Zhou W, Harrington L, Robinson MO . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 2388–2399.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. We thank Dr Asako Nakamura for technical advise for telomere ChIP assay. We thank Angie M Sera not only for critical reading of the manuscript, but also for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahara, H., Shin-ya, K., Seimiya, H. et al. G-Quadruplex stabilization by telomestatin induces TRF2 protein dissociation from telomeres and anaphase bridge formation accompanied by loss of the 3′ telomeric overhang in cancer cells. Oncogene 25, 1955–1966 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209217
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combining old and new concepts in targeting telomerase for cancer therapy: transient, immediate, complete and combinatory attack (TICCA)
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Ligands stimulating antitumour immunity as the next G-quadruplex challenge
Molecular Cancer (2022)
-
QSAR, pharmacophore modeling and molecular docking studies to identify structural alerts for some nitrogen heterocycles as dual inhibitor of telomerase reverse transcriptase and human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2021)
-
Chemical targeting of G-quadruplexes in telomeres and beyond for molecular cancer therapeutics
The Journal of Antibiotics (2021)
-
Targeting glioma stem cells in vivo by a G-quadruplex-stabilizing synthetic macrocyclic hexaoxazole
Scientific Reports (2017)