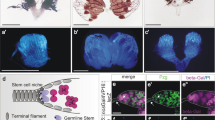
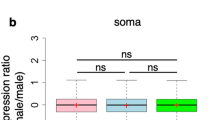
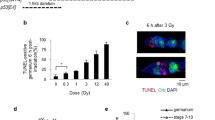
Abstract
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome (BHD) is a rare, inherited genodermatosis characterized by hair follicle hamartomas, kidney tumors and spontaneous pneumothorax. The BHD locus was mapped to chromosome 17p11.2 by linkage analysis, and germline mutations in a novel gene (BHD) were identified in a panel of BHD families. Using RNA interference to decrease expression of the Drosophila BHD homolog (DBHD), we have demonstrated that DBHD is required for male germline stem cell (GSC) maintenance in the fly testis. Reduction of DBHD gene activity suppresses the GSC overproliferation phenotype associated with overexpression of either unpaired (upd) or decapentaplegic (dpp). Further genetic interaction experiments suggest that DBHD regulates GSC maintenance downstream or in parallel of the JAK/STAT and Dpp signal-transduction pathways. These findings suggest that the BHD protein may regulate tumorigenesis through modulating stem cells in human.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baksa K, Parke T, Dobens LL, Dearolf CR . (2002). Dev Biol 243: 166–175.
Birt AR, Hogg GR, Dubé WJ . (1977). Arch Dermatol 113: 1674–1677.
Brand AH, Perrimon N . (1993). Development 118: 401–415.
Brawley C, Matunis E . (2004). Science 304: 1331–1334.
Chen D, McKearin D . (2003). Curr Biol 13: 1786–1791.
Chen D, McKearin D . (2005). Curr Biol 15: 179–184.
Chen HW, Chen X, Oh S, Marinissen MJ, Gutkind JS, Hou XS . (2002). Genes Dev 16: 388–398.
Chomette G, Delcourt A, Auriol M . (1985) In: Alan R (ed). Testicular Cancer. Liss: New York, pp 35–45.
Fabrizio JJ, Boyle M, DiNardo S . (2003). Dev Biol 258: 117–128.
Fuller MT . (1993) In: Bate M, Martinez-Arias A (eds). The Development of Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, pp 71–147.
Fuller MT . (1998). Semin Cell Dev Biol 9: 433–444.
Gilboa L, Lehmann R . (2004). Curr Biol 14: 981–986.
Giordano E, Rendina R, Peluso I, Furia M . (2002). Genetics 160: 637–648.
Hou XS, Melnick MB, Perrimon N . (1996). Cell 84: 411–419.
Kawase E, Wong MD, Ding BC, Xie T . (2003). Development 131: 1365–1375.
Kiger AA, Jones DL, Schulz C, Rogers MB, Fuller MT . (2001). Science 294: 2542–2545.
Kiger AA, White-Cooper H, Fuller MT . (2000). Nature 407: 750–754.
Lingaas F, Comstock KE, Kirkness EF, Sorensen A, Aarskaug T, Hitte C et al. (2003). Hum Mol Genet 12: 3043–3053.
Nickerson ML, Warren MB, Toro JR, Matrosova V, Glenn G, Turner ML et al. (2002). Cancer Cell 2: 157–164.
Okimoto K, Sakurai J, Kobayashi T, Mitani H, Hirayama Y, Nickerson M et al. (2004). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2023–2027.
Pavlovich CP, Walther MM, Eyler RA, Hewitt SM, Zbar B, Linehan WM et al. (2002). Am J Surg Pathol 26: 1542–1552.
Pignoni F, Zipursky SL . (1997). Development 124: 271–278.
Schmidt LS, Warren MB, Nickerson ML, Weirich G, Matrosova V, Toro JR et al. (2001). Am J Hum Genet 69: 876–882.
Szakmary A, Cox DN, Wang Z, Lin H . (2005). Curr Biol 15: 171–178.
Tran J, Brenner TJ, DiNardo S . (2000). Nature 407: 754–757.
Tulina N, Matunis N . (2001). Science 294: 2546–2549.
Vocke CD, Yang Y, Pavlovich CP, Schmidt LS, Nickerson ML, Torres-Cabala CA et al. (2005). J Natl Cancer Inst 97: 931–935.
Youngren KK, Coveney D, Peng X, Bhattacharya C, Schmidt LS, Nickerson ML et al. (2005). Nature 435: 360–364.
Zbar B, Alvord WG, Glenn G, Turner ML, Pavlovich CP, Schmidt L et al. (2002). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11: 393–400.
Acknowledgements
We thank C Dearolf, T Xie, S DiNardo, K Basler, T Neufeld, and the Bloomington Stock Center for fly stocks; R Lehmann and the Developmental Study Hybridoma Bank for antibodies; S Wincovith, S Garfield, E Cho, and S Lockett for help on the confocal microscope; H Shin for generating transgene lines; N Parrish for help on preparation of the manuscript. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of NIH, National Cancer Institute and by federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under Contract No. N01-C0-12400.The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products or organizations imply endorsement by the US government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Zhen, W., Zheng, Z. et al. The Drosophila homolog of the human tumor suppressor gene BHD interacts with the JAK-STAT and Dpp signaling pathways in regulating male germline stem cell maintenance. Oncogene 25, 5933–5941 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209593
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209593
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed genes between the ovary and testis of the honey bee Apis mellifera
Apidologie (2022)
-
α-Tubulin Regulates the Fate of Germline Stem Cells in Drosophila Testis
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Folliculin regulates mTORC1/2 and WNT pathways in early human pluripotency
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Expression and knockdown of zebrafish folliculin suggests requirement for embryonic brain morphogenesis
BMC Developmental Biology (2016)
-
Analyzing stem cell dynamics: use of cutting edge genetic approaches in model organisms
Frontiers in Biology (2015)