Abstract
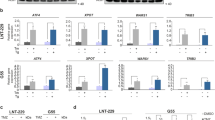
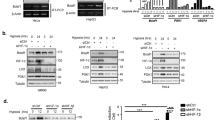
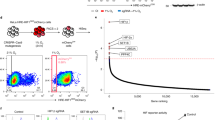
Solid tumors often have an inadequate blood supply, which results in large regions that are subjected to hypoxic or anoxic stress. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a transcription factor that regulates much of the transcriptional response of cells to hypoxia. Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) is another transcription factor that responds to a variety of stresses and is often upregulated in cancer. We investigated the regulation of ATF3 by oxygen deprivation. ATF3 induction occurred most robustly under anoxia, is common, and it is not dependent on presence of HIF-1 or p53, but is sensitive to the inhibition of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation and the antioxidant N-acetylcystein. ATF3 could also be induced by desferrioxamine but not by the mitochondrial poison cyanide or the nonspecific 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase inhibitor dimethyloxalylglycine. We also show that anoxic ATF3 mRNA is more stable than normoxic mRNA providing a mechanism for this induction. Thus, this study demonstrates that the regulation of ATF3 under anoxia is independent of 2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase, HIF-1 and p53, presumably involving multiple regulatory pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfranca A, Gutierrez MD, Vara A, Aragones J, Vidal F, Landazuri MO . (2002). Mol Cell Biol 22: 12–22.
Ameri K, Lewis CE, Raida M, Sowter H, Hai T, Harris AL . (2004). Blood 103: 1876–1882.
Amundson SA, Bittner M, Chen Y, Trent J, Meltzer P, Fornace Jr J . (1999). Oncogene 18: 3666–3672.
Blais JD, Filipenko V, Bi M, Harding HP, Ron D, Koumenis C et al. (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 7469–7482.
Bottone Jr FG, Moon Y, Alston-Mills B, Eling TE . (2005). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315: 668–677.
Cai Y, Zhang C, Nawa T, Aso T, Tanaka M, Oshiro S et al. (2000). Blood 96: 2140–2148.
Chilov D, Camenisch G, Kvietikova I, Ziegler U, Gassmann M, Wenger RH . (1999). J Cell Sci 112 (Part 8): 1203–1212.
Culmsee C, Siewe J, Junker V, Retiounskaia M, Schwarz S, Camandola S et al. (2003). J Neurosci 23: 8586–8595.
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J, Gleadle JM . (2006). J Biol Chem 281: 15215–15226.
Fan F, Jin S, Amundson SA, Tong T, Fan W, Zhao H et al. (2002). Oncogene 21: 7488–7496.
Francis JS, Dragunow M, During MJ . (2004). Brain Res Mol Brain Res 124: 199–203.
Goldberg-Cohen I, Furneauxb H, Levy AP . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 13635–13640.
Graeber TG, Osmanian C, Jacks T, Housman DE, Koch CJ, Lowe SW et al. (1996). Nature 379: 88–91.
Hai T, Hartman MG . (2001). Gene 273: 1–11.
Hai T, Wolfgang CD, Marsee DK, Allen AE, Sivaprasad U . (1999). Gene Exp 7: 321–335.
Hammond EM, Green SL, Giaccia AJ . (2003). Mutat Res 532: 205–213.
Hammond EM, Mandell DJ, Salim A, Krieg AJ, Johnson TM, Shirazi HA et al. (2006). Mol Cell Biol 26: 3492–3504.
Hartman MG, Lu D, Kim ML, Kociba GJ, Shukri T, Buteau J et al. (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 5721–5732.
Inoue K, Zama T, Kamimoto T, Aoki R, Ikeda Y, Kimura H et al. (2004). Genes Cells 9: 59–70.
Ishiguro T, Nagawa H . (2000). Oncol Res 12: 181–183.
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL . (1996). J Biol Chem 271: 17771–17778.
Kaelin Jr WG . (2005). Cell Metab 1: 357–358.
Koumenis C, Alarcon R, Hammond E, Sutphin P, Hoffman W, Murphy M et al. (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 1297–1310.
Le QT, Denko NC, Giaccia AJ . (2004). Cancer Metastasis Rev 23: 293–310.
Liang G, Wolfgang CD, Chen BP, Chen TH, Hai T . (1996). J Biol Chem 271: 1695–1701.
Lu D, Wolfgang CD, Hai T . (2006). J Biol Chem 281: 10473–10481.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. (1999). Nature 399: 271–275.
Okamoto A, Iwamoto Y, Maru Y . (2006). Mol Cell Biol 26: 1087–1097.
Pan YX, Chen H, Kilberg MS . (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 34609–34616.
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC . (2006). Cell Metab 3: 187–197.
Papandreou I, Krishna C, Kaper F, Cai D, Giaccia AJ, Denko NC . (2005). Cancer Res 65: 3171–3178.
Ryan HE, Poloni M, McNulty W, Elson D, Gassmann M, Arbeit JM et al. (2000). Cancer Res 60: 4010–4015.
Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ . (2004). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 343–354.
Scott PH, Paul A, Belham CM, Peacock AJ, Wadsworth RM, Gould GW et al. (1998). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158: 958–962.
Tournier C, Dong C, Turner TK, Jones SN, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . (2001). Genes Dev 15: 1419–1426.
Tournier C, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Barrett T, Davis RJ . (1997). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 7337–7342.
Vecsey-Semjen B, Becker KF, Sinski A, Blennow E, Vietor I, Zatloukal K et al. (2002). Oncogene 21: 4646–4662.
Vengellur A, Phillips JM, Hogenesch JB, LaPres JJ . (2005). Physiol Genomics 22: 308–318.
Ventura JJ, Cogswell P, Flavell RA, Baldwin Jr AS, Davis RJ . (2004). Genes Dev 18: 2905–2915.
Wei CL, Wu Q, Vega VB, Chiu KP, Ng P, Zhang T et al. (2006). Cell 124: 207–219.
Yan C, Lu D, Hai T, Boyd DD . (2005). EMBO J 24: 2425–2435.
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was supported by grants to K Ameri from the EU research training network for young scientists (HPRN-CT-2000-0089), to T Hai from NIH (DK59605), and to N Denko from the NCI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ameri, K., Hammond, E., Culmsee, C. et al. Induction of activating transcription factor 3 by anoxia is independent of p53 and the hypoxic HIF signalling pathway. Oncogene 26, 284–289 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209781
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209781
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of unfolded protein response and ER-associated degradation under freezing, anoxia, and dehydration stresses in the freeze-tolerant wood frogs
Cell Stress and Chaperones (2023)
-
Impact of the hypoxic phenotype on the uptake and efflux of nanoparticles by human breast cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Sufentanil Alleviates Intrathecal Lidocaine Induced Prolonged Sensory and Motor Impairments but not the Spinal Histological Injury in Rats
Neurochemical Research (2018)
-
Runx2, a target gene for activating transcription factor-3 in human breast cancer cells
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
Photodynamic therapy suppresses tumor growth in an in vivo model of human hemangioma
Archives of Dermatological Research (2014)