Abstract
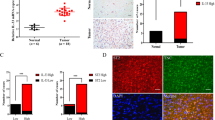
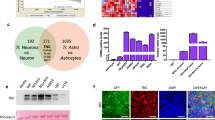
Transglutaminase 2 (TG2, a.k.a. tissue transglutaminase) belongs to a family of transglutaminase enzymes that stabilize proteins by affecting covalent crosslinking via formation of amide bonds. Cell surface TG2 is directly involved as an adhesive receptor in cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions. Here, we show that TG2 activity is elevated in glioblastomas compared with non-neoplastic brain. Immunofluorescent studies showed increased staining of fibronectin colocalized with TG2 in the ECM in glioblastomas. In addition, small clusters of invading human glioblastoma cells present in non-neoplastic brain parenchyma secrete high levels of TG2 and fibronectin that distinguish them from normal brain stroma. Downregulation of TG2 in U87MG glioblastoma cells with RNAi demonstrated decreased assembly of fibronectin in the ECM. Treatment with KCC009 blocked the remodeling of fibronectin in the ECM in glioblastomas in both in vitro and in vivo studies. KCC009 treatment in mice harboring orthotopic glioblastomas (DBT-FG) sensitized the tumors to N,N′-bis(2-chloroethyl)-N-nitrosourea chemotherapy, as measured by reduced bioluminescence, increased apoptosis and prolonged survival. The ability of KCC009 to interfere with the permissive remodeling of fibronectin in the ECM in glioblastomas suggests a novel target to enhance sensitivity to chemotherapy directed not only at the tumor mass, but also invading glioblastoma cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschlimann D, Thomazy V . (2000). Protein cross-linking in assembly and remodeling of extracellular matrices: the role of transglutaminases. Connect Tissue Res 41: 1–27.
Akimov SS, Belkin AM . (2001). Cell-surface transglutaminase promotes fibronectin assembly via interaction with the gelatin-binding domain of fibronectin: a role in TGFbeta-dependent matrix deposition. J Cell Sci 114: 2989–3000.
Akimov SS, Krylov D, Fleischman LF, Belkin AM . (2000). Tissue transglutaminase is an integrin-binding adhesion coreceptor for fibronectin. J Cell Bio 148: 825–838.
Buckley CD, Pilling D, Henriquez NV, Parsonage G, Threlfall K, Scheel-Toellner D et al. (1999). RGD peptides induce apoptosis by direct caspase-3 activation. Nature 397: 534–539.
Castellani P, Borsi L, Carnemolla B, Biro A, Dorcaratto A, Viale GL et al. (2002). Differentiation between high- and low-grade astrocytoma using a human recombinant antibody to the extra domain-B of fibronectin. Am J Pathol 161: 1695–1700.
Castro MG, Cowen R, Williamson IK, David A, Jimenez-Dalmaroni MJ, Yuan X et al. (2003). Current and future strategies for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. Pharmacol Ther 98: 71–108.
Chicoine MR, Won EK, Zahner M . (2001). Intra-tumoral injection of lipopolysaccharide causes regression of subcutaneously implanted mouse glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 48: 607–615.
Choi K, Siegel M, Piper JL, Yuan L, Cho E, Strnad P et al. (2005). Chemistry and biology of dihydroisoxazole derivatives: selective inhibitors of human transglutaminase 2. Chem Biol 12: 469–475.
Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA, Shtil AA, Dalton WS . (1999). Cell adhesion mediated-drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines. Blood 93: 1658–1667.
De Laurenzi V, Melino G . (2001). Gene disruption of tissue transglutaminase. Mol Cell Biol 21: 148–155.
Fesus L, Piacentini M . (2002). Transglutaminase 2: an enigmatic enzyme with diverse functions. Trends Biochem Sci 27: 534–539.
Gross S, Piwnica-Worms D . (2005). Monitoring proteasome activity in cellulo and in living animals by bioluminescent imaging: technical considerations for design and use of genetically encoded reporters. Methods Enzymol 399: 512–530.
Hadden HL, Henke CA . (2000). Introduction of lung fibroblast apoptosis by soluble fibronectin peptides. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162: 1553–1560.
Han JA, Park SC . (1999). Reduction of transglutaminase 2 expression is associated with an induction of drug sensitivity in the PC-14 human lung cancer cell line. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 125: 89–95.
Jiang Z, Zheng X, Lytle RA, Higashikubo R, Rich KM . (2004). Lovastatin-induced up-regulation of the BH3-only protein, Bim and cell death in glioblastoma cells. J Neurochem 89: 168–178.
Jiang Z, Zheng X, Rich KM . (2003). Down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression with bispecific antisense treatment of glioblastoma cell lines induces cell death. J Neurochem 84: 273–281.
Kumanishi T . (1967). Brain tumors induced with Rous sarcoma virus, Schmidt-Ruppin strain. I. Induction of brain tumors in adult mice with Rous chicken sarcoma cells. Jpn J Exp Med 37: 461–474.
Martinez J, Chalupowicz DG, Roush RK, Sheth A, Barsigian C . (1994). Transglutaminase-mediated processing of fibronectin by endothelial cell monolayers. Biochemistry 33: 2538–2545.
Mehta K . (1994). High levels of transglutaminase expression in doxorubicin-resistant human breast carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 58: 400–406.
Midulla M, Verma R, Pignatelli M, Ritter MA, Courtenay-Luck NS . (2000). Source of oncofetal ED-B-containing fibronectin: implications of production by both tumor and endothelial cells. Cancer Res 60: 164–169.
Nanda N, Iismaa SE, Owens WA, Husain A, Mackay F, Graham RM . (2001). Targeted inactivation of Gh/tissue transglutaminase II. J Biol Chem 23: 20673–20678.
Nicolo G, Salvi S, Oliveri G, Borsi L, Castellani P, Zardi L et al. (1990). Expression of tenascin and of the ED-B containing oncofetal fibronectin isoform in human cancer. Cell Differ Dev 32: 401–408.
Ohnishi T, Hiraga S, Izumoto S, Matsumura H, Kanemura Y, Arita N et al. (1998). Role of fibronectin-stimulated tumor cell migration in glioma invasion in vivo: clinical significance of fibronectin and fibronectin receptor expressed in human glioma tissues. Clin Exp Metastasis 16: 729–741.
Pupa SM, Menard S, Forti S, Tagliabue E . (2002). New insights into the role of extracellular matrix during tumor onset and progression. J Cell Physiol 192: 259–267.
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C et al. (1999). Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med 5: 662–668.
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson EN . (2004). CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64: 8604–8612.
Verderio EA, Telci D, Okoye A, Melino G, Griffin M . (2003). A novel RGD-independent cell adhesion pathway mediated by fibronectin-bound tissue transglutaminase rescues cells from anoikis. J Biol Chem 278: 42604–42614.
Wernert N . (1997). The multiple roles of tumour stroma. Virchows Arch 430: 433–443.
Yuan L, Choi K, Khosla C, Zheng X, Higashikubo R, Chicoine MR et al. (2005). Tissue transglutaminase 2 inhibition promotes cell death and chemosensitivity in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1293–1302.
Zemskov EA, Janiak A, Hang J, Waghray A, Belkin AM . (2006). The role of tissue transglutaminase in cell–matrix interactions. Frontiers Biosci 11: 1057–1076.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Alvine Pharmaceuticals (KMR); the NIH R01 DK63158 (CK) and P50 CA94056 (DP-W); the NCI T32CA009547 post-doctoral fellowship (CRM); and the Stanford-NIH Biotechnology Training Grant (MS). We thank the Alvin J Siteman Cancer Center at Washington University School of Medicine for the use of the Tissue Procurement Core which provided human glioblastoma frozen specimens (NCI Cancer Center Support Grant #P30 CA91842).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Siegel, M., Choi, K. et al. Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor, KCC009, disrupts fibronectin assembly in the extracellular matrix and sensitizes orthotopic glioblastomas to chemotherapy. Oncogene 26, 2563–2573 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210048
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210048
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transglutaminase 2 is associated with adverse colorectal cancer survival and represents a therapeutic target
Cancer Gene Therapy (2023)
-
Transglutaminase 2 expression is associated with increased risk of lymph node metastasis and recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer
Endocrine (2023)
-
Dissecting and rebuilding the glioblastoma microenvironment with engineered materials
Nature Reviews Materials (2019)
-
Transamidase site-targeted agents alter the conformation of the transglutaminase cancer stem cell survival protein to reduce GTP binding activity and cancer stem cell survival
Oncogene (2017)
-
Transglutaminase-2: evolution from pedestrian protein to a promising therapeutic target
Amino Acids (2017)