Abstract
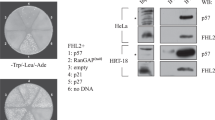
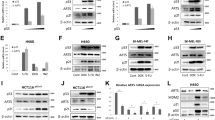
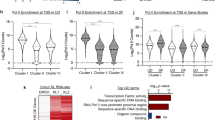
P27kip is a key inhibitory protein of the cell-cycle progression, which is rapidly downregulated in early G1 phase by a post-translational mechanism involving the proteosomal degradation. In this study, using a wounding model that induces cell-cycle entry of human dermal fibroblasts, we demonstrate that p27mRNA is downregulated when cells progress into the G1 phase, and then it returns to its basal level when cells approach the S phase. By using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction screening we identified inhibitors of differentiation (Id3), a bHLH transcriptional repressor, as a candidate mediator accounting for p27 mRNA decrease. Id3 silencing, using an small interfering RNA approach, reversed the injury mediated p27 downregulation demonstrating that Id3 is involved in the transcriptional repression of p27. Reporter gene experiments and a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay showed that Id3 likely exerts its repressive action through ELK1 inhibition. By inhibiting early p27 downregulation, Id3 depletion blocked (i) the G1-phase progression as assessed by the inhibition of pRb phosphorylation and p130 degradation and (ii) the G1/S transition as observed by the inhibition of cyclin A induction, demonstrating that p27 mRNA decrease is required for cell proliferation. Apart from its effect on the early p27 diminution, Id3 appears also involved in the control of the steady-state level of p27 at the G1/S boundary. In conclusion, this study identifies a novel mechanism of p27 regulation which besides p27 protein degradation also implicates a transcriptional mechanism mediated by Id3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alani RM, Young AZ, Shifflett CB . (2001). Id1 regulation of cellular senescence through transcriptional repression of p16/Ink4a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 7812–7816.
Bagui TK, Mohapatra S, Haura E, Pledger WJ . (2003). P27Kip1 and p21Cip1 are not required for the formation of active D cyclin-cdk4 complexes. Mol Cell Biol 23: 7285–7290.
Benezra R, Rafii S, Lyden D . (2001). Id proteins and angiogenesis. Oncogene 20: 8288–8289.
Blain SW, Montalvo E, Massague J . (1997). Differential interaction of the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p27Kip1 with cyclin A-Cdk2 and cyclin D2-Cdk4. J Biol Chem 272: 25863–25872.
Bloom J, Pagano M . (2003). Deregulated degradation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and malignant transformation. Semin Cancer Biol 13: 41–47.
Busca R, Berra E, Gaggioli C, Khaled M, Bille K, Marchetti B et al. (2005). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1{alpha} is a new target of microphthalmia-associat. J Cell Biol 170: 49–59.
Calderon M, Lawrence WT, Banes AJ . (1996). Increased proliferation in keloid fibroblasts wounded in vitro. J Surg Res 61: 343–347.
Cheng M, Olivier P, Diehl JA, Fero M, Roussel MF, Roberts JM et al. (1999). The p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) CDK ‘inhibitors’ are essential activators of cyclin D-dependent kinases in murine fibroblasts. EMBO J 18: 1571–1583.
Chraibi H, Dereure O, Teot L, Guillot B . (2004). The diagnosis and treatment of carcinomas occurring at the sites of chronic pressure ulcers. J Wound Care 13: 447–448.
Deed RW, Hara E, Atherton GT, Peters G, Norton JD . (1997). Regulation of Id3 cell-cycle function by CDK2-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6815–6821.
Engel I, Murre C . (2001). The function of E- and Id proteins in lymphocyte development. Nat Rev Immunol 1: 193–199.
Everly Jr DN, Mainou BA, Raab-Traub N . (2004). Induction of Id1 and Id3 by latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus and regulation of p27/Kip and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 in rodent fibroblast transformation. J Virol 78: 13470–13478.
Grana X, Garriga J, Mayol X . (1998). Role of the retinoblastoma protein family, pRB, p107 and p130 in the negative control of cell growth. Oncogene 17: 3365–3383.
Hosack DA, Dennis Jr G, Sherman BT, Lane HC, Lempicki RA . (2003). Identifying biological themes within lists of genes with EASE. Genome Biol 4: 11.
Janknecht R, Ernst WH, Pingoud V, Nordheim A . (1993). Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by MAP kinases. EMBO J 12: 5097–5104.
Kamura T, Hara T, Matsumoto M, Ishida N, Okumura F, Hatakeyama S et al. (2004). Cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase KPC regulates proteolysis of p27(Kip1) at G1 phase. Nat Cell Biol 6: 1229–1235.
Kee Y, Bronner-Fraser M . (2005). To proliferate or to die: role of Id3 in cell-cycle progression and survival of neural crest progenitors. Genes Dev 19: 744–755.
Kowanetz M, Valcourt U, Bergström R, Heldin CH, Moustakas A . (2004). Id2 and Id3 define the potency of cell proliferation and differentiation responses to transforming growth factor beta and bone morphogenic protein. Mol Cell Biol 24: 4241–4254.
Kudo Y, Kitajima S, Ogawa I, Miyauchi M, Takata T . (2005). Downregulation of Cdk inhibitor p27 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 41: 105–116.
LaBaer J, Garrett MD, Stevenson LF, Slingerland JM, Sandhu C, Chou HS et al. (1997). New functional activities for the p21 family of CDK inhibitors. Genes Dev 11: 847–862.
Lasorella A, Noseda M, Beyna M, Iavarone A . (2000). Id2 is a retinoblastoma protein target and mediates signalling by Myc oncoproteins. Nature 407: 592–598.
Loots MA, Lamme EN, Mekkes JR, Bos JD, Middelkoop E . (1999). Cultured fibroblasts from chronic diabetic wounds on the lower extremity (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) show disturbed proliferation. Arch Dermatol Res 291: 93–99.
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, Yan W, Gerald W, O'Reilly R et al. (1999). Id1 and Id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and vascularization of tumor xenografts. Nature 401: 670–677.
Malek NP, Sundberg H, McGrew S, Nakayama K, Kyriakides TR, Roberts JM . (2001). A mouse knock-in model exposes sequential proteolytic pathways that regulate p27Kip1 in G1 and S phase. Nature 413: 323–327.
Martin P . (1997). Wound healing – aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276: 75–81.
Massari ME, Murre C . (2000). Helix-loop-helix proteins: regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol Cell Biol 20: 429–440.
Minami S, Ohtani-Fujita N, Igata E, Tamaki T, Sakai T . (1997). Molecular cloning and characterization of the human p27Kip1 gene promoter. FEBS Lett 411: 1–6.
Montagnoli A, Fiore F, Eytan E, Carrano AC, Draetta GF, Hershko A et al. (1999). Ubiquitination of p27 is regulated by Cdk-dependent phosphorylation and trimeric complex formation. Genes Dev 13: 1181–1189.
Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N et al. (1996). Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell 85: 707–720.
Norton JD . (2000). ID helix-loop-helix proteins in cell growth, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Cell Sci 113: 3897–3905.
Ohtani N, Zebedee Z, Huot TJG, Stinson JA, Sugimoto M, Ohashi Y et al. (2001). Opposing effects of Ets and Id proteins on p16ink4 expression during cellular senescence. Nature 409: 1067–1070.
Okabe M, Inagaki H, Murase T, Inoue M, Nagai N, Eimoto T . (2001). Prognostic significance of p27 and Ki-67 expression in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the intraoral minor salivary gland. Mod Pathol 14: 1008–1014.
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V et al. (1995). Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269: 682–685.
Prabhu S, Ignatova A, Park S, Sun XH . (1997). Regulation of the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 by E2A and Id proteins. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5888–5896.
Rezzonico R, Ponzio G, Loubat A, Lallemand D, Proudfoot A, Rossi B . (1995). Two distinct signalling pathways are involved in the control of the biphasic junB transcription induced by interleukin-6 in the B cell hybridoma 7TD1. J Biol Chem 270: 1261–1268.
Rheinwald JG, Green H . (1975). Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell 6: 331–343.
Roberts EC, Deed RW, Inoue T, Norton JD, Sharrocks AD . (2001). Id helix-loop-helix proteins antagonize pax transcription factor activity by inhibiting DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol 21: 524–533.
Sakakibara K, Kubota K, Worku B, Ryer EJ, Miller JP, Koff A et al. (2005). PDGF-BB regulates p27 expression through ERK-dependent RNA turn-over in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chemi 280: 25470–25477.
Servant JM, Coulombe P, Turgeon B, Meloche S . (2000). Differential regulation of p27kip1 expression by mitogenic and hypertrophic factors: involvement of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. J Cell Biol 148: 543–556.
Sharma A, Henderson E, Gamer L, Zhuang Y, Stein R . (1997). Analysis of the role of E2A-encoded proteins in insulin gene transcription. Mol Endocrinol 11: 1608–1617.
Sherr CJ . (1995). D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci 20: 187–190.
Sherr CJ . (2002). D1 in G2 Mammalian G1 cyclins and cell-cycle progression. Cell-Cycle 1: 36–38.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . (1995). Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9: 1149–1163.
Takahashi E, Funato N, Higashihori N, Hata Y, Gridley T, Nakamura M . (2004). Snail regulates p21 waf/cip1 expression in cooperation with E2A and Twist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325: 1136–1144.
Trausch-Azar JS, Lingbeck J, Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL . (2004). Ubiquitin-Proteasome-mediated degradation of Id1 is modulated by MyoD. J Biol Chem 279: 32614–32619.
Turchi L, Chassot AA, Rezzonico R, Yeow K, Loubat A, Ferrua B et al. (2002). Dynamic characterization of the molecular events during in vitro epidermal wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 119: 56–63.
Yates PR, Atherton GT, Deed RW, Norton JD, Sharrocks AD . (1999). Id helix-loop-helix proteins inhibit nucleoprotein complex formation by the TCF ETS-domain transcription factors. EMBO J 18: 968–976.
Zheng W, Wang H, Xue L, Zhang Z, Tong T . (2004). Regulation of cellular senescence and p16ink4 expression by Id1 and E47 protein in human diploid fibroblast. J Biol Chem 279: 31524–31532.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs JD Norton for generous gifts of the expression vectors encoding wt-Id3 and Id3-ala5, to Dr T Sakai for the plasmid containing p27 promoter, to Dr R Stein for the E12 and E47 constructs, to Dr C Sardet and JM Blanchard for the p27-null MEFs and to Dr R Hipskind for kindly providing the elk1 constructs. AA Chassot is recipient of a fellowship from the INSERM/Région PACA and from la Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (LNCC). L Turchi is recipient of a fellowship of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) de Nice. This work was supported by grants of the Institut National de la Santé et la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), L'association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer, (ARC grant N° 5965 and 4500) and of the ‘Ministère de l'Education Nationale et de la Recherche’ (MENR) (ACI ACI: TS/0220045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chassot, AA., Turchi, L., Virolle, T. et al. Id3 is a novel regulator of p27kip1 mRNA in early G1 phase and is required for cell-cycle progression. Oncogene 26, 5772–5783 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210386
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210386
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Rewiring of the apoptotic TGF-β-SMAD/NFκB pathway through an oncogenic function of p27 in human papillary thyroid cancer
Oncogene (2017)
-
ID3 regulates the MDC1-mediated DNA damage response in order to maintain genome stability
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Comparison of human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) growth rate in culture media supplemented with or without basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)
Cell and Tissue Banking (2015)
-
ELK1
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2011)
-
Targeting Id protein interactions by an engineered HLH domain induces human neuroblastoma cell differentiation
Oncogene (2009)