Abstract
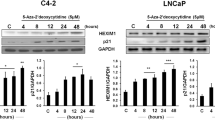
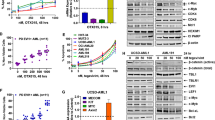
Human melanoma cell lines, SK-MEL-3 and SK-MEL-28, despite induction of the proapoptotic cytokine, Apo2L/TRAIL, did not undergo apoptosis in response to interferons (IFN-α2b or IFN-β). Postulating that genes important for apoptosis induction by IFNs might be silenced by methylation, the DNA demethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-AZAdC) was assessed. DR4 (TRAIL-R1) was identified as one of the genes reactivated by 5-AZAdC with a >3-fold increase in 8 of 10 melanoma cell lines. Pretreatment with 5-AZAdC sensitized SK-MEL-3 and SK-MEL-28 cells to apoptosis induced by IFN-α2b and IFN-β; methylation-specific PCR and bisulfite sequencing confirmed demethylation of 5′CpG islands of DR4 and flow cytometry showed an increase in DR4 protein on the cell surface. In cells with reactivated DR4, neutralizing mAB to TRAIL reduced apoptosis in response to IFN-β or Apo2L/TRAIL. To further confirm the role of DR4, it was expressed by retroviral vector in SK-MEL-3 and SK-MEL-28 cells with reversal of resistance to IFN-β and Apo2L/TRAIL. Thus, reexpressing DR4 by 5-AZAdC or retroviral transfection in melanoma cell in which promoter methylation had suppressed its expression, potentiated apoptosis by IFN-α2b, IFN-β and Apo2L/TRAIL. Reactivation of silenced proapoptotic genes by inhibitors of DNA methylation may enhance clinical response to IFNs or Apo2L/TRAIL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi A, Dixit V . (1998). Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281: 1305.
Borden EC . (2003). Interferons. In: Kufe D, Pollock R, Weichselbaum R, Bast R, Gansler T, Holland J, Frei T (eds). Cancer Medicine, 6th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Williams, pp 830–841.
Byun D, Cho K, Ryu B, Lee M, Kang M, Kim H et al. (2003). Hypermethylation of XIAP-associated factor 1, a putative tumor suppressor gene from the 17p13.2 locus, in human gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 63: 7068.
Chawla-Sarkar M, Bae S, Reu F, Jacobs B, Lindner D, Borden E . (2004). Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs (XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 11: 915.
Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner D, Liu Y, Williams B, Sen G, Silverman R et al. (2003). Apoptosis and interferons: role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis 8: 237.
Der S, Zhou A, Williams B, Silverman R . (1998). Identification of genes differentially regulated by interferon alpha, beta, or gamma using oligonucleotide arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15623.
Deveraux Q, Takahashi R, Salvesen G, Reed J . (1997). X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 388: 300.
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA . (2004). Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature 429: 457.
Esteller M, Corn P, Baylin S, Herman J . (2001). A gene hypermethylation profile of human cancer. Cancer Res 61: 3225.
Herman J, Baylin S . (2003). Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med 349: 2042.
Hoon D, Spugnardi M, Kuo C, Huang S, Morton D, Taback B . (2004). Profiling epigenetic inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in tumors and plasma from cutaneous melanoma patients. Oncogene 23: 4014.
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Ziegler A, Kurtz S, Bigosch C, Kandioler D, Ludwig C et al. (2003). Silencing of death receptor and caspase-8 expression in small cell lung carcinoma cell lines and tumors by DNA methylation. Cell Death Differ 10: 356.
Kulaeva O, Draghici S, Tang L, Kraniak J, Land S, Tainsky M . (2003). Epigenetic silencing of multiple interferon pathway genes after cellular immortalization. Oncogene 22: 4118.
Leaman D, Chawla-Sarkar M, Jacobs B, Vyas K, Sun Y, Ozdemir A et al. (2003). Novel growth and death related interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) in melanoma: greater potency of IFN-beta compared with IFN-alpha2. J Interferon Cytokine Res 23: 745.
Leaman D, Chawla-Sarkar M, Vyas K, Reheman M, Tamai K, Toji S et al. (2002). Identification of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor-1 as an interferon-stimulated gene that augments TRAIL Apo2L-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277: 28504.
Liston P, Fong W, Kelly N, Toji S, Miyazaki T, Conte D et al. (2001). Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-caspase activity. Nat Cell Biol 3: 128.
Lu R, Au W, Yeow W, Hageman N, Pitha P . (2000). Regulation of the promoter activity of interferon regulatory factor-7 gene. Activation by interferons and silencing by hypermethylation. J Biol Chem 275: 31805.
Ng K, Campos E, Martinka M, Li G . (2004). XAF1 expression is significantly reduced in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 123: 1127.
Pfeffer L, Dinarello C, Herberman R, Williams B, Borden E, Bordens R et al. (1998). Biological properties of recombinant alpha-interferons: 40th anniversary of the discovery of interferons. Cancer Res 58: 2489.
Reu F, Bae S, Cherkassky L, Leaman D, Lindner D, Beaulieu N et al. (2006a). Overcoming resistance to interferon-induced apoptosis of renal carcinoma and melanoma cells by DNA demethylation. J Clin Oncol 24: 3771.
Reu F, Leaman D, Maitra R, Bae S, Cherkassky L, Fox M et al. (2006b). Expression of RASSF1A, an epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor, overcomes resistance to apoptosis induction by interferons. Cancer Res 66: 2785.
Spugnardi M, Tommasi S, Dammann R, Pfeifer G, Hoon D . (2003). Epigenetic inactivation of RAS association domain family protein 1 (RASSF1A) in malignant cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Res 63: 1639.
Stark G, Kerr I, Williams B, Silverman R, Schreiber R . (1998). How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 227.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alex Rodriguez for technical assistance of FACS analyses, MethylGene for providing the DNMT1 antibody, Thomas S Griffith, University of Iowa for pCMV-FLAG-DR4 plasmid and Dustin Thomas for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH R01 CA 90914 and GCRC M01 RR-018390.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, S., Cheriyath, V., Jacobs, B. et al. Reversal of methylation silencing of Apo2L/TRAIL receptor 1 (DR4) expression overcomes resistance of SK-MEL-3 and SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells to interferons (IFNs) or Apo2L/TRAIL. Oncogene 27, 490–498 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210655
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210655
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Direct and indirect effects of IFN-α2b in malignancy treatment: not only an archer but also an arrow
Biomarker Research (2022)
-
Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2020)
-
Aberrant DNA methylation in melanoma: biomarker and therapeutic opportunities
Clinical Epigenetics (2017)
-
Upregulation of c-FLIP-short in response to TRAIL promotes survival of NSCLC cells, which could be suppressed by inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin signaling
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
Zebularine-induced apoptosis in Calu-6 lung cancer cells is influenced by ROS and GSH level changes
Tumor Biology (2013)