Abstract
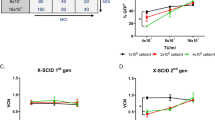
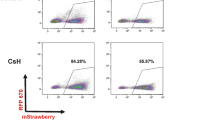
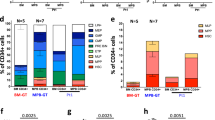
It has previously been shown that inhibition of CD26 (DPPIV/dipeptidylpeptidase IV) peptidase activity improves homing of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to the bone marrow and increases engraftment efficiency. Here, we demonstrate that treatment of retrovirally transduced mouse bone marrow cells with the tri-peptide Diprotin A (Ile-Pro-Ile), a specific inhibitor of CD26, significantly enhances engraftment of retrovirally transduced HSCs. Treatment of transduced bone marrow cells with Diprotin A permitted long-term expression of a retrovirally encoded MHC class I gene on multiple hematopoietic cell lineages after transplantation of a suboptimal number of transduced cells. Secondary transfer experiments revealed that expression of the transduced MHC class I gene resulted from engraftment of transduced HSCs. Expression of the allogeneic MHC class I antigen on bone marrow-derived cells following transplantation of Diprotin A-treated cells was sufficient to induce transplantation tolerance. Therefore, inhibition of CD26 activity significantly enhances engraftment of limited numbers of genetically modified HSCs, resulting in physiologically relevant levels of gene transfer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondo M, Wagers AJ, Manz MG, Prohaska SS, Scherer DC, Beilhack GF et al. Biology of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors: implications for clinical application. Annu Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 759–806.
Klein C, Baum C . Gene therapy for inherited disorders of haematopoietic cells. Hematol J 2004; 5: 103–111.
Fischer A, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Cavazzana-Calvo M . Gene therapy for immunodeficiency diseases. Semin Hematol 2004; 41: 272–278.
Bagley J, Iacomini J . Gene therapy progress and prospects: gene therapy in organ transplantation. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 605.
Tian C, Bagley J, Cretin N, Seth N, Wucherpfennig KW, Iacomini J . Prevention of type 1 diabetes by gene therapy. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 969–978.
Williams MA, Adams AB, Walsh MB, Shirasugi N, Onami TM, Pearson TC et al. Primary and secondary immunocompetence in mixed allogeneic chimeras. J Immunol 2003; 170: 2382.
Emery DW, Nishino T, Murata K, Fragkos M, Stamatoyannopoulos G . Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy. Int J Hematol 2002; 75: 228–236.
Hossle JP, Seger RA, Steinhoff D . Gene therapy of hematopoietic stem cells: strategies for improvement. News Physiol Sci 2002; 17: 87–92.
Christopherson II KW, Cooper S, Broxmeyer HE . Cell surface peptidase CD26/DPPIV mediates G-CSF mobilization of mouse progenitor cells. Blood 2003; 101: 4680–4686.
De Meester I, Korom S, Van Damme J, Scharpe S . CD26, let it cut or cut it down. Immunol Today 1999; 20: 367–375.
Baggiolini M . Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature 1998; 392: 565–568.
Aiuti A, Webb IJ, Bleul C, Springer T, Gutierrez-Ramos JC . The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral blood. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 111–120.
Kim CH, Broxmeyer HE . In vitro behavior of hematopoietic progenitor cells under the influence of chemoattractants: stromal cell-derived factor-1, steel factor, and the bone marrow environment. Blood 1998; 91: 100–110.
Christopherson II KW, Hangoc G, Broxmeyer HE . Cell surface peptidase CD26/dipeptidylpeptidase IV regulates CXCL12/stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha-mediated chemotaxis of human cord blood CD34+ progenitor cells. J Immunol 2002; 169: 7000–7008.
Sadir R, Imberty A, Baleux F, Lortat-Jacob H . Heparan sulfate/heparin oligosaccharides protect stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCL12 against proteolysis induced by CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 43854–43860.
Christopherson II KW, Hangoc G, Mantel CR, Broxmeyer HE . Modulation of hematopoietic stem cell homing and engraftment by CD26. Science 2004; 305: 1000–1003.
Bagley J, Tian C, Sachs DH, Iacomini J . Induction of T-cell tolerance to an MHC class I alloantigen by gene therapy. Blood 2002; 99: 4394–4399.
Hodgson GS, Bradley TR . Properties of haematopoietic stem cells surviving 5-fluorouracil treatment: evidence for a pre-CFU-S cell? Nature 1979; 281: 381–382.
Van Zant G . Studies of hematopoietic stem cells spared by 5-fluorouracil. J Exp Med 1984; 159: 679–690.
Aguila HL, Akashi K, Domen J, Gandy KL, Lagasse E, Mebius RE et al. From stem cells to lymphocytes: biology and transplantation. Immunol Rev 1997; 157: 13–40.
Akashi K, Reya T, Dalma-Weiszhausz D, Weissman IL . Lymphoid precursors. Curr Opin Immunol 2000; 12: 144–150.
Kondo M, Weissman IL, Akashi K . Identification of clonogenic common lymphoid progenitors in mouse bone marrow. Cell 1997; 91: 661–672.
Bleul CC, Fuhlbrigge RC, Casasnovas JM, Aiuti A, Springer TA . A highly efficacious lymphocyte chemoattractant, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). J Exp Med 1996; 184: 1101–1109.
Nagasawa T, Kikutani H, Kishimoto T . Molecular cloning and structure of a pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 2305–2309.
Oberlin E, Amara A, Bachelerie F, Bessia C, Virelizier JL, Arenzana-Seisdedos F et al. The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature 1996; 382: 833–835.
Abe M, Akiyama T, Nakamura H, Kojima F, Harada S, Muraoka Y . First synthesis and determination of the absolute configuration of sulphostin, a novel inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. J Nat Prod 2004; 67: 999–1004.
Adams S, Miller GT, Jesson MI, Watanabe T, Jones B, Wallner BP . PT-100, a small molecule dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitor, has potent antitumor effects and augments antibody-mediated cytotoxicity via a novel immune mechanism. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5471–5480.
Ahn JH, Kim HM, Jung SH, Kang SK, Kim KR, Rhee SD et al. Synthesis and DP-IV inhibition of cyano-pyrazoline derivatives as potent anti-diabetic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 4461–4465.
Balzarini J, Andersson E, Schols D, Proost P, Van Damme J, Svennerholm B et al. Obligatory involvement of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the activation of the antiretroviral tripeptide glycylprolylglycinamide (GPG-NH(2)). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004; 36: 1848–1859.
Cheon HG, Lee CM, Kim BT, Hwang KJ . Lead discovery of quinoxalinediones as an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) by high-throughput screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 2661–2664.
Senten K, Van Der Veken P, De Meester I, Lambeir AM, Scharpe S, Haemers A et al. Gamma-amino-substituted analogues of 1-[(S)-2,4-diaminobutanoyl]piperidine as highly potent and selective dipeptidyl peptidase II inhibitors. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 2906–2916.
Takasaki K, Nakajima T, Ueno K, Nomoto Y, Higo K . Effects of combination treatment with dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor and sulfonylurea on glucose levels in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 2004; 95: 291–293.
Wesley UV, Tiwari S, Houghton AN . Role for dipeptidyl peptidase IV in tumor suppression of human non small cell lung carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 2004; 109: 855–866.
Kim D, Wang L, Beconi M, Eiermann GJ, Fisher MH, He H et al. (2R)-4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin -7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: a potent, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem 2005; 48: 141–151.
Tian C, Bagley J, Forman D, Iacomini J . Induction of central tolerance by mature T cells. J Immunol 2004; 173: 7217–7222.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Drs Mohamed Sayegh and Anil Chandraker for critical review of the manuscript, and members of the Iacomini laboratory for helpful discussions. Jessamyn Bagley is supported in part by a grant from the A-T Children's Project. Daron Forman is supported in part by NIH Training Grant T32 AI07529. This work was supported by Grants R01AI43619-06 and R01AI50602-02 from the National Institutes of Health, and a grant from the American Diabetes Association (7-04-RA-45) to JI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, C., Bagley, J., Forman, D. et al. Inhibition of CD26 peptidase activity significantly improves engraftment of retrovirally transduced hematopoietic progenitors. Gene Ther 13, 652–658 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302695
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302695
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tolerance to MHC class II disparate allografts through genetic modification of bone marrow
Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 negatively regulates colony-stimulating factor activity and stress hematopoiesis
Nature Medicine (2012)
-
Experimental basis of cord blood transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2009)
-
The Genetic Engineering of Hematopoietic Stem Cells: the Rise of Lentiviral Vectors, the Conundrum of the LTR, and the Promise of Lineage-restricted Vectors
Molecular Therapy (2007)