Abstract
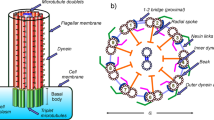
Microtubules are cylindrically shaped cytoskeletal biopolymers that are essential for cell motility, cell division and intracellular trafficking. Here, we investigate their polyelectrolyte character that plays a very important role in ionic transport throughout the intra-cellular environment. The model we propose demonstrates an essentially nonlinear behavior of ionic currents which are guided by microtubules. These features are primarily due to the dynamics of tubulin C-terminal tails which are extended out of the surface of the microtubule cylinder. We also demonstrate that the origin of nonlinearity stems from the nonlinear capacitance of each tubulin dimer. This brings about conditions required for the creation and propagation of solitonic ionic waves along the microtubule axis. We conclude that a microtubule plays the role of a biological nonlinear transmission line for ionic currents. These currents might be of particular significance in cell division and possibly also in cognitive processes taking place in nerve cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Amos, Trends Cell Biol. 5, 48 (1995)
G. Matsumoto, M. Ishikawa, A. Tasaki, H. Murofushi, H. Sakai, J. Membr. Biol. 77, 77 (1989)
P.K. Hepler, Plant Cell 17, 2142 (2005)
D.H. Chang, P. Wadsworth, P.K. Hepler, J. Cell Sci. 102, 79 (1992)
L. Matsson, J. Biol. Phys. 31, 303 (2005)
L. Matsson, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 502101 (2009)
E. Nogales, H.W. Wang, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 179 (2006)
H. Freedman, V. Rezania, A. Priel, E. Carpenter, S.Y. Noskov, J.A. Tuszynski, Phys. Rev. E 81, 051912 (2010)
J.F. Diaz, I. Barasoain, J.M. Andren, J. Biol. Chem. 278, 8407 (2003)
M.V. Satarić, D.I. Ilić, N. Ralević, J.A. Tuszynski, Eur. Biophys. J. 38, 637 (2009)
M.V. Satarić, D. Sekulić, M. Zivanov, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 7, 2281 (2010)
Z.S. Siwy, M.R. Powell, A. Petrov, E. Kalman, C. Trantmann, R.S. Eisenberg., Nano Lett. 6, 1729 (2006)
W. Im, B. Roux, J. Mol. Biol. 322, 851 (2002)
L. Serrano, J. de la Torre, R.B. Maccioni, Y. Avila, Biochemistry 23, 4675 (1984)
M.V. Satarić, J.A. Tuszynski, Phys. Rev. E 67, 011901 (2003)
N.A. Baker, D. Sept, S. Joseph, M.J. Holst, J.A. McCammon, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 10037 (2001)
J.A. Tuszynski, J.A. Brown, E. Crowford, E.J. Carpenter, M.L.A. Nip, J.M. Dixon, M.V. Satarić, Math. Comput. Modell. 41, 1055 (2005)
G.S. Manning, Rev. Biophys. 2, 179 (1978)
J.A. Tuszynski, A. Priel, J.A. Brown, H.F. Cantiello, J.M. Dixon, Nano and Molecular Electronics Handbook, Electronic and Ionic Conductivities of Microtubules and Actin Filaments: Their Consequences for Cell Signaling and Applications to Bioelectronics (Taylor and Francis, London, 2007)
A. Priel, J.A. Tuszynski, H. Cantielo, Molecular Biology of the Cell, Ionic Waves Propagation Along the Dendritic Cytoskeleton as a Signaling Mechanism (Elsevier, 2006)
A. Priel, J.A. Tuszynski, EPL 83, 68004 (2008)
J.A. Tuszynski, S. Portet, J.M. Dixon, C. Luxford, H.F. Cantiello, Biophys. J. 86, 1890 (2004)
A. Priel, A.J. Ramos, J.A. Tuszynski, H.F. Contiello, Biophys. J. 90, 4639 (2006)
B. O'Shanghnessy, Q. Yang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 048302 (2005)
I. Minoura, E. Muto, Biophys. J. 90, 3739 (2006)
C. Lin, H.F. Cantiello, Biophys. J. 65, 1371 (1993)
K. Wang, W.J. Rappel, H. Levine, Phys. Biol. 1, 27 (2004)
S. Maxon, J. Viecelli, Phys. Rev. Lett. 32, 4 (1974)
S. Maxon, J. Viecelli, Phys. Fluids 17, 1614 (1974)
T. Yagy, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 50, 2737 (1981)
J.A. Tuszynski, S. Hameroff, M.V. Satarić, B. Tripisova, M.L.A. Nip, J. Theor. Biol. 174, 371 (1995)
L.J. Gagliardi, J. Electrostat. 54, 219 (2002)
T. Duke, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15, S1747 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekulić, D.L., Satarić, B.M., Tuszynski, J.A. et al. Nonlinear ionic pulses along microtubules. Eur. Phys. J. E 34, 49 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2011-11049-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2011-11049-0