Abstract
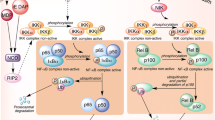
Intrauterine infection/inflammation complicates 25% to 40% of preterm births (PTB). The human vagina is normally populated by Lactobacillus species, some of which upregulate interleukin 10 (IL-10) output in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated human placental trophoblast cells. We hypothesize that a probiotic strain, L rhamnosus GR-1 exerts its anti-inflammatory effect through activation of the Janus Kinases/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (JAK/STAT) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. Placental trophoblasts from term healthy pregnancies were treated with LPS in the presence or absence of pretreatments with GR-1 supernatant and/or chemical inhibitors of the intracellular signaling pathways. Phosphorylation of STAT3 and p38 was measured by Western Blot analysis, and output of IL-10 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Phosphorylation of STAT-3 and p38 was upregulated by GR-1 supernatant alone or in combination with LPS, while IL-10 output was inhibited by both JAK and p38 inhibitors. These data provide an underlying intracellular mechanism for cytokine regulation in the human placenta by L rhamnosus GR-1 and potential prevention of infection/inflammation-mediated PTB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGregor JA, French JI. Bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2000;55(5 suppl 1):S1–S19.
Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, Romero R. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet. 2008; 371(9606):75–84.
Peltier MR. Immunology of term and preterm labor. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003;1:122.
Gomez R, Romero R, Edwin SS, David C. Pathogenesis of preterm labor and preterm premature rupture of membranes associated with intraamniotic infection. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1997;11(1):135–176.
Dudley DJ. Pre-term labor: an intra-uterine inflammatory response syndrome? J Reprod Immunol. 1997;36(1–2):93–109.
Challis JRG, Matthews SG, Gibb W, Lye SJ. Endocrine and paracrine regulation of birth at term and preterm. Endocr Rev. 2000;21(5):514–550.
Hitti J, Hillier SL, Agnew KJ, Krohn MA, Reisner DP, Eschenbach DA. Vaginal indicators of amniotic fluid infection in preterm labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;97(2):211–219.
von MG, Grischke EM, Schwab S, et al. Predictive value of serum interleukin-6 and -8 levels in preterm labor or rupture of the membranes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2000;79:667–672.
El-Bastawissi AY, Williams MA, Riley DE, Hitti J, Krieger JN. Amniotic fluid interleukin-6 and preterm delivery: a review. Obstet Gynecol. 2000;95(6 pt 2):1056–1064.
Coultrip LL, Lien JM, Gomez R, Kapernick P, Khoury A, Grossman JH. The value of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 determination in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes in the detection of microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171(4):901–911.
Yeganegi M, Watson CS, Martins A, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 supernatant and fetal sex on lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine and prostaglandin-regulating enzymes in human placental trophoblast cells: implications for treatment of bacterial vaginosis and prevention of preterm labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200(5):532–538.
Bowen JM, Chamley L, Mitchell MD, Keelan JA. Cytokines of the placenta and extra-placental membranes: biosynthesis, secretion and roles in establishment of pregnancy in women. Placenta. 2002;23(4):239–256.
de Moraes-Pinto MI, Vince GS, Flanagan BF, Hart CA, Johnson PM. Localization of IL-4 and IL-4 receptors in the human term placenta, decidua and amniochorionic membranes. Immunology. 1997;90(1):87–94.
Roth I, Corry DB, Locksley RM, Abrams JS, Litton MJ, Fisher SJ. Human placental cytotrophoblasts produce the immunosuppressive cytokine interleukin 10. J Exp Med. 1996;184(2): 539–548.
Sadowsky DW, Novy MJ, Witkin SS, Gravett MG. Dexamethasone or interleukin-10 blocks interleukin-1beta-induced uterine contractions in pregnant rhesus monkeys. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188(1):252–263.
Rodts-Palenik S, Wyatt-Ashmead J, Pang Y, et al. Maternal infection-induced white matter injury is reduced by treatment with interleukin-10. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;191(4):1387–1392.
Terrone DA, Rinehart BK, Granger JP, Barrilleaux PS, Martin JN Jr., Bennett WA. Interleukin-10 administration and bacterial endotoxin-induced preterm birth in a rat model. Obstet Gynecol. 2001; 98(3):476–480.
Rivera DL, Olister SM, Liu X, et al. Interleukin-10 attenuates experimental fetal growth restriction and demise. FASEB J. 1998;12(2):189–197.
Leitich H, Brunbauer M, Bodner-Adler B, Kaider A, Egarter C, Husslein P. Antibiotic treatment of bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188(3): 752–758.
Okun N, Gronau KA, Hannah ME. Antibiotics for bacterial vaginosis or Trichomonas vaginalis in pregnancy: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105(4):857–868.
Shennan A, Crawshaw S, Briley A, et al. A randomised controlled trial of metronidazole for the prevention of preterm birth in women positive for cervicovaginal fetal fibronectin: the PRE-MET Study. BJOG. 2006;113(1):65–74.
Falagas ME, Betsi GI, Athanasiou S. Probiotics for the treatment of women with bacterial vaginosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13(7):657–664.
Anukam KC, Osazuwa E, Osemene GI, Ehigiagbe F, Bruce AW, Reid G. Clinical study comparing probiotic Lactobacillus GR-1 and RC-14 with metronidazole vaginal gel to treat symptomatic bacterial vaginosis. Microbes Infect. 2006;8(12–13): 2772–2776.
Cadieux P, Burton J, Gardiner G, et al. Lactobacillus strains and vaginal ecology. JAMA. 2002;287(15):1940–1941.
Reid G, Millsap K, Bruce AW. Implantation of Lactobacillus casei var rhamnosus into vagina. Lancet. 1994;344(8931):1229.
Kim SO, Sheikh HI, Ha SD, Martins A, Reid G. G-CSF-mediated inhibition of JNK is a key mechanism for Lactobacillus rhamnosus-induced suppression of TNF production in macrophages. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8(12):1958–1971.
Murray PJ. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: input and output integration. J Immunol. 2007;178(5):2623–2629.
Kniss DA, Rovin B, Fertel RH, Zimmerman PD. Blockade NFkappaB activation prohibits TNF-alpha-induced cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in ED27 trophoblast-like cells. Placenta. 2001;22(1):80–89.
Herve R, Schmitz T, Evain-Brion D, Cabrol D, Leroy MJ, Mehats C. The PDE4 inhibitor rolipram prevents NF-kappaB binding activity and proinflammatory cytokine release in human chorionic cells. J Immunol. 2008;181(3):2196–2202.
Sun K, Yang K, Challis JR. Differential regulation of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and 2 by nitric oxide in cultured human placental trophoblast and chorionic cell preparation. Endocrinology. 1997;138(11):4912–4920.
Marino VJ, Roguin LP. The granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) activates Jak/STAT and MAPK pathways in a trophoblastic cell line. J Cell Biochem. 2008;103(5):1512–1523.
Shoji T, Yoshida S, Mitsunari M, et al. Involvement of p38 MAP kinase in lipopolysaccharide-induced production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandin E(2) in human choriodecidua. J Reprod Immunol. 2007;75(2):82–90.
Saccani S, Pantano S, Natoli G. p38-Dependent marking of inflammatory genes for increased NF-kappa B recruitment. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(1):69–75.
Otkjaer K, Holtmann H, Kragstrup TW, et al. The p38 MAPK regulates IL-24 expression by stabilization of the 3’ UTR of IL-24 mRNA. PLoS One. 2010;5(1):e8671.
Riley JK, Takeda K, Akira S, Schreiber RD. Interleukin-10 receptor signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway. Requirement for two distinct receptor-derived signals for anti-inflammatory action. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(23):16513–16521.
Lappas M, Permezel M, Rice GE. Mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins regulate LPS-stimulated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins from human gestational tissues. Placenta. 2007;28(8–9):936–945.
Chon H, Choi B, Jeong G, Lee E, Lee S. Suppression of proinflammatory cytokine production by specific metabolites of Lactobacillus plantarum 10hk2 via inhibiting NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK expressions. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 [Epub ahead of print].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeganegi, M., Leung, C.G., Martins, A. et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1-Induced IL-10 Production in Human Placental Trophoblast Cells Involves Activation of JAK/STAT and MAPK Pathways. Reprod. Sci. 17, 1043–1051 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110377237
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719110377237