Abstract
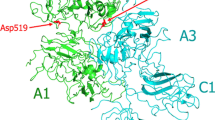
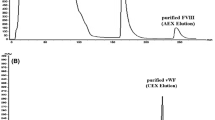
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an important cofactor in the blood coagulation cascade. A deficiency or dysfunction of FVIII causes hemophilia A, a life-threatening bleeding disorder. FVIII circulates in plasma as a heterodimer comprising 6 domains (heavy chain, A1-A2-B and light chain A3-C1-C2). Replacement therapy using FVIII is the leading therapy in the management of hemophilia A. However, ∼15% to 30% of patients develop inhibitory antibodies that neutralize the activity of the protein. Neutralizing antibodies to epitopes in the lipid binding region of FVIII are commonly identified in patients' plasma. In this report, we investigated the effect of O-phospho-L-serine (OPLS), which binds to the lipid bindinding region, on the immunogenicity of B domain deleted recombinant factor VIII (BDDrFVIII). Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) studies showed that OPLS specifically bind to the lipid binding region, localized in the C2 domain of the coagulation factor. Size exclusion chromatography and fluorescence anisotropy studies showed that OPLS interfered with the aggregation of BDDrFVIII. Immunogenicity of free-vs BDDrFVIII-OPLS complex was evaluated in a murine model of hemophilia A. Animals administered subcutaneous (sc) injections of BDDrFVIII-OPLS had lower neutralizing titers compared with animals treated with BDDRFVIII alone. Based on these studies, we hypothesize that specific molecular interactions between OPLS and BDDrFVIII may improve the stability and reduce the immunogenicity of BDDrFVIII formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufiman RJ, Wasley LC, Dorner AJ. Synthesis, processing, and secretion of recombinant human factor VIII expressed in mammalian cells.J Biol Chem. 1988;263:6352–6362.
Bovenschen N, Rijken DC, Havekes LM, van Vlijmen BJ, Mertens K. The B domain of coagulation factor VIII interacts with the asialoglycoprotein receptor.J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1257–1265.
Kaufman RJ. Biological regulation of factor VIII activity.Annu Rev Med. 1992;43:325–339.
Larner AJ. The molecular pathology of haemophilia.Q J Med. 1987;63:473–491.
Klinge J, Ananyeva NM, Hauser CA, Saenko EL. Hemophilia A—from basic science to clinical practice.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2002;28:309–322.
Lollar P. Molecular characterization of the immune response to factor VIII.Vox Sang. 2002;83:403–408.
Fijnvandraat K, Bril WS, Voorberg J. Immunobiology of inhibitor development in hemophilia A.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003;29:61–68.
Reding MT, Okita DK, Diethelm-Okita BM, Anderson TA, Conti-Fine BM. Human CD4+T-cell epitope repertoire on the C2 domain of coagulation factor VIII.J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1777–1784.
Pratt KP, Shen BW, Takeshima K, Davie EW, Fujikawa K, Stoddard BL. Structure of the C2 domain of human factor VIII at 1.5A resolution.Nature. 1999;402:439–442.
Pratt KP, Qian J, Ellaban E, et al. Immodominant T-cell epitopes in the factor VIII C2 domain are located within an inhibitory antibody binding site.Thromb Haemost. 2004;92:522–528.
Purohit VS, Jr, Ramani K, Jr, Sarkar R, Jr, Kazazian HH, Jr, Balasubramanian SV. Lower inhibitor development in hemophilia A mice following administration of recombinant factor VIII-O-phospho-L-serine complex.J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17593–17600.
Toole JJ, Pittman DD, Orr EC, Murtha P, Wasley LC, Kaufman RJ. A large region (approximately equal to 95 kDa) of human factor VIII is dispensable for in vitro procoagulant activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:5939–5942.
Pittman DD, Alderman EM, Tomkinson KN, Wang JH, Giles AR, Kaufman RJ. Biochemical immunological, and in vivo functional characterization of B-domain-deleted factor VIII.Blood. 1993;81:2925–2935.
Ramani K, Balasubramanian SV. Fluorescence properties of Laurdan in cochleate phases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1618:67–78.
Over J. Methodology of the one-stage assay of Factor VIII (VIII:C).Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1984;41:13–24.
Ramani K, Purohit V, Middaugh CR, Balasubramanian SV. Aggregation kinetics of recombinant human FVIII (rFVIII).J Pharm Sci. 2005;94:2023–2029.
Lakowicz J.Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. New York, NY: Kluwer Academic/Plenum; 1999.
Wu H, Reding M, Qian J, et al. Mechanism of the immune response to human factor VIII in murine hemophilia A.Thromb Haemost. 2001;85:125–133.
Verbruggen B, Novakova I, Wessels H, Boezeman J, van den Berg M, Mauser-Bunschoten E. The Nijmegen modification of the Bethesda assay for factor VIII:C inhibitors: improved specificity and reliability.Thromb Haemost. 1995;73:247–251.
Saenko EL, Scandella D, Yakhyaev AV, Greco NJ. Activation of factor VIII by thrombin increases its affinity for binding to synthetic phospholipid membranes and activated platelets.J Biol Chem. 1998;273:27918–27926.
Gilbert GE, Drinkwater D. Specific membrane binding of factor VIII is mediated by O-phospho-L-serine, a moiety of phosphatidylserine.Biochemistry. 1993;32:9577–9585.
Purohit VS, Ramani K, Kashi RS, Durrani MJ, Kreiger TJ, Balasubramanian SV. Topology of factor VIII bound to phosphatidylserine-containing model membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1617:31–38.
Griffin BD, Micklem LR, McCann MC, James K, Pepper DS. The production and characterisation of a panel of ten murine monoclonal antibodies to human procoagulant factor VIII.Thromb Haemost. 1986;55:40–46.
Zhai X, Srivastava A, Drummond DC, Daleke D, Lentz BR. Phosphatidylserine binding alters the conformation and specifically enhances the cofactor activity of bovine factor Va.Biochemistry. 2002;41:5675–5684.
Li X, Gabriel DA. The physical exchange of factor VIII (FVIII) between von Willebrand factor and activated platelets and the effect of the FVIII B-domain on platelet binding.Biochemistry. 1997;36:10760–10767.
Ramani K, Purohit VS, Miclea RD, Middaugh CR, Balasubramanian SV. Lipid binding region (2303–2332) is involved in aggregation of recombinant human FVIII (rFVIII).J Pharm Sci. 2005;94:1288–1299.
Falls LA, Furie B, Furie BC. Role of phosphatidylethanolamine in assembly and function of the factor IXa-factor VIIIa complex on membrane surfaces.Biochemistry. 2000;39:13216–13222.
Grillo AO, Edwards KL, Kashi RS, et al. Conformatinal origin of the aggregation of recombinant human factor VIII.Biochemistry. 2001;40:586–595.
Derrick TS, Kashi RS, Durrani M, Jhingan A, Middaugh CR. Effect of metal cations on the conformation and inactivation of recombinant human factor VIII.J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:2549–2557.
Fatouros A, Liden Y, Sjostrom B. Recombinant factor VIII SQ—stability of VIII: C in homogenates from porcine, monkey and human subcutaneous tissue.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000;52:797–805.
Wang W, Kelner DN. Correlation of rFVIII inactivation with aggregation in solution.Pharm Res. 2003;20:693–700.
Carpenter JF, Kendrick BS, Chang BS, Manning MC, Randolph TW. Inhibition of stress-induced aggregation of protein therapeutics.Methods Enzymol. 1999;309:236–255.
Kendrick BS, Carpenter JF, Cleland JL, Randolph TW. A transient expansion of the native state precedes aggregation of recombinant human interferon-gamma.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14142–14146.
Kendrick BS, Chang BS, Arakawa T, et al. Preferential exclusion of sucrose from recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in restricted conformational mobility and compaction of native state.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11917–11922.
Stoilova-McPhie S, Villoutreix BO, Mertens K, Kemball-Cook G, Holzenburg A. 3-Dimensional structure of membrane-bound coagulation factor VIII: modeling of the factor VIII heterodimer within a 3-dimensional density map derived by electron crystallography.Blood. 2002;99:1215–1223.
Qian J, Jr, Borovok M, Jr, Bi L, Jr, Kazazian HH, Jr, Hoyer LW. Inhibitor antibody development and T-cell response to human factor VIII in murine hemophilia A.Thromb Haemost. 1998;81:240–244.
Hoffimann PR, Kench JA, Vondracek A, et al. Interaction between phosphatidylserine and the phosphatidylserine receptor inhibits immune responses in vivo.J Immunol. 2005;174:1393–1404.
Moore WV, Leppert P. Role of aggregated human growth hormone (hGH) in development of antibodies to hGH.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980;51:691–697.
Rosenberg AS. Effects of protein aggregates: an immunologic perspective.AAPS J. 2006;8:E501-E507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: June 29, 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miclea, R.D., Purohit, V.S. & Balu-Iyer, S.V. O-phospho-L-serine, multi-functional excipient for B domain deleted recombinant factor VIII. AAPS J 9, 28 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj0902028
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj0902028