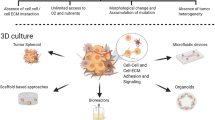
Summary
Classically, most cell culture experiments have been performed under adherent 2D conditions. Cells in the human body grow within an organized 3D matrix, surrounded by other cells. The behavior of individual cells is controlled through their interactions with their immediate neighbors and the extracellular matrix. The complex summation of these multiple signals determines whether a given cell undergoes differentiation, apoptosis, proliferation, or invasion. In 2D culture many of these complex interactions are lost. As a result, there are a growing number of studies which report differences in phenotype, cellular signaling, cell migration, and drug responses when the same cells are grown under 2D or 3D culture conditions. One potential application of these techniques is to anticancer drug discovery, which has long been hampered by the lack of good preclinical models. Compounds with good antitumor activity in 2D cell culture models often fail to translate into the clinic. Here we suggest that the response of cancer cells to drugs is determined in part by the 3D tumor microenvironment and discuss models to re-create the 3D tumor microenvironment in vitro. It is likely that the adoption of these and other 3D models will allow us to more closely re-create the behavior of the tumor in vivo which may lead to identifying better anticancer drug candidates at an earlier stage of development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andl, C. D.; Mizushima, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Oyama, K.; Harada, H.; Chruma, K.; Herlyn, M.; Rustgi, A. K. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 278:1824–1830; 2003.
Bao, W.; Stromblad, S. Integrin alphav-mediated inactivation of p53 controls a MEK1-dependent melanoma cell survival pathway in three-dimensional collagen. J. Cell. Biol. 167:745–756; 2004.
Berking, C.; Herlyn, M. Human skin reconstruct models: a new application for studies of melanocyte and melanoma biology. Histol. Histopathol. 16:669–674; 2001.
Bissell, M. J.; Radisky, D. Putting tumours in context. Nat. Rev. Cancer 1:46–54; 2001.
Cukierman, E.; Pankov, R.; Stevens, D. R.; Yamada, K. M. Taking cell-matrix adhesions to the third dimension. Science 294:1708–1712; 20001.
Desoize, B.; Gimonet, D.; Jardiller, J. C. Cell culture as spheroids: an approach to multicellular resistance. Anticancer Res. 18:4147–4158; 1998.
Hsu, M. Y.; Shih, D. T.; Meier, F. E.; Van Belle P.; Hsu, J. Y.; Elder, D. E.; Buck C. A.; Herlyn, M. Adenoviral gene transfer of beta 3 integrin subunit induces conversion from radial to vertical growth phase in primary human melanoma. Am. J. Pathol. 153:1435–1442; 1998.
Kalabis, J.; Patterson, M. J.; Enders, G. H.; Marian, B.; Iozzo, R. V.; Rogler, G.; Gimotty, P. A.; Herlyn, M. Stimulation of human colonic epithelial cells by leukemia inhibitory factor is dependent on collagen-embedded fibroblasts in organotypic culture. FASEB J. 17:1115–1117; 2003.
LaRue, K. E.; Khalil, M.; Freyer, J. P. Microenvironmental regulation of proliferation in multicellular spheroids is mediated through differential expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 64:1621–1631; 2004.
Leek, R. D.; Stratford, I.; Harris, A. L. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in three-dimensional tumor growth, apoptosis, and regulation by the insulin-signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 65:4147–4152; 2005.
Li, S.; Lao, J.; Chen, B. P., et al. Genomic analysis of smooth muscle cells in 3-dimensional collagen matrix. FASEB J. 17:97–99; 2003.
Margulis, A.; Zhang, W.; Alt-Holland, A.; Crawford, H. C.; Fusenig, N. E.; Garlick, J. A. E-cadherin suppression accelerates squamous cell carcinoma progression in three-dimensional, human tissue constructs. Cancer Res. 65:1783–1791; 2005.
Margulis, A.; Zhang, W.; Alt-Holland, A., et al. Loss of intercellular adhesion activates a transition from low- to high-grade human squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 118:821–831; 2006.
Masters, J. R. Human cancer cell lines: fact and fantasy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1:233–236; 2000.
Meier, F.; Nesbit, M.; Hsu, M. Y., et al. Human melanoma progression in skin reconstructs—Biological significance of bFGF. Am. J. Pathol. 156:193–200; 2000.
Mellor, H. R.; Ferguson, D. J.; Callaghan R. A model of quiescent tumour microregions for evaluating multicellular resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Br. J. Cancer 93:302–309; 2005.
Mueller-Klieser, W. Tumor biology and experimental therapeutics. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 36:123–139; 2000.
Paszek, M. J.; Zahir, N.; Johnson, K. R., et al. Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell 8:241–254; 2005.
Petersen, O. W.; Ronnov-Jenssen, L.; Howlett, A. R.; Bissell, M. J. Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:9064–9068; 1992.
Ross, D. T.; Scherf, U.; Eisen, M. B., et al. Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human cancer cell lines. Nat. Genet. 24:227–235; 2000.
Sethi, T.; Rintoul, R. C.; Moore, S. M., et al. Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat. Med. 5:662–668; 1999.
Smalley, K. S.; Bradford, P.; Haass, N. K.; Brandner, J. M.; Brown, E.; Herlyn M. Up-regulated expression of zonula occludens protein-1 in human melanoma associates with N-cadherin and contributes to invasion and adhesion. Am. J. Pathol. 166:1541–1554; 2005a.
Smalley, K. S.; Brafford, P. A.; Herlyn, M. Selective evolutionary pressure from the tissue microenvironment drives tumor progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 15:451–459; 2005b.
Smalley, K. S.; Herlyn, M. Targeting intracellular signaling pathways as a novel strategy in melanoma therapeutics. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1059:16–25; 2005.
Smalley, K. S.; Lioni, M.; Herlyn M. Targeting the stromal fibroblasts: a novel approach to melanoma therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 5:1069–1078; 2005c.
Smalley, K. S. M.; Haass, N. K.; Brafford, P.; Lioni, M.; Flaherty, K. T.; Herlyn, M. Multiple signaling pathways must be targeted to overcome drug resistance in cell lines derived from melanoma metastases. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5:1136–1144; 2006.
Wartenberg, M.; Frey, C.; Diedershagen, H.; Ritgen, J.; Hescheler, J.; Sauer H. Development of an intrinsic P-glycoprotein-mediated doxorubicin resistance in quiescent cell layers of large, multicellular prostate tumor spheroids. Int. J. Cancer 75:855–863; 1998.
Weaver, V. M.; Lelievre, S.; Lakins, J. N.; Chrenek, M. A.; Jones, J. C. R.; Giancotti, F.; Werb, Z.; Bissell, M. J. β4 integrin-dependent formation of three-dimensional architecture confers resistance to apoptosis in normal and malignant epithelium. Cancer Cell 2:205–216; 2002.
Wistuba, I. I.; Bryant, D.; Behrens, C.; Milchgrub, S.; Virmani, A. K.; Ashfaq, R.; Minna J. D.; Gazdar A. F. Comparison of features of human lung cancer cell lines and their corresponding tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 5:991–1000; 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smalley, K.S.M., Lioni, M. & Herlyn, M. Life ins't flat: Taking cancer biology to the next dimension. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 42, 242–247 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1290/0604027.1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/0604027.1