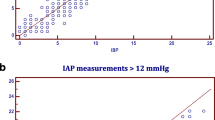
Background: Recent data suggests that increased intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) is one factor associated with the morbidity of morbidly obese patients, who have a BMI >35 kg/m2. IAP has been proposed to be an abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). This study investigated the characteristics of IAP in morbidly obese patients. Methods: 45 morbidly obese patients (mean BMI 55±2 kg/m2) had IAP measured using urinary bladder pressure. Results: The mean IAP for the morbidly obese group was 12±0.8 cmH2O, increased when compared to controls (IAP=0±2 cmH2O). The IAP correlated to the sagittal abdominal diameter, an index of the degree of central obesity (r=+0.83, P<0.02); however, it did not correlate to basal insulin, body weight, or BMI. The end-expiratory IAP did not change when measured after the laparotomy incision was made, but IAP measured in the last 15 patients increased during the first 2 postoperative days. The IAP for patients with pressure-related morbidity (gastroesophageal reflux disease, hernia, stress incontinence, diabetes, hypertension, and venous insufficiency) was 12±1 cmH2O, while those without these morbidities had an IAP of 9±0.8 cmH2O. Conclusion: We conclude that IAP is increased in morbid obesity. This increased IAP is a function of central obesity and is associated with increased morbidity. The degree of IAP elevation correlates with increased co-morbidities. We also conclude that elevation in IAP in morbid obesity is not a true ACS but represents a direct mass effect of the visceral obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, D.M., Marceau, S. & Forse, R.A. Intra-abdominal Pressure in the Morbidly Obese. OBES SURG 15, 1225–1232 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1381/096089205774512546
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1381/096089205774512546