Abstract
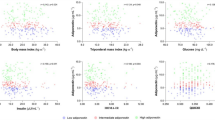
An increase of insulin resistance and a worsening of lipid profile during 6 mo of military service in young male Finnish population has previously been shown by us. The present study demonstrates unfavorable changes of serum adiponectin concentrations and their association with weight loss in these particular circumstances. Adiponectin in a range of 4.3–21.2 μg/mL was present in the serum samples and had a significant negative correlation with weight, body mass index, waist to hip ratio, and insulin. Fasting serum lipids and plasma insulin significantly increased and serum adiponectin levels significantly decreased during the military service. Even the subjects with a 5–10% decrease in body weight showed the same result. In cases with more than 10% weight reduction and a significant decrease of fasting insulin concentration, the total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol significantly increased and adiponectin concentration tended to decreased. Only in severely obese cases (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) with more than 10% decrease in body mass index adiponectin levels tended to increase, although not statistically significantly. This study shows that serum adiponectin concentrations decreased during a 6 mo high-caloric diet in military service, and even a moderate weight reduction induced by high-energy expenditure in exercise during service did not increase its levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiecek, A., Kokot, F., Chudek, J., and Adamczak, M. (2002). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 17, 191–195.
Yamauchi, T., Kamon, J., Waki, H., et al. (2001). Nat. Med. 7, 941–946.
Yukio, A., Shinji, K., Norijuki, O., et al. (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 79–83.
Weyer, C., Funahashi, T., Tanaka, S., et al. (2001). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1930–1935.
Spranger, J., Kroke, A., Möhlig, M., et al. (2003). Lancet 361, 226–228.
Kikuko, H., Tohru, F., Yukio, A., et al. (2000). Atheroscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20, 1595–1599.
Lihn, A. S., Ostergård, T., Nyholm, B., Pedersen, S. B., Richelsen, B., and Schmitz, O. (2003). Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284, E443-E448.
Kumada, M., Kihara, S., Sumitsuji, S., et al. (2003). Atheroscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 85–89.
Matsubara, M., Maruoka, S., and Katayose, S. (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 2764–2769.
Hulver, M. W., Zheng, D., Tanner, C. J., et al. (2002). Am. J. Physical. Endocrinol. Metab. 283, 861–865.
Shiung Yang, W., Lee, W. J., Funahashi, T., et al. (2001). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 3815–3819.
Tähtinen, T., Vanhala, M., Oikarinen, J., and Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S. (2002). Ann. Med. Fenn. 75, 163–169.
Tähtinen, T., Vanhala, M., Oikarinen, J., and Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S. (2001). Ann. Med. Fenn. 76, 239–246.
Yamamoto, Y., Hirose, H., Saito, I., et al. (2002). Clin. Sci. 103, 137–142.
Motoshima, H., Wu, X., Madhur, K. S., et al. (2002). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 5662–5667.
Dubois, M., Vantyghem, M. C., Schoonjans, K., et al. (2002). Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris) 63, (6 pt 1).
Combs, T. P., Wagner, J. A., Berger, J., et al. (2002). Endocrinology 143, 998–1007.
Yang, W. S., Matsuzawa, Y., Jeng, C. Y., et al. (2002). Diabetes Care 25, 376–380.
Fleming, R. M. (2002). Prev. Cardiol. 5, 110–118 (erratum 5, 203.)
Abbasi, F., Lamendola, C., Mclaughling, T., Hayden, G., Reaven, G. M., and Reaven, P. T. (2004). Metabolism 53, 280–283.
Ryan, A. S., Nicklas, B. J., Berman, D. M., and Elahi, D. (2003). Int. J. Obes. 27, 1066–1071.
Tähtinen, T., Vanhala, M., Oikarinen, J., and Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S. (1998). J. Cardiovasc. Risk 5, 319–323.
Katz, A., Nambi, S. S., Mather, K., et al. (2000). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 2402–2410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavinasab, F., Tähtinen, T., Jokelainen, J. et al. Lack of increase of serum adiponectin concentrations with a moderate weight loss during six months on a high-caloric diet in military service among a young male finnish population. Endocr 26, 65–69 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:26:1:065
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:26:1:065