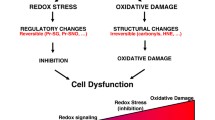
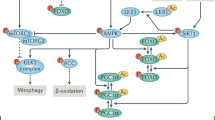
Abstract
Aging can be defined as a progressive decline in the ability of the organism to resist stress, damage, and diseas. Although there are currently over 300 theories to explain the aging phenomenon, it is still not well understood why organisms age and why the aging process can vary so much in speed and quality from individual to individual. The oxidative stress hypothesis is one of the prevailing theories of aging. This theory states that free radicals produced during cellular respiration damage lipids, proteins, and DNA thereby accelerating the aging process and increasing disease risk. Under normal conditions, the electron transport chain is the primary producer of the superoxide anion, which is precursor to other highly reactive species such as hydrogen peroxide and the hydroxyl radical. Oxidative stress accumulates when prooxidants overwhelm the antioxidant defense mechanisms. This is dependent on a number of factors including free radical production, susceptibility of tissue to stress, and strength of the defense and repair system. Oxidative stress has been implicated in a number of chronic disease states usually grouped under the umbrella of the metabolic syndrome and is thought to contribute to the aging process. It has been hypothesized that the production of free radicals is dependent on resting metabolic rate and this may have an impact on the aging process. However, other factors, such as mitochondrial function, may be important in the production of free radicals and the subsequent effect on aging and disease states.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finch, C. E. (1990). Longevity, senescence and the genome. Chicago University Press: Chicago.
Ames, B. N., Shigenaga, M. K., and Hagen, T. M. (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90(17), 7915–7922.
Austad, S. N. (1998). Aging (Milano) 10(2), 146–147.
Harman, D. (1956). J. Gerontol. 11(3), 298–300.
Sohal, R. S. and Allen, R. G. (1985). Basic Life Sci. 35, 75–104.
Hamilton, M. L., et al. (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 (18), 10469–10474.
Roberts, L. J. 2nd and Reckelhoff, J. F. (2001). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 287(1), 254–256.
Zainal, T. A., et al. (2000). FASEB J. 14(12), 1825–1836.
Orr, W. C. and Sohal, R. S. (1994). Science. 263(5150) 1128–1130.
Sohal, R. S., et al. (1994). Mech. Ageing Dev. 76(2–3), 215–224.
Youngman, L. D., Park, J. Y., and Ames, B. N. (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89(19), 9112–9116.
Turrens, J. F. and Boveris, A. (1980). Biochem. J. 191(2), 421–427.
Batandier, C., et al. (2002). J. Cell. Mol. Med. 6(2), 175–187.
Cadenas, E., et al. (1977). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 180(2), 248–257.
Boveris, A., Oshino, N., and Chance, B. (1972). Biochem. J. 128(3), 617–630.
Chance, B., Sies, H., and Boveris, A. (1979). Physiol. Rev. 59(3), 527–605.
St-Pierre, J., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277(47), 44784–44790.
Herrero, A. and Barja, G. (1997). J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 29(3), 241–249.
Arnaiz, S. L., et al. (1995). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1272(3), 175–180.
Strobel, H. W. and Coon, M. J. (1971). J. Biol. Chem. 246(24), 7826–7829.
Ramos, C. L., et al. (1992). J. Biol. Chem. 267(12), 8307–8312.
Halliwell, B. (1997). In: Oxygen radicals and the disease process. Thomas, K. B. (ed.). Harwood Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, pp. 1–14.
Schulz, J. B., et al. (2000). Eur. J. Biochem. 267(16), 4904–4911.
Halliwell, B., et al. (1999). Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press: New York.
Bielski, B. H., Arudi, R. L., and Sutherland, M. W. (1983). J. Biol. Chem. 258(8), 4759–4761.
Wagner, B. A., Buettner, G. R., and Burns, C. P. (1994). Biochemistry 33(15), 4449–4453.
Gardner, H. W. (1989). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 7(1), 65–86.
Cai, Q., Tian, L., and Wei, H. (1996). Exp. Gerontol. 31(3), 373–385.
Stadtman, E. R. (1992). Science 257(5074), 1220–1224.
Yan, L. J., Levine, R. L., and Sohal, R. S. (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94(21), 11168–11172.
Yan, L. J. and Sohal, R. S. (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95(22), 12896–12901.
Barja, G. (2004). Trends Neurosci. 27(10), 595–600.
Drew, B., et al. (2003). Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 284(2), R474–480.
Hamilton, M. L., et al. (2001). Nucleic Acids Res. 29(10), 2117–2126.
Gredilla, R., et al. (2001). FASEB J. 15(9), 1589–1591.
Bandy, B. and Davison, A. J. (1990). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 8(6), 523–539.
Carrozzo, R., et al. (2001). Neurology 56(5), 687–690.
Wallace, D. C. (1992). Science 256(5057), 628–632.
Araujo, F. B., et al. (1995). Atherosclerosis 117(1), 61–71.
Keaney, J. F. Jr., et al. (2003). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23(3), 434–439.
Redon, J., et al. (2003). Hypertension 41(5), 1096–1101.
Reilly, M. P., et al. (1998). Circulation 98(25), 2822–2828.
Stojiljkovic, M. P., et al. (2002). J. Hypertens. 20(6), 1215–1221.
Vassalle, C., et al. (2004). J. Intern. Med. 256(4), 308–315.
Sigurdardottir, V., Fagerberg, B., and Hulthe, J. (2002). J. Intern. Med. 252(5), 440–447.
Furukawa, S., et al. (2004). J. Clin. Invest. 114(12), 1752–1761.
Block, G., et al. (2002). Am. J. Epidemiol. 156(3), 274–285.
Devaraj, S., O'Keefe, G., and Jialal, I. (2005). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90(8), 4549–4554.
Urakawa, H., et al. (2003). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88(10), 4673–4676.
Hansel, B., et al. (2004). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89(10), 4963–4971.
Mecocci, P., MacGarvey, U., and Beal, M. F. (1994). Ann. Neurol. 36(5), 747–751.
Milton, N. G. (2004). Drugs Aging 21(2), 81–100.
Nishioka, N. and Arnold, S. E. (2004). Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 12(2), 167–175.
Ravussin, E. and Gautier, J. F. (1999). Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 23(Suppl. 1), 37–41.
Tataranni, P. A. and Ravussin, E. (1995). Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 19(Suppl. 4), S102–106.
Ravussin, E. and Swinburn, B. A. (1993). In: Obesity, theory and therapy. Stunkard, A. J. and Wadden, T. A. (eds.). Raven Press: New York, pp. 97–123.
Levine, J. A., Eberhardt, N. L., and Jensen, M. D. (1999). Science 283(5399), 212–214.
Ravussin, E., et al. (1986). J. Clin. Invest. 78(6), 1568–1578.
Ravussin, E. and Boyd, S. (1993). Energy metabolism. In: Obesity theory and therapy. Stunkard, A. J. and Wadden, T. A. (eds.). Raven Press: New York.
Pearl, R. I. (1928). The rate of living. Alfred Knopf: New York.
Cutler, R. G. (1985). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82(14), 4798–4802.
Ku, H. H., Brunk, U. T., and Sohal, R. S. (1993). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 15(6), 621–627.
Sohal, R. S. and Weindruch, R. (1996). Science 273(5271), 59–63.
Speakman, J. R., et al. (2004). Aging Cell 3(3), 87–95.
Promislow, D. E. and Haselkorn, T. S. (2002). Aging Cell 1(1), 66–74.
Sacher, G. A. and Duffy, P. H. (1979). Fed. Proc. 38(2), 184–188.
Heymsfield, S. B., et al. (2002). Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 282(1), E132–138.
Ravussin, E., et al. (1988). N. Engl. J. Med. 318(8), 467–472.
Prentice, A. M., et al. (1996). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 50(2), 93–97.
Desai, V. G., et al. (1996). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 333(1), 145–151.
Cooper, J. M., Mann, V. M., and Schapira, A. H. (1992). J. Neurol. Sci. 113(1), 91–98.
Trounce, I., Byrne, E., and Marzuki, S. (1989). Lancet 1(8639), 637–639.
Petersen, K. F., et al. (2003). Science 300(5622), 1140–1142.
Conley, K. E., Jubrias, S. A., and Esselman, P. C. (2000). J. Physiol. 526(Pt. 1), 203–210.
Kelley, D. E., et al. (2002). Diabetes 51(10), 2944–2950.
Kelley, D. E. and Simoneau, J. A. (1994). J. Clin. Invest. 94(6), 2349–2356.
Schrauwen, P. and Hesselink, M. K. (2004). Diabetes 53(6), 1412–1417.
Michikawa, Y., et al. (1999). Science 286(5440), 774–779.
Russell, A. P., et al. (2003). FEBS Lett. 551(1–3), 104–106.
Ceriello, A., et al. (2000). Diabetes 49(12), 2170–2177.
Beckman, K. B. and Ames, B. N. (1998). Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 854, 118–127.
Beckman, K. B. and Ames, B. N. (1998). Physiol. Rev. 78(2), 547–581.
Lee, H. C. and Wei, Y. H. (2005). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37(4), 822–834.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frisard, M., Ravussin, E. Energy metabolism and oxidative stress. Endocr 29, 27–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:29:1:27
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:29:1:27