Abstract
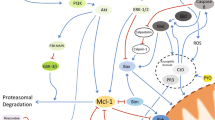
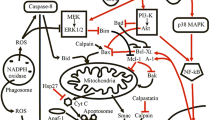
Central in the regulation of the short life span of neutrophils are their mitochondria. These organelles hardly contribute to the energy status of neutrophils but play a vital role in the apoptotic process. Not only do the mitochondria contain cytotoxic proteins that are released during apoptosis and contribute to caspase activation, but they also act as sensors of the metabolic and redox state of the cell and as scavengers of free Ca2+. The balance of the expression and activity of the proapoptotic and antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins determines the life span of neutrophils, because these proteins are essential for the formation of a permeability transition pore in the mitochondria and also seem to control the release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum and thereby mitochondrial energy metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klebanoff SJ, Clark RX. The Neutrophil: Function and Clinical Disorders. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: North-Holland Publishing Co; 1978.
Weiss SJ. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320:365–376.
Kuijpers TW, Maianski NA, Tool AT, et al. Apoptotic neutrophils in the circulation of patients with glycogen storage disease type 1b (GSD1b). Blood. 2003;101:5021–5024.
Kuijpers TW, Maianski NA, Tool AT, et al. Neutrophils in Barth syndrome (BTHS) avidly bind annexin-V in the absence of apoptosis. Blood. 2004;103:3915–3923.
Altznauer F, Conus S, Cavalli A, Folkers G, Simon HU. Calpain-1 regulates Bax and subsequent Smac-dependent caspase-3 activation in neutrophil apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:5947–5957.
Baumann R, Casaulta C, Simon D, Conus S, Yousefi S, Simon HU. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor delays apoptosis in neutrophils by inhibiting the mitochondria-dependent death pathway. FASEB J. 2003;17:2221–2230.
Kobayashi S, Yamashita K, Takeoka T, et al. Calpain-mediated X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis degradation in neutrophil apoptosis and its impairment in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33968–33977.
Wesche DE, Lomas-Neira JL, Perl M, Chung CS, Ayala A. Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis and shock. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:325–337.
Maianski NA, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Bid truncation, Bid/Bax targeting to the mitochondria, and caspase activation associated with neutrophil apoptosis are inhibited by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 2004;172:7024–7030.
Francois S, El BJ, Dang PM, Pedruzzi E, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Elbim C. Inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis by TLR agonists in whole blood: involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways, leading to increased levels of Mcl-1, A1, and phosphorylated Bad. J Immunol. 2005;174:3633–3642.
van den Berg JM, Weyer S, Weening JJ, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Divergent effects of tumor necrosis factor α on apoptosis of human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:467–473.
Alvarado-Kristensson M, Porn-Ares MI, Grethe S, Smith D, Zheng L, Andersson T. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activities have opposite effects on human neutrophil apoptosis. FASEB J. 2002;16:129–131.
Cowburn AS, Deighton J, Walmsley SR, Chilvers ER. The survival effect of TNF-α in human neutrophils is mediated via NF-κB-dependent IL-8 release. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1733–1743.
Derouet M,Thomas L, Cross A, Moots RJ, Edwards SW. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling and proteasome inhibition delay neutrophil apoptosis by increasing the stability of Mcl-1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:26915–26921.
Walmsley SR, Cowburn AS, Sobolewski A, et al. Characterization of the survival effect of tumour necrosis factor-α in human neutrophils. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32(pt 3):456–460.
Watson RW, Rotstein OD, Parodo J, Bitar R, Marshall JC. The IL-1β-converting enzyme (caspase-1) inhibits apoptosis of inflammatory neutrophils through activation of IL-1β. J Immunol. 1998; 161:957–962.
Kobayashi SD, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, et al. Bacterial pathogens modulate an apoptosis differentiation program in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:10948–10953.
Watson RW, Redmond HP, Wang JH, Condron C, Bouchier-Hayes D. Neutrophils undergo apoptosis following ingestion of Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1996;156:3986–3992.
Lum JJ, Bren G, McClure R, Badley AD. Elimination of senescent neutrophils by TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Immunol. 2005;175:1232–1238.
Liles WC, Klebanoff SJ. Regulation of apoptosis in neutrophils: Fas track to death? J Immunol. 1995;155:3289–3291.
Lavastre V, Pelletier M, Saller R, Hostanska K, Girard D. Mechanisms involved in spontaneous and Viscum album agglutinin-I-induced human neutrophil apoptosis: Viscum album agglutinin-I accelerates the loss of antiapoptotic Mcl-1 expression and the degradation of cytoskeletal paxillin and vimentin proteins via caspases. J Immunol. 2002;168:1419–1427.
Maianski NA, Geissler J, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Functional characterization of mitochondria in neutrophils: a role restricted to apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11: 143–153.
Scheel-Toellner D,Wang KQ, Webb PR, et al. Early events in spontaneous neutrophil apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32(pt 3): 461–464.
Maianski NA, Maianski AN, Kuijpers TW, Roos D. Apoptosis of neutrophils. Acta Haematol. 2004;111:56–66.
Fossati G, Moulding DA, Spiller DG, Moots RJ, White MR, Edwards SW. The mitochondrial network of human neutrophils: role in chemotaxis, phagocytosis, respiratory burst activation, and commitment to apoptosis. J Immunol. 2003;170:1964–1972.
Borregaard N, Herlin T. Energy metabolism of human neutrophils during phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1982;70:550–557.
Peachman KK, Lyles DS, Bass DA. Mitochondria in eosinophils: functional role in apoptosis but not respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:1717–1722.
Levene PA, Meyer GM. The action of leukocytes on glucose. J Biol Chem. 1912;11:361–370.
Minamikawa T, Williams DA, Bowser DN, Nagley P. Mitochondrial permeability transition and swelling can occur reversibly without inducing cell death in intact human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1999; 246:26–37.
Brookes PS, Yoon Y, Robotham JL, Anders MW, Sheu SS. Calcium, ATP, and ROS: a mitochondrial love-hate triangle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287:C817-C833.
Maianski NA, Mul FP, van Buul JD, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor inhibits the mitochondria-dependent activation of caspase-3 in neutrophils. Blood. 2002;99:672–679.
Pryde JG, Walker A, Rossi AG, Hannah S, Haslett C. Temperature-dependent arrest of neutrophil apoptosis: failure of Bax insertion into mitochondria at 15 degrees C prevents the release of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33574–33584.
Cowburn AS, Cadwallader KA, Reed BJ, Farahi N, Chilvers ER. Role of PI3-kinase-dependent Bad phosphorylation and altered transcription in cytokine-mediated neutrophil survival. Blood. 2002;100:2607–2616.
Weinmann P, Gaehtgens P, Walzog B. Bcl-Xl-and Bax-α-mediated regulation of apoptosis of human neutrophils via caspase-3. Blood. 1999;93:3106–3115.
Saelens X, Festjens N, Walle LV, van Gurp M, van Loo G, Vanden-abeele P. Toxic proteins released from mitochondria in cell death. Oncogene. 2004;23:2861–2874.
Puthalakath H, Strasser A. Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ. 2002;9:505–512.
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G, et al. Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell. 2002;111:331–342.
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, et al. Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 2003; 162:59–69.
White C, Li C, Yang J, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum gateway to apoptosis by Bcl-XL modulation of the InsP3R. Nat Cell Biol. 2005; 7:1021–1028.
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, et al. BAX and BAK regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: a control point for apoptosis. Science. 2003;300:135–139.
Bathori G, Csordas G, Garcia-Perez C, Davies E, Hajnoczky G. Ca2+-dependent control of the permeability properties of the mitochondrial outer membrane and voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC). J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17347–17358.
Rapizzi E, Pinton P, Szabadkai G, et al. Recombinant expression of the voltage-dependent anion channel enhances the transfer of Ca2+ microdomains to mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 2002;159:613–624.
Ayub K, Hallett MB. The mitochondrial ADPR link between Ca2+ store release and Ca2+ influx channel opening in immune cells. FASEB J. 2004;18:1335–1338.
Ayub K, Hallett MB. Ca2+ influx shutdown during neutrophil apoptosis: importance and possible mechanism. Immunology. 2004; 111:8–12.
Polster BM, Basanez G, Etxebarria A, Hardwick JM, Nicholls DG. Calpain I induces cleavage and release of apoptosis-inducing factor from isolated mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:6447–6454.
Yang KY, Arcaroli J, Kupfner J, et al. Involvement of phosphatidyli-nositol 3-kinase γ in neutrophil apoptosis. Cell Signal. 2003;15: 225–233.
Crossley LJ. Neutrophil activation by fMLP regulates FOXO (fork-head) transcription factors by multiple pathways, one of which includes the binding of FOXO to the survival factor Mcl-1. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:583–592.
Birkenkamp KU, Coffer PJ. FOXO transcription factors as regulators of immune homeostasis: molecules to die for? J Immunol. 2003;171:1623–1629.
Jonsson H, Allen P, Peng SL. Inflammatory arthritis requires Foxo3a to prevent Fas ligand-induced neutrophil apoptosis. Nat Med. 2005;11:666–671.
Boatright KM, Salvesen GS. Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:725–731.
Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:745–756.
Vaux DL, Silke J. IAPs, RINGs and ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:287–297.
Verhagen AM, Coulson EJ, Vaux DL. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and their relatives: IAPs and other BIRPs. Genome Biol. 2001;2:reviews3009.1-reviews3009.10.
Blink E, Maianski NA, Alnemri ES, Zervos AS, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Intramitochondrial serine protease activity of Omi/HtrA2 is required for caspase-independent cell death of human neutrophils. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:937–939.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 2000;102:33–42.
Adams JM, Cory S. Apoptosomes: engines for caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14:715–720.
Murphy BM, O’Neill AJ, Adrain C, Watson RW, Martin SJ. The apoptosome pathway to caspase activation in primary human neutrophils exhibits dramatically reduced requirements for cytochrome c. J Exp Med. 2003;197:625–632.
Power CP, Wang JH, Manning B, et al. Bacterial lipoprotein delays apoptosis in human neutrophils through inhibition of caspase-3 activity: regulatory roles for CD14 and TLR-2. J Immunol. 2004; 173:5229–5237.
Hong SJ, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:259–264.
Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, et al. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie. 2002;84:215–222.
Klein JA, Longo-Guess CM, Rossmann MP, et al. The harlequin mouse mutation downregulates apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 2002;419:367–374.
Hegde R, Srinivasula SM, Zhang Z, et al. Identification of Omi/ HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:432–438.
Martins LM, Iaccarino I, Tenev T, et al. The serine protease Omi/ HtrA2 regulates apoptosis by binding XIAP through a Reaper-like motif. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:439–444.
Garrido C, Kroemer G. Life’s smile, death’s grin: vital functions of apoptosis-executing proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:639–646.
Maianski NA, Roos D, Kuijpers TW. Tumor necrosis factor α induces a caspase-independent death pathway in human neutrophils. Blood. 2003;101:1987–1995.
Liu CY, Takemasa A, Liles WC, et al. Broad-spectrum caspase inhibition paradoxically augments cell death in TNF-α-stimulated neutrophils. Blood. 2003;101:295–304.
Cowburn AS, White JF, Deighton J, Walmsley SR, Chilvers ER. z-VAD-fmk augmentation of TNF α-stimulated neutrophil apoptosis is compound specific and does not involve the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood. 2005;105:2970–2972.
Walmsley SR, Print C, Farahi N, et al. Hypoxia-induced neutrophil survival is mediated by HIF-1α-dependent NF-κB activity. J Exp Med. 2005;201:105–115.
Mecklenburgh KI, Walmsley SR, Cowburn AS, et al. Involvement of a ferroprotein sensor in hypoxia-mediated inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis. Blood. 2002;100:3008–3016.
Haddad JJ, Olver RE, Land SC. Antioxidant/pro-oxidant equilibrium regulates HIF-1α and NF-κB redox sensitivity: evidence for inhibition by glutathione oxidation in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:21130–21139.
Selak MA, Armour SM, MacKenzie ED, et al. Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-α prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:77–85.
Piret JP, Minet E, Cosse JP, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent overexpression of myeloid cell factor-1 protects hypoxic cells against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9336–9344.
Zinkel SS, Hurov KE, Ong C, Abtahi FM, Gross A, Korsmeyer SJ. A role for proapoptotic BID in the DNA-damage response. Cell. 2005;122:579–591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
van Raam, B.J., Verhoeven, A.J. & Kuijpers, T.W. Mitochondria in Neutrophil Apoptosis. Int J Hematol 84, 199–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06131
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.06131