Abstract
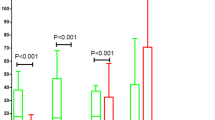
To screen and evaluate protein biomarkers for the detection of gliomas (Astrocytoma grade I–IV) from healthy individuals and gliomas from brain benign tumors by using surface enhanced laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF-MS) coupled with an artificial neural network (ANN) algorithm. SELDI-TOF-MS protein fingerprinting of serum from 105 brain tumor patients and healthy individuals, included 28 patients with glioma (Astrocytoma I–IV), 37 patients with brain benign tumor, and 40 age-matched healthy individuals. Two thirds of the total samples of every compared pair as training set were used to set up discriminating patterns, and one third of total samples of every compared pair as test set were used to cross-validate; simultaneously, discriminate-cluster analysis derived SPSS 10.0 software was used to compare Astrocytoma grade I–II with grade III–IV ones. An accuracy of 95.7%, sensitivity of 88.9%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value of 90% and negative predictive value of 100% were obtained in a blinded test set comparing gliomas patients with healthy individuals; an accuracy of 86.4%, sensitivity of 88.9%, specificity of 84.6%, positive predictive value of 90% and negative predictive value of 85.7% were obtained when patient’s gliomas was compared with benign brain tumor. Total accuracy of 85.7%, accuracy of grade I–II Astrocytoma was 86.7%, accuracy of III–IV Astrocytoma was 84.6% were obtained when grade I–II Astrocytoma was compared with grade III–IV ones (discriminant analysis). SELDI-TOF-MS combined with bioinformatics tools, could greatly facilitate the discovery of better biomarkers. The high sensitivity and specificity achieved by the use of selected biomarkers showed great potential application for the discrimination of gliomas patients from healthy individuals and glioma from brain benign tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, G., Mian, S., Holding, F., Allibone, R.O., Lowe, J., Ali, S., Li, G., Mccardle, S., ElLis, I.Q., Creaser, C., Rees, R.C., 2002. An integrated approach utilizing artificial neural networks and SELDI mass spectrometry for the classification of human tumours and rapid identification of potential biomarkers.Bioinformatics,18(3):395–404.
Bast, R.C.Jr., 2003. Status of tumor markers in ovarian cancer screening.J Clin Oncol,21(10 Suppl):200–205.
Cazares, L.H., Adam, B.L., Ward, M.D., Nasim, S., Schellhammer, P.F., Semmes, O.J., Wright, G.L.J., 2002. Normal, benign, preneoplastic, and malignant prostate cells have distinct protein expression profiles resolved by Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption/Ionization mass spectrometry.Clin Cancer Res,8(8): 2541–2552.
DeAngelis, L.M., 2001. Brain tumors.New England J Medicine,344(2):114–123.
Jemal, A., Murray, T., Samuels, A., Chafoor, A., Ward, E., Thun, M.J., 2003. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer JCLIN,53(l):5–26.
Li, J., Zhang, Z., Rosenzweig, J., Wang, Y.Y., Chan, D.W., 2002. Proteomics and bioinformatics approaches for identification of serum biomarkers to detect breast cancer.Clin Chem,48(8):1296–1304.
Mannes, A.J., Martin, B.M., Yang, H.Y., Keller, J.M., Lewin, S., Gaiser, R.R., Iadarola, M.J., 2003. Cystatin C as a cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for pain in humans.Pain,102(3):251–256.
Merchant, M., Weinberger, S.R., 2000. Recent advancements in surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry.Electrophoresis,21:1164–1177.
Petricoin, E.F., Liotta, L.A., 2004. SELDI-TOF-based serum proteomic pattern diagnostics for early detection of cancer.Curr Opin Biotechnol,15(l):24–30.
Samoylova, T.I., Morrison, N.E., Cox, N.R., 2003. Molecular markers of glial tumors: current targeting strategies.Curr Med Chem,10(10):831–843.
Srinivas, P.R., Verma, M., Zhao, Y., Srivastava, S., Clark, R.A., Tockman, M.S., 2002. Proteomics for cancer biomarker discovery.Clin Chem,48(8): 1160–1169.
Wiesner, A., 2004. Detection of tumor markers with proteinchip technology.Curr Pharm Biotechnol,5(l):45–67.
Zhukov, T.A., Johanson, R.A., Cantor, A.B., Clark, R.A., Tockman, M.S., 2003. Discovery of distinct protein profiles specific for lung tumors and pre-malignant lung lesions by SELDI mass spectrometry.Lung Cancer,40(3):267–279.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. G1998051200) supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zheng, S., Yu, Jk. et al. Serum protein fingerprinting coupled with artificial neural network distinguishes glioma from healthy population or brain benign tumor. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 4–10 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0004
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0004