Abstract
Objective: Buprenorphine and buprenorphine/naloxone combinations are effective pharmacotherapies for opioid dependence, but doses are considerably greater than analgesic doses. Because dose-related buprenorphine opioid agonist effects may plateau at higher doses, we evaluated the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of expected therapeutic doses.
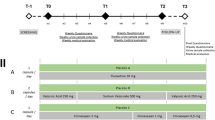
Design: The first experiment examined a range of sublingual buprenorphine solution doses with an ascending dose design (n = 12). The second experiment examined a range of doses of sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets along with one dose of buprenorphine alone tablets with a balanced crossover design (n = 8).
Participants: Twenty nondependent, opioid-experienced volunteers.
Methods: Subjects in the solution experiment received sublingual buprenorphine solution in single ascending doses of 4, 8, 16 and 32mg. Subjects in the tablet experiment received sublingual tablets combining buprenorphine 4, 8 and 16mg with naloxone at a 4: 1 ratio or buprenorphine 16mg alone, given as single doses. Plasma buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone concentrations and pharmacodynamic effects were measured for 48–72 hours after administration.
Results: Buprenorphine concentrations increased with dose, but not proportionally. Dose-adjusted areas under the concentration-time curve for buprenorphine 32mg solution, buprenorphine 16mg tablet and buprenorphine/naloxone 16/4mg tablet were only 54 ± 16%, 70 ± 25% and 72 ± 17%, respectively, of that of the 4mg dose of sublingual solution or tablet. No differences were found between dose strengths for most subjective and physiological effects. Pupil constriction at 48 hours after administration of solution did, however, increase with dose. Subjects reported greater intoxication with the 32mg solution dose, even though acceptability of the 4mg dose was greatest. Naloxone did not change the bioavailability or effects of the buprenorphine 16mg tablet.
Conclusion: Less than dose-proportional increases in plasma buprenorphine concentrations may contribute to the observed plateau for most pharmacodynamic effects as the dose is increased.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade names is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Strain EC, Stitzer ML, Liebson IA, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone in the treatment of opioid-dependence: self-reports, urinalysis, and Addiction Severity Index. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1996; 16: 59–67
Johnson RE, Chutuape MA, Strain EC, et al. A comparison of levomethadyl acetate, buprenorphine, and methadone for opioid dependence. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1290–7
Schottenfeld RS, Pakes JR, Oliveto A, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone maintenance for concurrent opioid dependence and cocaine abuse. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1997; 54: 713–20
Ling W, Charuvastra C, Collins JF, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance treatment of opiate dependence: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial. Addiction 1998; 93: 475–86
Brewster D, Humphrey MJ, McLeavy MA. The systemic bioavailability of buprenorphine by various routes of administration. J Pharm Pharmacol 1981; 33: 500–6
Iribarne C, Picart D, Dreano Y, et al. Involvement of cytochrome P450 3A4 in N-dealkylation of buprenorphine in human liver microsomes. Life Sci 1997; 60: 1953–64
Walsh SL, Preston KL, Stitzer ML, et al. Clinical pharmacology of buprenorphine: ceiling effects at high doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1994; 55: 569–80
Walsh SL, Preston KL, Bigelow GE, et al. Acute administration of buprenorphine in humans: partial agonist and blockade effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995; 274: 361–72
Preston KL, Bigelow GE, Liebson IA. Effects of sublingually given naloxone in opioid-dependent human volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend 1990; 25: 27–34
Mendelson J, Jones RT, Welm S, et al. Buprenorphine and naloxone combinations: the effects of three dose ratios in morphine-stabilized, opiate-dependent volunteers. Psychopharmacology 1999; 141: 37–46
Harris DS, Jones RT, Welm S, et al. Buprenorphine and naloxone co-administration in opiate-dependent patients stabilized on sublingual buprenorphine. Drug Alcohol Depend 2000; 61: 85–94
Strain EC, Stoller K, Walsh SL, et al. Effects of buprenorphine versus buprenorphine/naloxone tablets in non-dependent opioid abusers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000; 148: 374–83
Stoller KB, Bigelow GE, Walsh SL, et al. Effects of buprenorphine/naloxone in opioid-dependent humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001; 154: 230–42
Weinberg DS, Inturrisi CE, Reidenberg B, et al. Sublingual absorption of selected opioid analgesics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1988; 44: 335–42
Bullingham RES, McQuay HJ, Porter EJB, et al. Sublingual buprenorphine used postoperatively: ten-hour plasma drug concentration analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1982; 13: 665–73
Mendelson J, Upton RA, Everhart ET, et al. Bioavailability of sublingual buprenorphine. J Clin Pharmacol 1997; 37: 31–7
Kuhlman Jr JJ, Lalani S, Magluilo Jr J, et al. Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J Anal Toxicol 1996; 20: 369–78
Hsieh Y, Shi R, Evangelista D, et al. Simultaneous determination of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone in human urine by LC/MS/MS [abstract]. Pharm Res 1997; 14(11 Suppl.): 738
Bickel WK, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE, et al. A clinical trial of buprenorphine: comparison with methadone in the detoxification of heroin addicts. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1988; 43: 72–8
Jones RT, Mendelson J, Upton R, Relative bioavailability of oral and sublingual buprenorphine and naloxone tablets (study 97-1): final report. March 3, 2000. San Francisco (CA): University of California, 2000
Kuhlman Jr JJ, Magluilo Jr J, Cone E, et al. Simultaneous assay of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine by negative chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 1996; 20: 229–35
Cone EJ, Dickerson SL, Darwin WD, et al. Elevated drug saliva levels suggest a ‘depot-like’ effect in subjects treated with sublingual buprenorphine [abstract]. NIDA Res Monogr 1991; 105: 569
Ohtani M, Kotaki H, Uchino K, et al. Pharmacokinetic analysis of enterohepatic circulation of buprenorphine and its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 1994; 22: 2–7
Tracqui A, Kintz P, Ludes B. Buprenorphine-related deaths among drug addicts in France: a report on 20 fatalities. J Anal Toxicol 1998; 22: 430–4
Nath RP, Upton RA, Everhart ET, et al. Buprenorphine pharmacokinetics: relative bioavailability of sublingual tablet and liquid formulations. Clin Pharmacol 1999; 39: 619–23
Schuh KJ, Johanson CE. Pharmacokinetic comparison of the buprenorphine sublingual liquid and tablet. Drug Alcohol Depend 1999; 56: 55–60
Umbricht A, Huestis MA, Cone EJ, et al. Safety of buprenorphine: ceiling for cardiorespiratory effects at high IV doses [abstract]. NIDA Res Monogr 1999; 179: 225
Boas RA, Villiger JW. Clinical actions of fentanyl and buprenorphine: the significance of receptor binding. Br J Anaesth 1985; 57: 192–6
Fox AW. Opioid chronopharmacology [letter]. Cephalgia 2001; 21: 708
Dum JE, Herz A. In vivo receptor binding of the opiate partial agonist, buprenorphine, correlated with its agonistic and antagonistic actions. Br J Pharmacol 1981; 74: 627–33
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by US Public Health Service grants DA12393 and DA00053 and contract no. N01DA-4-8306 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and carried out in part in the General Clinical Research Center at the University of California, San Francisco, with support of the Division of Research Resources, National Institutes of Health (RR-00079).
The authors thank Tina Melby, Emilio Fernandez, Alan Dearborn, and the staff of the Drug Dependence Research Center and the UCSF General Clinical Research Center for assistance in conducting the study; Susette Welm, Alan Bostrom, Robert Jimison, and Gina Sequeira for data analysis and presentation; and Kaye Welch for editorial assistance. There are no potential conflicts of interest that the authors may have that are directly relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, D.S., Mendelson, J.E., Lin, E.T. et al. Pharmacokinetics and Subjective Effects of Sublingual Buprenorphine, Alone or in Combination with Naloxone. Clin Pharmacokinet 43, 329–340 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200443050-00005
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200443050-00005