Abstract
-
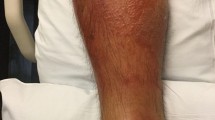
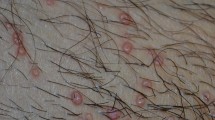
▴ Daptomycin is a lipopeptide antibacterial with rapid in vitro activity against Gram-positive cocci. It is approved for use in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSIs) caused by specified Gram-positive cocci.
-
▴ In vitro, daptomycin was active against Staphylococcus aureus (including meticillin-resistantstrains), Streptococcus pyogenes, S. agalactiae, group C and G β-haemolytic streptococci and vancomycin-susceptible Enterococcus faecalis. Bactericidal activity in vitro was rapid and concentration dependent.
-
▴ In two randomised, investigator-blinded, multicentre trials in patients with cSSSIs, intravenous daptomycin 4 mg/kg once daily was as effective as standard therapy (intravenous semi-synthetic penicillin 4–12 g/day or vancomycin 1g 12-hourly). Clinical success rates assessed 6–20 days after treatment end were 82.1% in daptomycin recipients and 82.9% in recipients of standard therapy (pooled data).
-
▴ In patients with cSSSIs, the adverse event profiles of daptomycin and vancomycin were similar. Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels increased in 2.8% of daptomycin recipients and 1.8% of patients who received standard therapy; only one daptomycin recipient (0.2%) experienced increased CPK levels and muscle symptoms that were not associated with any comorbid factors.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Use of tradenames is for product identification purposes only and does not imply endorsement.
References
Tally FP, DeBruin MF. Development of daptomycin for Gram-positive infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 2000 Oct; 46(4): 523–6
FDA US Food and Drug Administration. FDA talk paper: FDA approves first in new class of antibiotic [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gOv//bbs/topics/ANSWERS/2003/ANS01252.html [Accessed 2003 Sep 25]
Nichols RL. Optimal treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 1999 Sep; 44 Suppl. A: 19–23
Gorbach SL. IDCP guidelines: superficial skin and soft tissue infections: part I. Infect Dis Clin Pract 1996 Dec; 5: 521–7
Cubist Pharmaceuticals. Cubicin (daptomycin for injection) full prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://www.cubicin.com/fullprescribingl.htm [Accessed 2003 Oct 3]
Alborn WE Jr, Allen NE, Preston DA. Daptomycin disrupts membrane potential in growing Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1991 Nov; 35(11): 2282–7
Canepari P, Boaretti M, del Mar Lleo M, et al. Lipoteichoic acid as a new target for activity of antibiotics: mode of action of daptomycin (LY146032). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1990 Jun; 34(6): 1220–6
Allen NE, Alborn Jr WE, Hobbs Jr JN. Inhibition of membrane potential-dependent amino acid transport by daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1991 Dec; 35(12): 2639–42
Fuchs PC, Barry AL, Brown SD. Daptomycin susceptibility tests: interpretive criteria, quality control, and effect of calcium on in vitro tests. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2000 Sep; 38(1): 51–8
Hanberger H, Nilsson LE, Maller R, et al. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin and vancomycin on Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated by studies of initial killing and postantibiotic effect and influence of Ca2+ and albumin on these drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1991 Sep; 35(9): 1710–6
Barry AL, Fuchs PC, Brown SD. In vitro activities of daptomycin against 2,789 clinical isolates from 11 North American medical centers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001 Jun; 45(6): 1919–22
Jones RN, Barry AL. Antimicrobial activity and spectrum of LY146032, a lipopeptide antibiotic, including susceptibility testing recommendations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987 Apr; 31(4): 625–9
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; approved standard M7-A 6. 6th ed. Wayne (PA): National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, 2003
Fluit AC, Milatovic D, Verhoef J. Activity of daptomycin, a novel lipopeptide, against European Gram-positive cocci [abstract no. E-527]. 41st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2001 Dec 16–19; Chicago, 174
Klein JD, Ludlam E, Steele-Moore L. In vitro activity of ABT-773, telithromycin and daptomycin against group C and G Streptococci [abstract no. E-1894]. 42nd Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2002 Sep 27–30; San Diego, 167
King A, Phillips I. The in vitro activity of daptomycin against 514 Gram-positive aerobic clinical isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother 2001 Aug; 48(2): 219–23
Critchley IA, Blosser-Middleton RS, Jones ME, et al. Baseline study to determine in vitro activities of daptomycin against Gram-positive pathogens isolated in the United States in 2000–2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003 May; 47(5): 1689–93
Critchley IA, Draghi DC, Sahm DF, et al. Activity of daptomycin against susceptible and multidrug-resistant Gram-positive pathogens collected in the SECURE study (Europe) during 2000–2001. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003 Mar; 51(3): 639–49
Petersen PJ, Bradford PA, Weiss WJ, et al. In vitro and in vivo activities of tigecycline (GAR-936), daptomycin, and comparative antimicrobial agents against glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus and other resistant Gram-positive pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002 Aug; 46(8): 2595–601
Jones ME, Draghi DC, Critchley IA, et al. In vitro activity of daptomycin against a prospective collection of European enterococci [abstract plus poster P812]. 12th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; 2002 Apr 24–27; Milan
Chang S, Sievert DM, Hageman JC, et al. Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N Engl J Med 2003 Apr 3; 348(14): 1342–7
Snydman DR, McDermott LA, Jacobus NV. Determination of synergistic effects of daptomycin with gentamicin or in vitro effect of beta-lactam antibiotics against S. aureus and enterococci by FIC index and time-kill kinetics [abstract no. E-533]. 41st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2001 Dec 16–19; Chicago, 175
Stratton CW, Liu C, Weeks LS. Activity of LY146032 compared with that of methicillin, cefazolin, cefamandole, cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin, and vancomycin against staphylococci as determined by kill-kinetic studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987 Aug; 31(8): 1210–5
Vance-Bryan K, Larson TA, Rotschafer JC, et al. Investigation of the early killing of Staphylococcus aureus by daptomycin by using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1992 Oct; 36(10): 2334–7
Lamp KC, Rybak MJ, Bailey EM, et al. In vitro pharmacodynamic effects of concentration, pH, and growth phase on serum bactericidal activities of daptomycin and vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1992 Dec; 36(12): 2709–14
Garrison MW, Vance-Bryan K, Larson TA, et al. Assessment of effects of protein binding on daptomycin and vancomycin killing of Staphylococcus aureus by using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1990 Oct; 34(10): 1925–31
Rand K, Houck H. Daptomycin synergy with oxacillin against methicillin resistant Staphylococcuc aureus (MRSA) [abstract no. C-091]. 103rd Annual Meeting of American Society for Microbiology; 2003 18–22 May; Washington, DC
Lamp KC, Rybak MJ. Teicoplanin and daptomycin bactericidal activities in the presence of albumin or serum under controlled conditions of pH and ionized calcium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993 Mar; 37(3): 605–9
Louie A, Kaw P, Liu W, et al. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin in a murine thigh model of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001 Mar; 45(3): 845–51
Dandekar PK, Tessier PR, Williams P, et al. Pharmacodynamic profile of daptomycin against Enterococcus species and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a murine thigh infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003 Sep; 52(3): 405–11
Vaudaux P, Francois P, Bisognano C, et al. Comparative efficacy of daptomycin and vancomycin in the therapy of experimental foreign body infection due to Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003 Jul; 52(1): 89–95
Cha R, Grucz RGJr, Rybak MJ. Daptomycin dose-effect relationship against resistant Gram-positive organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003 May; 47(5): 1598–603
Rybak M, McKinnon P, Cha R, et al. Daptomycin pharmacodynamics versus MRSA at various doses as assessed by a Monte Carlo prediction model [abstract no. A-2195]. 41st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2001 Dec 16–19; Chicago, 37
Safdar N, Andes DR, Craig WA. In-vivo pharmacodynamics of daptomycin [abstract no. 72]. Clin Infect Dis 1999 Oct; 29(4): 974
Silverman JA, Oliver N, Andrew T, et al. Resistance studies with daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2001 Jun; 45(6): 1799–802
Kaatz GW, Seo SM. Analysis of the mechanism(s) of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus [abstract no. CI-1803]. 41st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2001 Dec 16–19; Chicago, 99
Tawfik AF. Effects of vancomycin, teicoplanin, daptomycin and coumermycin on normal immune capabilities. J Chemother 1991 Aug; 3(4): 226–31
Schubert S, Ullmann U. Influence of Lyl46032 on chemotaxis, chemiluminescence of PMN and lymphocyte transformation in vitro. Infection 1989 Nov; 17(6): 374–7
Woodworth JR, Nyhart EH, Wolny JD, et al. Tobramycin and daptomycin disposition when co-administered to healthy volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother 1994 Mar; 33(3): 655–9
Oleson FB Jr, Berman CL, Kirkpatrick JB, et al. Once-daily dosing in dogs optimizes daptomycin safety. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2000 Nov; 44(11): 2948–53
Tally FP, Zeckel M, Wasilewski MM, et al. Daptomycin: A novel agent for Gram-positive infections. Expert Opin Invest Drugs 1999; 8(8): 1223–38
Dvorchik BH, Brazier D, DeBruin MF, et al. Daptomycin pharmacokinetics and safety following administration of escalating doses once daily to healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003 Apr; 47(4): 1318–23
Wise R, Gee T, Andrews JM, et al. Pharmacokinetics and inflammatory fluid penetration of intravenous daptomycin in volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002 Jan; 46(1): 31–3
Woodworth JR, Nyhart Jr EH, Brier GL, et al. Single-dose pharmacokinetics and antibacterial activity of daptomycin, a new lipopeptide antibiotic, in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1992 Feb; 36(2): 318–25
Dvorchik B, Sica D, Gehr T. Pharmacokinetics (PK) and safety of single-dose daptomycin in subjects with graded renal insufficiency and end-stage renal disease [abstract no. A-1387]. 42nd Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2002 Sep 27–30; San Diego
Campanaro ES, Talley FP, Eisenstein BI, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of daptomycin (DAP) versus semi-synthetic penicillin (SSP) and vancomycin (VAN) in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) [abstract no. L-737 plus poster DapIV-0209]. 43rd Annual Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2003 Sep 14–17; Chicago [abstracts on disk]
Roditi D, Arbeit RD. Clinical significance of dual infection with Staphylococcus aureus and hemolytic streptococci in complicated skin and soft tissue infections: results from Daptomycin Trial 99-01 [abstract no. L-1482]. 41st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2001 Dec 16–19; Chicago, 471
Matthews PP, Debruin MF. Faster resolution of clinical signs in complicated skin and soft tissue infections by daptomycin vs standard therapy in a randomised, blinded, comparative study [abstract no. 112]. Clin Infect Dis 2001 Oct; 33(7): 1107
Knapp AG, Tally FP, Arbeit RD. Skeletal muscle effects in patients receiving once-daily daptomycin (DAP) for complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) [abstract no. L-736 plus poster DAPIV-0214]. 43rd Interscience Conference of Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2003 Sep 14–17; Chicago [abstracts on disk]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fenton, C., Fenton, C., Keating, G.M. et al. Daptomycin. Drugs 64, 445–455 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200464040-00009
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200464040-00009