Abstract
▴ Ropinirole prolonged release is a non-ergoline dopamine receptor agonist that is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
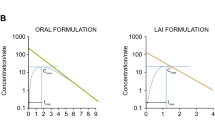
▴ Once-daily ropinirole prolonged release and threetimes-daily ropinirole immediate release have similar exposure over 24 hours. The prolonged-release formulation is associated with fewer fluctuations in plasma ropinirole concentrations.
▴ Two well designed, placebo- or active comparatorcontrolled trials examined the efficacy of ropinirole prolonged release in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease suboptimally controlled by levodopa. In the placebo-controlled trial, 24 weeks’ therapy with ropinirole prolonged release 6–24 mg once daily reduced hours of ‘off’ time (primary endpoint) to a significantly greater extent than placebo. In the active comparator-controlled trial, significantly more ropinirole prolonged-release recipients than ropinirole immediate-release recipients maintained a ≥20% reduction from baseline in ‘off’ time at week 24 (primary endpoint).
▴ Ropinirole prolonged release 6–24 mg once daily was generally well tolerated in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease; adverse events were generally typical of non-ergoline dopamine receptor agonists.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Registered as Requip-Modutab®, ReQuip® LP, ReQuip® XL™, ReQuip® Depot and ReQuip® Prolib.
References
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Parkinson’s disease: diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care (NICE clinical guideline 35) [online]. Available from URL: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/cg035niceguideline.pdf [Accessed 2007 Sep 18]
Olanow CW, Watts RL, Koller WC. An algorithm (decision tree) for the management of Parkinson’s disease (2001): treatment guidelines. Neurology 2001 Jun; 56(11 Suppl. 5): S1–88
Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004 May 29; 363: 1783–93
Pahwa R, Factor SA, Lyons KE, et al. Practice parameter: treatment of Parkinson disease with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2006 Apr 11; 66(7): 983–95
National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions. Parkinson’s disease: national clinical guideline for diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care. London: Royal College of Physicians, 2006
Pahwa R, Stacy MA, Factor SA, et al. Ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release: randomized, controlled study in advanced Parkinson disease. Neurology 2007 Apr 3; 68(14): 1108–15
Tompson DJ, Vearer D. Steady-state pharmacokinetic properties of a 24-hour prolonged-release formulation of ropinirole: results of two randomized studies in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin Ther 2007 Dec; 29(12): 2654–66
Tompson D, Oliver-Willwong, R. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic comparison of ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release and ropinirole immediate release in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol. Epub 2008 Oct 23
GlaxoSmithKline UK. Requip tablets: UK summary of product characteristics [online]. Available from URL: http://emc.medicines.org.uk/emc/assets/c/html/displayDocPrinter-Friendly.asp?documentid=2056 [Accessed 2008 Nov 17]
GlaxoSmithKline. Ropinirole 2, 3, 4 and 8 mg prolongedrelease tablets: EU mutual recognition summary of product characteristics. GlaxoSmithKline, 2007 Nov 27
GlaxoSmithKline. Requip® XL™ (ropinirole extended-release tablets): US prescribing information [online]. Available from URL: http://us.gsk.com/products/assets/us_requipxl.pdf [Accessed 2008 Nov 17]
Matheson AJ, Spencer CM. Ropinirole: a review of its use in the management of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs 2000 Jul; 60(1): 115–37
Jost WH, Angersbach D. Ropinirole, a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. CNS Drug Rev 2005; 11(3): 253–72
Kaye CM, Nicholls B. Clinical pharmacokinetics of ropinirole. Clin Pharmacokinet 2000 Oct; 39(4): 243–54
Stocchi F, Stover NP, Giorgi L. Ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release as adjunct to L-dopa in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease: efficacy according to baseline depression score [abstract no. 295]. Mov Disord 2007; 22Suppl. 16: S90
Hersh BP, Stover NP, Elmer LW, et al. Early efficacy of adjunctive ropinirole 24-hour in patients with advanced PD [abstract no. M-78]. Ann Neurol 2007; 62Suppl. 11: S35
Isaacson S, Pahwa R, Earl N. Ropinirole 24-hour prolongedrelease adjunctive therapy improves cardinal symptoms in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease not optimally controlled with L-dopa [abstract no. 2.238]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2007; 13Suppl. 2: S108
Sethi KD, Stocchi F, Giorgi L. Ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release in advanced Parkinson’s disease: relationship between treatment response and disease severity [abstract no. 301]. Mov Disord 2007; 22Suppl. 16: S92–3
Stocchi F, Hunter B, Giorgi L, et al. An evaluation of symptom control in patients with advanced PD receiving adjunctive ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release versus ropinirole immediate release: results from the PREPARED study [abstract]. 12th Congress of the European Federation of Neurological Societies; 2008 Aug 23–26; Madrid
Stocchi F, Hunter B, Giorgi L, et al. Adjunctive ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release compared with ropinirole immediate release in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD): the PREPARED study [abstract]. 12th Congress of the European Federation of Neurological Societies; 2008 Aug 23–26; Madrid
Schapira AHV, Stocchi F, Hunter B, et al. Adjunctive ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release compared with adjunctive ropinirole immediate release in patients with advanced PD: results from a per-protocol analysis of the PREPARED study [abstract]. 12th Congress of the European Federation of Neurological Societies; 2008 Aug 23–26; Madrid
Watts RL, Sethi KD, Pahwa R, et al. Ropinirole 24-hour prolonged release delays the onset of dyskinesia compared with carbidopa/levodopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease treated with levodopa [abstract no. PI 138]. Eur J Neurol 2007; 14Suppl. 1: 65
Educational highlights from data presented at the XVIIth World Federation of Neurology (WFN) World Congress on Parkinson’s Disease; 2007 December 9–13; Amsterdam [online]. Available from URL: http://clienti.tio.ch/img_articoli/20080925_233206_WFNRopinirole-v2.02007.pdf [Accessed 2008 Dec 8]
Acknowledgements and Disclosures
The manuscript was reviewed by: L. Elmer, Department of Neurology, Medical College of Ohio, Toledo, Ohio, USA; K. Sethi, Department of Neurology, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia, USA; F. Stocchi, Institute of Neurology, IRCCS San Raffaele Pisana, Rome, Italy.
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, J., Keating, G.M. Ropinirole Prolonged Release. CNS Drugs 23, 81–90 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/0023210-200923010-00006
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/0023210-200923010-00006